Abstract
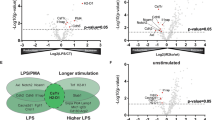
Innate-like CD5+ B1a cells localized in serous cavities are activated by innate stimuli, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), leading to T cell–independent antibody responses. Although ion channels play crucial roles in the homeostasis and activation of immune cells, the electrophysiological properties of B1a cells have not been investigated to date. Previously, in the mouse B cell lymphoma cells, we found that the voltage-independent two-pore-domain potassium (K2P) channels generate a negative membrane potential and drive Ca2+ influx. Here, we newly compared the expression and activities of K2P channels in mouse splenic follicular B (FoB), marginal zone B (MZB), and peritoneal B1a cells. Next-generation sequencing analysis showed higher levels of transcripts for TREK-2 and TWIK-2 in B1a cells than those in FoB or MZB cells. Electrophysiological analysis, using patch clamp technique, revealed higher activity of TREK-2 with the characteristic large unitary conductance (~ 250 pS) in B1a than that in FoB or MZB cells. TREK-2 activity was further increased by LPS treatment (>2 h), which was more prominent in B1a than that in MZB or FoB cells. The cytosolic Ca2+ concentration of B cells was decreased by high-K+-induced depolarization (ΔRKCl (%)), suggesting the basal Ca2+ influx to be driven by negative membrane potential. The LPS treatment significantly increased the ΔRKCl (%) in B1a, though not in FoB and MZB cells. Our study was the first to compare the K2P channels in mouse primary B cell subsets, elucidating the functional upregulation of TREK-2 and augmentation of Ca2+ influx by the stimulation of Toll-like receptor 4 in B1a cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andronic J, Bobak N, Bittner S, Ehling P, Kleinschnitz C, Herrmann AM, Zimmermann H, Sauer M, Wiendl H, Budde T, Meuth SG, Sukhorukov VL (2013) Identification of two-pore domain potassium channels as potent modulators of osmotic volume regulation in human T lymphocytes. Bba-Biomembranes 1828:699–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.09.028
Balazs M, Martin F, Zhou T, Kearney J (2002) Blood dendritic cells interact with splenic marginal zone B cells to initiate T-independent immune responses. Immunity 17:341–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00389-8
Bang H, Kim Y, Kim D (2000) TREK-2, a new member of the mechanosensitive tandem-pore K+ channel family. J Biol Chem 275:17412–17419. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M000445200
Baumgarth N (2011) The double life of a B-1 cell: self-reactivity selects for protective effector functions. Nat Rev Immunol 11:34–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2901
Bittner S, Bobak N, Herrmann AM, Gobel K, Meuth P, Hohn KG, Stenner MP, Budde T, Wiendl H, Meuth SG (2010) Upregulation of K2P5.1 potassium channels in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 68:58–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22010
Bittner S, Bobak N, Feuchtenberger M, Herrmann AM, Gobel K, Kinne RW, Hansen AJ, Budde T, Kleinschnitz C, Frey O, Tony HP, Wiendl H, Meuth SG (2011) Expression of K2P5.1 potassium channels on CD4+ T lymphocytes correlates with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R21. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3245
Chen Y, Park YB, Patel E, Silverman GJ (2009) IgM antibodies to apoptosis-associated determinants recruit C1q and enhance dendritic cell phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. J Immunol 182:6031–6043. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0804191
Chiang EY, Li T, Jeet S, Peng I, Zhang J, Lee WP, DeVoss J, Caplazi P, Chen J, Warming S, Hackos DH, Mukund S, Koth CM, Grogan JL (2017) Potassium channels Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 cooperatively and compensatorily regulate antigen-specific memory T cell functions. Nat Commun 8:14644. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14644
Choi MS, Boise LH, Gottschalk AR, Quintans J, Thompson CB, Klaus GG (1995) The role of bcl-XL in CD40-mediated rescue from anti-mu-induced apoptosis in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol 25:1352–1357. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830250533
Chumley MJ, Dal Porto JM, Cambier JC (2002) The unique antigen receptor signaling phenotype of B-1 cells is influenced by locale but induced by antigen. J Immunol 169:1735–1743. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.169.4.1735
Cid LP, Roa-Rojas HA, Niemeyer MI, Gonzalez W, Araki M, Araki K, Sepulveda FV (2013) TASK-2: a K2P K+ channel with complex regulation and diverse physiological functions. Front Physiol 4:198. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2013.00198
Dasari P, Nicholson IC, Hodge G, Dandie GW, Zola H (2005) Expression of toll-like receptors on B lymphocytes. Cell Immunol 236:140–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2005.08.020
Deng J, Wang X, Chen Q, Sun X, Xiao F, Ko KH, Zhang M, Lu L (2016) B1a cells play a pathogenic role in the development of autoimmune arthritis. Oncotarget 7:19299–19311. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8244
Di A, Xiong S, Ye Z, Malireddi RKS, Kometani S, Zhong M, Mittal M, Hong Z, Kanneganti TD, Rehman J, Malik AB (2018) The TWIK2 potassium efflux channel in macrophages mediates NLRP3 inflammasome-induced inflammation. Immunity 49:56–65.e54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.032
Duan B, Morel L (2006) Role of B-1a cells in autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 5:403–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2005.10.007
Enyedi P, Czirjak G (2010) Molecular background of leak K+ currents: two-pore domain potassium channels. Physiol Rev 90:559–605. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00029.2009
Feliciangeli S, Chatelain FC, Bichet D, Lesage F (2015) The family of K2P channels: salient structural and functional properties. J Physiol 593:2587–2603. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2014.287268
Feske S, Skolnik EY, Prakriya M (2012) Ion channels and transporters in lymphocyte function and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 12:532–547. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3233
Feske S, Wulff H, Skolnik EY (2015) Ion channels in innate and adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 33:291–353. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112212
Frances R, Tumang JR, Rothstein TL (2005) B-1 cells are deficient in Lck: defective B cell receptor signal transduction in B-1 cells occurs in the absence of elevated Lck expression. J Immunol 175:27–31. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.175.1.27
Igarashi H, Kuwahara K, Nomura J, Matsuda A, Kikuchi K, Inui S, Sakaguchi N (1994) B-Cell Ag receptor mediates different types of signals in the protein-kinase activity between immature b-cell and mature B-Cell. J Immunol 153:2381–2393
Kang D, Hogan JO, Kim D (2014) THIK-1 (K2P13.1) is a small-conductance background K+ channel in rat trigeminal ganglion neurons. Pflugers Arch 466:1289–1300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1358-1
Kennard LE, Chumbley JR, Ranatunga KM, Armstrong SJ, Veale EL, Mathie A (2005) Inhibition of the human two-pore domain potassium channel, TREK-1, by fluoxetine and its metabolite norfluoxetine. Br J Pharmacol 144:821–829. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706068
Khoubza L, Chatelain FC, Feliciangeli S, Lesage F, Bichet D (2020) Physiological roles of heteromerization: focus on the two-pore domain potassium channels. J Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP279870
Kim KS, Jang JH, Lin H, Choi SW, Kim HR, Shin DH, Nam JH, Zhang YH, Kim SJ (2015) Rise and fall of Kir2.2 current by TLR4 signaling in human monocytes: PKC-dependent trafficking and PI3K-mediated PIP2 decrease. J Immunol 195:3345–3354. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1500056
Lesage F, Terrenoire C, Romey G, Lazdunski M (2000) Human TREK2, a 2P domain mechano-sensitive K+ channel with multiple regulations by polyunsaturated fatty acids, lysophospholipids, and Gs, Gi, and Gq protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem 275:28398–28405. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M002822200
Lolicato M, Arrigoni C, Mori T, Sekioka Y, Bryant C, Clark KA, Minor DL Jr (2017) K2P2.1 (TREK-1)-activator complexes reveal a cryptic selectivity filter binding site. Nature 547:364–368. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature22988
Mahtani T, Treanor B (2019) Beyond the CRAC: diversification of ion signaling in B cells. Immunol Rev 291:104–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12770
Meuth SG, Bittner S, Meuth P, Simon OJ, Budde T, Wiendl H (2008) TWIK-related acid-sensitive K+ channel 1 (TASK1) and TASK3 critically influence T lymphocyte effector functions. J Biol Chem 283:14559–14570. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M800637200
Nakakura S, Matsui M, Sato A, Ishii M, Endo K, Muragishi S, Murase M, Kito H, Niguma H, Kurokawa N, Fujii M, Araki M, Araki K, Ohya S (2015) Pathophysiological significance of the two-pore domain K+ channel K2P5.1 in splenic CD4+CD25- T cell subset from a chemically-induced murine inflammatory bowel disease model. Front Physiol 6:299. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00299
Nam JH, Woo JE, Uhm DY, Kim SJ (2004) Membrane-delimited regulation of novel background K+ channels by MgATP in murine immature B cells. J Biol Chem 279:20643–20654. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M312547200
Nam JH, Shin DH, Zheng H, Lee DS, Park SJ, Park KS, Kim SJ (2011) Expression of TASK-2 and its upregulation by B cell receptor stimulation in WEHI-231 mouse immature B cells. Am J Phys Cell Phys 300:C1013–C1022. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00475.2010
Noel J, Sandoz G, Lesage F (2011) Molecular regulations governing TREK and TRAAK channel functions. Channels (Austin) 5:402–409. https://doi.org/10.4161/chan.5.5.16469
Park C, Kim TJ (2018) Expansion and sub-classification of T cell-dependent antibody responses to encompass the role of innate-like T cells in antibody responses. Immune Netw 18:e34. https://doi.org/10.4110/in.2018.18.e34
Park H, Kim EJ, Han J, Han J, Kang D (2016) Effects of analgesics and antidepressants on TREK-2 and TRESK currents. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 20:379–385. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.4.379
Patel AJ, Maingret F, Magnone V, Fosset M, Lazdunski M, Honore E (2000) TWIK-2, an inactivating 2P domain K+ channel. J Biol Chem 275:28722–28730. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M003755200
Prieto JMB, Felippe MJB (2017) Development, phenotype, and function of non-conventional B cells. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 54:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cimid.2017.08.002
Savage HP, Baumgarth N (2015) Characteristics of natural antibody-secreting cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1362:132–142. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12799
Shin DH, Lin H, Zheng H, Kim KS, Kim JY, Chun YS, Park JW, Nam JH, Kim WK, Zhang YH, Kim SJ (2014) HIF-1alpha-mediated upregulation of TASK-2 K+ channels augments Ca2+ signaling in mouse B cells under hypoxia. J Immunol 193:4924–4933. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1301829
Sim JH, Kim KS, Park H, Kim KJ, Lin H, Kim TJ, Shin HM, Kim G, Lee DS, Park CW, Lee DH, Kang I, Kim SJ, Cho CH, Doh J, Kim HR (2017) Differentially expressed potassium channels are associated with function of human effector memory CD8+ T cells. Front Immunol 8:859. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00859
Sindhava VJ, Bondada S (2012) Multiple regulatory mechanisms control B-1 B cell activation. Front Immunol 3:372. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00372
Tumurkhuu G, Koide N, Dagvadorj J, Noman AS, Khuda II, Naiki Y, Komatsu T, Yoshida T, Yokochi T (2010) B1 cells produce nitric oxide in response to a series of toll-like receptor ligands. Cell Immunol 261:122–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2009.11.009
Vaeth M, Feske S (2018) Ion channelopathies of the immune system. Curr Opin Immunol 52:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2018.03.021
Weber GF, Chousterman BG, Hilgendorf I, Robbins CS, Theurl I, Gerhardt LM, Iwamoto Y, Quach TD, Ali M, Chen JW, Rothstein TL, Nahrendorf M, Weissleder R, Swirski FK (2014) Pleural innate response activator B cells protect against pneumonia via a GM-CSF-IgM axis. J Exp Med 211:1243–1256. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20131471
Williams BA, Buckler KJ (2004) Biophysical properties and metabolic regulation of a TASK-like potassium channel in rat carotid body type 1 cells. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 286:L221–L230. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00010.2003
Woo J, Shin DH, Kim HJ, Yoo HY, Zhang YH, Nam JH, Kim WK, Kim SJ (2016) Inhibition of TREK-2 K+ channels by PI(4,5)P2: an intrinsic mode of regulation by intracellular ATP via phosphatidylinositol kinase. Pflugers Arch 468:1389–1402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1847-0
Zheng H, Nam JH, Nguen YH, Kang TM, Kim TJ, Earm YE, Kim SJ (2008) Arachidonic acid-induced activation of large-conductance potassium channels and membrane hyperpolarization in mouse B cells. Pflugers Arch 456:867–881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0445-1
Zheng H, Nam JH, Pang B, Shin DH, Kim JS, Chun YS, Park JW, Bang H, Kim WK, Earm YE, Kim SJ (2009) Identification of the large-conductance background K+ channel in mouse B cells as TREK-2. Am J Phys Cell Phys 297:C188–C197. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00052.2009
Zhuo RG, Liu XY, Zhang SZ, Wei XL, Zheng JQ, Xu JP, Ma XY (2015) Insights into the stimulatory mechanism of 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate on TREK-2 potassium channel. Neuroscience 300:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.05.012
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF- 2018R1A5A2025964). Also, it was partly supported by the 2019 Research Fund from Seoul National University Hospital to Dr. SJ Kim.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SiW Choi, J Woo, KS Park, J Ko, I Kho, and YK Jun conducted experiments and performed data analysis. SW Choi and HY Yoo helped with data analysis and designed the study. TJ Kim and SJ Kim designed the study and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Si Won Choi and Joohan Woo are co-first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, S.W., Woo, J., Park, K.S. et al. Higher expression of KCNK10 (TREK-2) K+ channels and their functional upregulation by lipopolysaccharide treatment in mouse peritoneal B1a cells. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 473, 659–671 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-021-02526-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-021-02526-1