Abstract
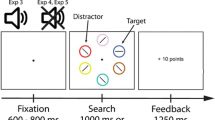
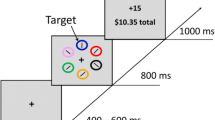
Reward has been known to render the reward-associated stimulus more salient to block effective attentional orienting in space. However, whether and how reward influences goal-directed attention in time remains unclear. Here, we used a modified attentional cueing paradigm to explore the effect of reward on temporal attention, in which the valid targets were given a low monetary reward and invalid targets were given a high monetary reward. The results showed that the temporal cue validity effect was significantly smaller when the competitive reward structure was employed (Experiment 1), and we ruled out the possibility that the results were due to the practice effect (Experiment 2a) or a reward-promoting effect (Experiment 2b). When further strengthening the intensity of the reward from 1:10 to 1:100 (Experiment 3), we found a similar pattern of results to those in Experiment 1. These results suggest that reward information which was based on relative instead of absolute values can weaken, but not reverse, the orienting attention in time.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, B. A. (2016). The attention habit: How reward learning shapes attentional selection. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1369(1), 24–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12957.
Anderson, B. A., & Kim, H. (2018). Mechanisms of value-learning in the guidance of spatial attention. Cognition, 178, 26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2018.05.005.
Anderson, B. A., Laurent, P. A., & Yantis, S. (2011). Value-driven attentional capture. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(25), 10367–10371. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1104047108.
Bucker, B., & Theeuwes, J. (2014). The effect of reward on orienting and reorienting in exogenous cuing. Cognitive Affective & Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(2), 635–646. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-014-0278-7.
Camara, E., Manohar, S., & Husain, M. (2013). Past rewards capture spatial attention and action choices. Experimental Brain Research, 230(3), 291–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3654-6.
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 155–159. https://doi.org/10.1037//0033-2909.112.1.155.
Corbetta, M., & Shulman, G. L. (2002). Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 3(3), 201–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn755.
Correa, A., Lupiáñez, J., & Tudela, P. (2006). The attentional mechanism of temporal orienting: Determinants and attributes. Experimental Brain Research, 169(1), 58–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0131-x.
Coull, J. T., & Nobre, A. C. (1998). Where and when to pay attention: The neural systems for directing attention to spatial locations and to time intervals as revealed by both PET and fMRI. Journal of Neuroscience, 18(18), 7426–7435. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.18-18-07426.1998.
Coull, J. T., Frith, C. D., Buchel, C., & Nobre, A. C. (2000). Orienting attention in time: Behavioural and neuroanatomical distinction between exogenous and endogenous shifts. Neuropsychologia, 38(6), 808–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(99)00132-3.
Engelmann, J. B., & Pessoa, L. (2007). Motivation sharpens exogenous spatial attention. Emotion, 7(3), 668–674. https://doi.org/10.1037/1528-3542.7.3.668.
Failing, M. F., & Theeuwes, J. (2015). Nonspatial attentional capture by previously rewarded scene semantics. Visual Cognition, 23(1–2), 82–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506285.2014.990546.
Failing, M. F., & Theeuwes, J. (2016). Reward alters the perception of time. Cognition, 148, 19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2015.12.005.
Failing, M., & Theeuwes, J. (2017). Don’t let it distract you: How information about the availability of reward affects attentional selection. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 79(8), 2275–2298. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-017-1376-8.
Failing, M., & Theeuwes, J. (2018). Selection history: How reward modulates selectivity of visual attention. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 25(2), 514–538. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-017-1380-y.
Failing, M., Nissens, T., Pearson, D., Le Pelley, M., & Theeuwes, J. (2015). Oculomotor capture by stimuli that signal the availability of reward. Journal of Neurophysiology, 114(4), 2316–2327. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00441.2015.
Griffin, I. C., Miniussi, C., & Nobre, A. C. (2001). Orienting attention in time. Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark, 6(3), 660–671. https://doi.org/10.2741/Griffin.
Gutiérrez-Cobo, M. J., Luque, D., Most, S. B., Fernández-Berrocal, P., & Le Pelley, M. E. (2019). Reward and emotion influence attentional bias in rapid serial visual presentation. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 72(9), 2155–2167. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747021819840615.
Hickey, C., & Los, S. A. (2015). Reward priming of temporal preparation. Visual Cognition, 23(1–2), 25–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506285.2014.998325.
Kahneman, D. (1973). Attention and effort (Vol. 1063). Prentice Hall.
Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 47(2), 263–292. https://doi.org/10.2307/1914185.
Kim, S., & Beck, M. R. (2020). Impact of relative and absolute values on selective attention. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 27(4), 735–741. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-020-01729-4.
Kingstone, A. (1992). Combining expectancies. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology Section A, 44(1), 69–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/14640749208401284.
Le Pelley, M. E., Pearson, D., Griffiths, O., & Beesley, T. (2015). When goals conflict with values: Counterproductive attentional and oculomotor capture by reward-related stimuli. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 144(1), 158–171. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000037.
Le Pelley, M. E., Mitchell, C. J., Beesley, T., George, D. N., & Wills, A. J. (2016). Attention and associative learning in humans: An integrative review. Psychological Bulletin, 142(10), 1111–1140. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000064.
Le Pelley, M. E., Seabrooke, T., Kennedy, B. L., Pearson, D., & Most, S. B. (2017). Miss it and miss out: Counterproductive nonspatial attentional capture by task-irrelevant, value-related stimuli. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 79(6), 1628–1642. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-017-1346-1.
Le Pelley, M. E., Watson, P., Pearson, D., Abcywickrama, R. S., & Most, S. B. (2019). Winners and losers: Reward and punishment produce biases in temporal selection. Journal of Experimental Psychology-Learning Memory and Cognition, 45(5), 822–833. https://doi.org/10.1037/xlm0000612.
Lin, A., Adolphs, R., & Rangel, A. (2012). Social and monetary reward learning engage overlapping neural substrates. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 7(3), 274–281. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsr006.
Miniussi, C., Wilding, E. L., Coull, J. T., & Nobre, A. C. (1999). Orienting attention in time: Modulation of brain potentials. Brain, 122(8), 1507–1518. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/122.8.1507.
Müller-Gethmann, H., Ulrich, R., & Rinkenauer, G. (2003). Locus of the effect of temporal preparation: Evidence from the lateralized readiness potential. Psychophysiology, 40(4), 597–611. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-8986.00061.
Murayama, K., & Kitagami, S. (2014). Consolidation power of extrinsic rewards: Reward cues enhance long-term memory for irrelevant past events. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 143(1), 15–20. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0031992.
Niemi, P., & Näätänen, R. (1981). Foreperiod and simple reaction time. Psychological Bulletin, 89(1), 133–162. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.89.1.133.
Nissens, T., Failing, M., & Theeuwes, J. (2017). People look at the object they fear: Oculomotor capture by stimuli that signal threat. Cognition & Emotion, 31(8), 1707–1714. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699931.2016.1248905.
Nobre, A. C., & van Ede, F. (2018). Anticipated moments: Temporal structure in attention. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 19(1), 34–48. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2017.141.
Noudoost, B., Chang, M. H., Steinmetz, N. A., & Moore, T. (2010). Top-down control of visual attention. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 20(2), 183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2010.02.003.
Padmala, S., & Pessoa, L. (2008). Affective learning enhances visual detection and responses in primary visual cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 28(24), 6202–6210. https://doi.org/10.1523/Jneurosci.1233-08.2008.
Padmala, S., & Pessoa, L. (2011). Reward reduces conflict by enhancing attentional control and biasing visual cortical processing. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 23(11), 3419–3432. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00011.
Preciado, D., Munneke, J., & Theeuwes, J. (2017). Mixed signals: The effect of conflicting reward- and goal-driven biases on selective attention. Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 79(5), 1297–1310. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-017-1322-9.
Raymond, J. E., & O’Brien, J. L. (2009). Selective visual attention and motivation: The consequences of Value Learning in an attentional Blink Task. Psychological Science, 20(8), 981–988. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2009.02391.x.
Rusz, D., Le Pelley, M. E., Kompier, M. A. J., Mait, L., & Bijleveld, E. (2020). Reward-driven distraction: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 146(10), 872–899. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000296.
Seibold, V. C., Stepper, M. Y., & Rolke, B. (2020). Temporal attention boosts perceptual effects of spatial attention and feature-based attention. Brain and Cognition, 142, 105570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2020.105570.
Shomstein, S., & Johnson, J. (2013). Shaping attention with reward: Effects of reward on space- and object-based selection. Psychological Science, 24(12), 2369–2378. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797613490743.
Small, D. M., Gitelman, D., Simmons, K., Bloise, S. M., Parrish, T., & Mesulam, M. M. (2005). Monetary incentives enhance processing in brain regions mediating top-down control of attention. Cerebral Cortex, 15(12), 1855–1865. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhi063.
Theeuwes, J., Kramer, A. F., Hahn, S., & Irwin, D. E. (1998). Our eyes do not always go where we want them to go: Capture of the eyes by new objects. Psychological Science, 9(5), 379–385.
Trivino, M., Correa, A., Arnedo, M., & Lupianez, J. (2010). Temporal orienting deficit after prefrontal damage. Brain, 133, 1173–1185. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp346.
Watson, P., Pearson, D., Theeuwes, J., Most, S. B., & Le Pelley, M. E. (2020). Delayed disengagement of attention from distractors signalling reward. Cognition 195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2019.104125.
Weinbach, N., Shofty, I., Gabay, S., & Henik, A. (2015). Endogenous temporal and spatial orienting: Evidence for two distinct attentional mechanisms. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 22(4), 967–973. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-014-0750-y.
Xia, T., Li, H., & Wang, L. (2016). Implicitly strengthened task-irrelevant stimulus-response associations modulate cognitive control: Evidence from an fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 37(2), 756–772. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23064.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Humanity and Social Science Youth Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (22YJC190030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: JZ, SZ, YW, FK. Methodology: JZ, SZ, YW, FK. Data curation: SZ, YG, CY, XH, FS, SH. Formal analysis: SZ, YG, CY, XH, FS, SH. Supervision: JZ, FK, YW. Writing-original draft: JZ, SZ, YG, YW, FK. Writing-review & editing & revision: JZ, YG.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Gao, Y., Zhou, S. et al. Impact of relative and absolute values on orienting attention in time. Psychological Research (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-024-01965-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-024-01965-6