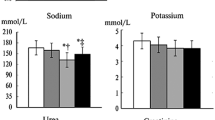
Abstract.
Arginine (Arg) produced from citrulline originates mostly from kidneys. Arg is involved in guanidino compound biosynthesis, which requires inter-organ co-operation. In renal insufficiency, citrulline accumulates in the plasma in proportion to renal damage. Thus, disturbances in Arg and guanidino compound metabolism are expected in several tissues. An original use of the model of nephrectomy based on ligating branches of the renal artery allowed us to investigate Arg and guanidino compound metabolism simultaneously in injured (left) and healthy (right) kidneys. The left kidney of adult rats was subjected to 72% nephrectomy. Non-operated, sham-operated and nephrectomized rats were studied for a period of 21 days. Constant renal growth was observed only in the healthy kidneys. Guanidino compound levels were modified transiently during the first 48 h. The metabolism and/or tissue content of several guanidino compounds were disturbed throughout the experimental period. Arg synthesis was greatly reduced in the injured kidney, while it increased in the healthy kidney. The renal production of guanidinoacetic acid decreased in the injured kidney and its urinary excretion was reduced. The experimentally proven toxins α-keto-δ-guanidinovaleric acid and guanidinosuccinic acid (GSA) accumulated only in the injured kidney. The urinary excretion of GSA and methylguanidine increased in nephrectomized rats.When the injured kidney grew again, the level of some guanidino compounds tended to normalize. Nephrectomy affected the guanidino compound levels and metabolism in muscles and liver. In conclusion, the specific accumulation of toxic guanidino compounds in the injured kidney reflects disturbances in renal metabolism and function. The healthy kidney compensates for the injured kidney's loss of metabolic functions (e.g. Arg: production). This model is excellent for investigating renal metabolism when a disease destroys a limited area in one kidney, as is observed in patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levillain, O., Marescau, B., Possemiers, I. et al. Influence of 72% injury in one kidney on several organs involved in guanidino compound metabolism: a time course study. Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 442, 558–569 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100581
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100581