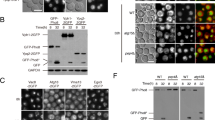
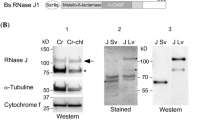
Abstract
Main conclusion
Localization of the RNase RNS2 to the vacuole via a C-terminal targeting signal is essential for its function in rRNA degradation and homeostasis.
RNase T2 ribonucleases are highly conserved enzymes present in the genomes of nearly all eukaryotes and many microorganisms. Their constitutive expression in different tissues and cell types of many organisms suggests a housekeeping role in RNA homeostasis. The Arabidopsis thaliana class II RNase T2, RNS2, is encoded by a single gene and functions in rRNA degradation. Loss of RNS2 results in RNA accumulation and constitutive activation of autophagy, possibly as a compensatory mechanism. While the majority of RNase T2 enzymes is secreted, RNS2 is located within the vacuole and in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), possibly within ER bodies. As RNS2 has a neutral pH optimum, and the endomembrane organelles are connected by vesicle transport, the site within the endomembrane system at which RNS2 functions is unclear. Here we demonstrate that localization to the vacuole is essential for the physiological function of RNS2. A mutant allele of RNS2, rns2-1, results in production of an active RNS2 RNase but with a mutation that removes a putative C-terminal vacuolar targeting signal. The mutant protein is, therefore, secreted from the cell. This results in a constitutive autophagy phenotype similar to that observed in rns2 null mutants. These findings illustrate that the intracellular retention of RNS2 and localization within the vacuole are critical for its cellular function.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ConcA:
-
Concanamycin A
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- MDC:
-
Monodansylcadaverine
- WT:
-
Wild-type
References
Ahmed SU, Rojo E, Kovaleva V, Venkataraman S, Dombrowski JE, Matsuoka K, Raikhel NV (2000) The plant vacuolar sorting receptor AtELP is involved in transport of NH2-terminal propeptide-containing vacuolar proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Cell Biol 149:1335–1344. doi:10.1083/jcb.149.7.1335
Andersen KL, Collins K (2012) Several RNase T2 enzymes function in induced tRNA and rRNA turnover in the ciliate Tetrahymena. Mol Biol Cell 23(1):36–44. doi:10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0689
Andersen KR, Jensen TH, Brodersen DE (2008) Take the “A” tail–quality control of ribosomal and transfer RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 1779(9):532–537. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.06.011
Balagopal V, Parker R (2009) Polysomes, P bodies and stress granules: states and fates of eukaryotic mRNAs. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21(3):403–408. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.005
Bariola PA, Howard CJ, Taylor CB, Verburg MT, Jaglan VD, Green PJ (1994) The Arabidopsis ribonuclease gene RNS1 is tightly controlled in response to phosphate limitation. Plant J 6(5):673–685
Bariola PA, MacIntosh GC, Green PJ (1999) Regulation of S-like ribonuclease levels in Arabidopsis. Antisense inhibition of RNS1 or RNS2 elevates anthocyanin accumulation. Plant Physiol 119(1):331–342
Bednarek SY, Wilkins TA, Dombrowski JE, Raikhel NV (1990) A carboxyl-terminal propeptide is necessary for proper sorting of barley lectin to vacuoles of tobacco. Plant Cell 2(12):1145–1155. doi:10.1105/tpc.2.12.1145
Carter C, Pan S, Zouhar J, Avila E, Girke T, Raikhel N (2004) The vegetative vacuole proteome of Arabidopsis thaliana reveals predicted and unexpected proteins. Plant Cell 16(12):3285–3303
Cervelli M, Di Caro O, Di Penta A, Angelini R, Federico R, Vitale A, Mariottini P (2004) A novel C-terminal sequence from barley polyamine oxidase is a vacuolar sorting signal. Plant J 40(3):410–418. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02221.x
Chou KC, Shen HB (2010) Plant-mPLoc: a top-down strategy to augment the power for predicting plant protein subcellular localization. PLoS One 5(6):e11335. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011335
Clough S, Bent A (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16(6):735–743
Condon C, Putzer H (2002) The phylogenetic distribution of bacterial ribonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res 30(24):5339–5346
Contento AL, Xiong Y, Bassham DC (2005) Visualization of autophagy in Arabidopsis using the fluorescent dye monodansylcadaverine and a GFP-AtATG8e fusion protein. Plant J 42(4):598–608
Dettmer J, Hong-Hermesdorf A, Stierhof YD, Schumacher K (2006) Vacuolar H+ -ATPase activity is required for endocytic and secretory trafficking in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18(3):715–730. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.037978
Drose S, Bindseil KU, Bowman EJ, Siebers A, Zeeck A, Altendorf K (1993) Inhibitory effect of modified bafilomycins and concanamycins on P- and V-type adenosinetriphosphatases. Biochemistry 32(15):3902–3906
Dyer KD, Rosenberg HF (2006) The RNase A superfamily: generation of diversity and innate host defense. Mol Divers 10(4):585–597. doi:10.1007/s11030-006-9028-2
Einhauer A, Jungbauer A (2001) The FLAG peptide, a versatile fusion tag for the purification of recombinant proteins. J Biochem Biophys Methods 49(1–3):455–465
Floyd BE, Morriss SC, Macintosh GC, Bassham DC (2012) What to eat: evidence for selective autophagy in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 54(11):907–920. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7909.2012.01178.x
Floyd BE, Morriss SC, MacIntosh GC, Bassham DC (2015) Evidence for autophagy-dependent pathways of rRNA turnover in Arabidopsis. Autophagy 11(12):2199–2212. doi:10.1080/15548627.2015.1106664
Fuji K, Shirakawa M, Shimono Y, Kunieda T, Fukao Y, Koumoto Y, Takahashi H, Hara-Nishimura I, Shimada T (2016) The adaptor complex AP-4 regulates vacuolar protein sorting at the trans-Golgi network by interacting with VACUOLAR SORTING RECEPTOR1. Plant Physiol 170(1):211–219. doi:10.1104/pp.15.00869
Hanaoka H, Noda T, Shirano Y, Kato T, Hayashi H, Shibata D, Tabata S, Ohsumi Y (2002) Leaf senescence and starvation-induced chlorosis are accelerated by the disruption of an Arabidopsis autophagy gene. Plant Physiol 129(3):1181–1193
Haud N, Kara F, Diekmann S, Henneke M, Willer JR, Hillwig MS, Gregg RG, Macintosh GC, Gartner J, Alia A, Hurlstone AF (2011) rnaset2 mutant zebrafish model familial cystic leukoencephalopathy and reveal a role for RNase T2 in degrading ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(3):1099–1103. doi:10.1073/pnas.1009811107
Henneke M, Diekmann S, Ohlenbusch A, Kaiser J, Engelbrecht V, Kohlschutter A, Kratzner R, Madruga-Garrido M, Mayer M, Opitz L, Rodriguez D, Ruschendorf F, Schumacher J, Thiele H, Thoms S, Steinfeld R, Nurnberg P, Gartner J (2009) RNASET2-deficient cystic leukoencephalopathy resembles congenital cytomegalovirus brain infection. Nat Genet 41(7):773–775. doi:10.1038/ng.398
Hillwig MS, Rizhsky L, Wang Y, Umanskaya A, Essner JJ, MacIntosh GC (2009) Zebrafish RNase T2 genes and the evolution of secretory ribonucleases in animals. BMC Evol Biol 9:170. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-9-170
Hillwig MS, Contento AL, Meyer A, Ebany D, Bassham DC, Macintosh GC (2011) RNS2, a conserved member of the RNase T2 family, is necessary for ribosomal RNA decay in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(3):1093–1098. doi:10.1073/pnas.1009809108
Houseley J, Tollervey D (2009) The many pathways of RNA degradation. Cell 136(4):763–776. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.019
Hua ZH, Fields A, Kao TH (2008) Biochemical models for S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Mol Plant 1(4):575–585. doi:10.1093/mp/ssn032
Huang H, Kawamata T, Horie T, Tsugawa H, Nakayama Y, Ohsumi Y, Fukusaki E (2015) Bulk RNA degradation by nitrogen starvation-induced autophagy in yeast. EMBO J 34(2):154–168. doi:10.15252/embj.201489083
Hugot K, Ponchet M, Marais A, Ricci P, Galiana E (2002) A tobacco S-like RNase inhibits hyphal elongation of plant pathogens. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15(3):243–250. doi:10.1094/mpmi.2002.15.3.243
Igic B, Kohn JR (2001) Evolutionary relationships among self-incompatibility RNases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(23):13167–13171. doi:10.1073/pnas.231386798
Irie M (1999) Structure-function relationships of acid ribonucleases: lysosomal, vacuolar, and periplasmic enzymes. Pharmacol Ther 81(2):77–89
Jost W, Bak H, Glund K, Terpstra P, Beintema JJ (1991) Amino acid sequence of an extracellular, phosphate-starvation-induced ribonuclease from cultured tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) cells. Eur J Biochem 198(1):1–6
Kang H, Kim SY, Song K, Sohn EJ, Lee Y, Lee DW, Hara-Nishimura I, Hwang I (2012) Trafficking of vacuolar proteins: the crucial role of Arabidopsis vacuolar protein sorting 29 in recycling vacuolar sorting receptor. Plant Cell 24(12):5058–5073. doi:10.1105/tpc.112.103481
Koide Y, Matsuoka K, Ohto M, Nakamura K (1999) The N-terminal propeptide and the C terminus of the precursor to 20-kilo-dalton potato tuber protein can function as different types of vacuolar sorting signals. Plant Cell Physiol 40(11):1152–1159
Kothke S, Kock M (2011) The Solanum lycopersicum RNaseLER is a class II enzyme of the RNase T2 family and shows preferential expression in guard cells. J Plant Physiol 168(8):840–847. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2010.11.012
Kraft C, Deplazes A, Sohrmann M, Peter M (2008) Mature ribosomes are selectively degraded upon starvation by an autophagy pathway requiring the Ubp3p/Bre5p ubiquitin protease. Nat Cell Biol 10(5):602–610. doi:10.1038/ncb1723
Kurata N, Kariu T, Kawano S, Kimura M (2002) Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding ribonuclease-related proteins in Nicotiana glutinosa leaves, as induced in response to wounding or to TMV-infection. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66(2):391–397. doi:10.1271/bbb.66.391
Lehmann K, Hause B, Altmann D, Kock M (2001) Tomato ribonuclease LX with the functional endoplasmic reticulum retention motif HDEF is expressed during programmed cell death processes, including xylem differentiation, germination, and senescence. Plant Physiol 127(2):436–449
Liu Y, Burgos JS, Deng Y, Srivastava R, Howell SH, Bassham DC (2012) Degradation of the endoplasmic reticulum by autophagy during endoplasmic reticulum stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24(11):4635–4651. doi:10.1105/tpc.112.101535
Loffler A, Abel S, Jost W, Beintema JJ, Glund K (1992) Phosphate-regulated induction of intracellular ribonucleases in cultured tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) cells. Plant Physiol 98(4):1472–1478
MacIntosh GC (2011) RNase T2 Family: Enzymatic properties, functional diversity, and evolution of ancient ribonucleases. In: Nicholson AWW (ed) ribonucleases, vol 26. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 89–114
MacIntosh GC, Bariola PA, Newbigin E, Green PJ (2001) Characterization of Rny1, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae member of the T2 RNase family of RNases: unexpected functions for ancient enzymes? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(3):1018–1023. doi:10.1073/pnas.98.3.1018
MacIntosh GC, Hillwig MS, Meyer A, Flagel L (2010) RNase T2 genes from rice and the evolution of secretory ribonucleases in plants. Mol Genet Genomics 283(4):381–396. doi:10.1007/s00438-010-0524-9
Matsushima R, Hayashi Y, Kondo M, Shimada T, Nishimura M, Hara-Nishimura I (2002) An endoplasmic reticulum-derived structure that is induced under stress conditions in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 130(4):1807–1814. doi:10.1104/pp.009464
Meng X, Sun P, Kao TH (2011) S-RNase-based self-incompatibility in Petunia inflata. Ann Bot 108(4):637–646. doi:10.1093/aob/mcq253
Nakano RT, Yamada K, Bednarek P, Nishimura M, Hara-Nishimura I (2014) ER bodies in plants of the Brassicales order: biogenesis and association with innate immunity. Front Plant Sci 5:73. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00073
Neuhaus JM, Sticher L, Meins F Jr, Boller T (1991) A short C-terminal sequence is necessary and sufficient for the targeting of chitinases to the plant vacuole. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(22):10362–10366
Niemes S, Labs M, Scheuring D, Krueger F, Langhans M, Jesenofsky B, Robinson DG, Pimpl P (2010a) Sorting of plant vacuolar proteins is initiated in the ER. Plant J 62(4):601–614
Niemes S, Langhans M, Viotti C, Scheuring D, San Wan Yan M, Jiang L, Hillmer S, Robinson DG, Pimpl P (2010b) Retromer recycles vacuolar sorting receptors from the trans-Golgi network. Plant J 61(1):107–121. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04034.x
Noda T, Kim J, Huang WP, Baba M, Tokunaga C, Ohsumi Y, Klionsky DJ (2000) Apg9p/Cvt7p is an integral membrane protein required for transport vesicle formation in the Cvt and autophagy pathways. J Cell Biol 148(3):465–480
Okabe T, Yoshimoto I, Hitoshi M, Ogawa T, Ohyama T (2005) An S-like ribonuclease gene is used to generate a trap-leaf enzyme in the carnivorous plant Drosera adelae. FEBS Lett 579(25):5729–5733. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.09.043
Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8(10):785–786. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1701
Robert S, Zouhar J, Carter C, Raikhel N (2007) Isolation of intact vacuoles from Arabidopsis rosette leaf-derived protoplasts. Nat Protoc 2(2):259–262
Rojas H, Floyd B, Morriss S, Bassham D, MacIntosh G, Goldraij A (2015) NnSR1, a class III non-S-RNase specifically induced in Nicotiana alata under Pi deficiency, is localized in endoplasmic reticulum compartments. Plant Sci 236:250–259
Saalbach G, Rosso M, Schumann U (1996) The vacuolar targeting signal of the 2S albumin from Brazil nut resides at the C terminus and involves the C-terminal propeptide as an essential element. Plant Physiol 112(3):975–985
Sanderfoot A, Ahmed S, Marty-Mazars D, Rapoport I, Kirchhausen T, Marty F, Raikhel N (1998) A putative vacuolar cargo receptor partially colocalizes with AtPEP12p on a prevacuolar compartment in Arabidopsis roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(17):9920–9925
Sanderfoot AA, Kovaleva V, Bassham DC, Raikhel NV (2001) Interactions between syntaxins identify at least five SNARE complexes within the Golgi/prevacuolar system of the Arabidopsis cell. Mol Biol Cell 12(12):3733–3743
Sheen J (2002) A transient expression assay using Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts. Available online at http://molbio.mgh.harvard.edu/sheenweb/protocols_reg.html
Tapernoux-Luthi EM, Schneider T, Keller F (2007) The C-terminal sequence from common bugle leaf galactan:galactan galactosyltransferase is a non-sequence-specific vacuolar sorting determinant. FEBS Lett 581(9):1811–1818. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.03.068
Taylor CB, Green PJ (1991) Genes with homology to fungal and S-Gene RNases are expressed in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 96(3):980–984
Taylor CB, Bariola PA, delCardayre SB, Raines RT, Green PJ (1993) RNS2: a senescence-associated RNase of Arabidopsis that diverged from the S-RNases before speciation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(11):5118–5122
Vitale A, Denecke J (1999) The endoplasmic reticulum-gateway of the secretory pathway. Plant Cell 11(4):615–628
Webber JL, Tooze SA (2010) New insights into the function of Atg9. FEBS Lett 584(7):1319–1326. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2010.01.020
Yamamoto H, Kakuta S, Watanabe TM, Kitamura A, Sekito T, Kondo-Kakuta C, Ichikawa R, Kinjo M, Ohsumi Y (2012) Atg9 vesicles are an important membrane source during early steps of autophagosome formation. J Cell Biol 198(2):219–233. doi:10.1083/jcb.201202061
Yang X, Bassham DC (2015) New insight into the mechanism and function of autophagy in plant cells. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 320:1–40. doi:10.1016/bs.ircmb.2015.07.005
Ye ZH, Droste DL (1996) Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding xylogenesis-associated and wounding-induced ribonucleases in Zinnia elegans. Plant Mol Biol 30(4):697–709
Yen Y, Green PJ (1991) Identification and properties of the major ribonucleases of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 97(4):1487–1493
Yoshida H (2001) The ribonuclease T1 family. Methods Enzymol 341:28–41
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant No. MCB-1051818 from the United States National Science Foundation to GCM and DCB and Grant No. DE-SC0014038 from the United States Department of Energy to DCB. We thank Danielle Ebany for isolation of an rns2-1 homozygote and Junmarie Soto-Burgos for assistance with confocal microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
B. E. Floyd and Y. Mugume contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Floyd, B.E., Mugume, Y., Morriss, S.C. et al. Localization of RNS2 ribonuclease to the vacuole is required for its role in cellular homeostasis. Planta 245, 779–792 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2644-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2644-x