Abstract
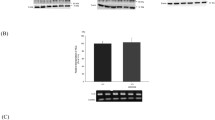
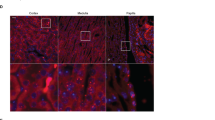
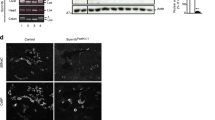
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)/cGMPs cause diuresis and natriuresis. Their downstream effectors beyond cGMP remain unclear. To elucidate a probable function of cGMP-dependent protein kinase II (cGKII), we investigated renal parameters in different conditions (basal, salt diets, starving, water load) using a genetically modified mouse model (cGKII-KO), but did not detect any striking differences between WT and cGKII-KO. Thus, cGKII is proposed to play only a marginal role in the adjustment of renal concentration ability to varying salt loads without water restriction or starving conditions. When WT mice were subjected to a volume load (performed by application of a 10-mM glucose solution (3 % of BW) via feeding needle), they exhibited a potent diuresis. In contrast, urine volume was decreased significantly in cGKII-KO. We showed that AQP2 plasma membrane (PM) abundance was reduced for about 50 % in WT upon volume load, therefore, this might be a main cause for the enhanced diuresis. In contrast, cGKII-KO mice almost completely failed to decrease AQP2-PM distribution. This significant difference between both genotypes is not induced by an altered p-Ser256-AQP2 phosphorylation, as phosphorylation at this site decreases similarly in WT and KO. Furthermore, sodium excretion was lowered in cGKII-KO mice during volume load. In summary, cGKII is only involved to a minor extent in the regulation of basal renal concentration ability. By contrast, cGKII-KO mice are not able to handle an acute volume load. Our results suggest that membrane insertion of AQP2 is inhibited by cGMP/cGKII.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agre P, King LS, Yasui M, Guggino WB, Ottersen OP, Fujiyoshi Y, Engel A, Nielsen S (2002) Aquaporin water channels — from atomic structure to clinical medicine. J Physiol 542:3–16
Aperia A, Holtback U, Syren ML, Svensson LB, Fryckstedt J, Greengard P (1994) Activation/deactivation of renal Na+, K(+)-ATPase: a final common pathway for regulation of natriuresis. FASEB J 8:436–439
Armaly Z, Assady S, Abassi Z (2013) Corin: a new player in the regulation of salt–water balance and blood pressure. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 22:713–722
Barile M, Pisitkun T, Yu MJ, Chou CL, Verbalis MJ, Shen RF, Knepper MA (2005) Large scale protein identification in intracellular aquaporin-2 vesicles from renal inner medullary collecting duct. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:1095–1106
Biel M, Zong X, Ludwig A, Sautter A, Hofmann F (1999) Structure and function of cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 135:151–171
Boone M, Kortenoeven M, Robben JH, Deen PMT (2010) Effect of the cGMP pathway on AQP2 expression and translocation: potential implications for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:48–54
Bouley R, Breton S, Sun T-X, McLaughlin M, Nsumu NN, Lin HY, Ausiello DA, Brown D (2000) Nitric oxide and atrial natriuretic factor stimulate cGMP-dependent membrane insertion of aquaporin 2 in renal epithelial cells. J Clin Investig 106:1115–1126
Bouley R, Pastor-Soler N, Cohen O, McLaughlin M, Breton S, Brown D (2005) Stimulation of AQP2 membrane insertion in renal epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo by the cGMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor sildenafil citrate (Viagra). Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 288:F1103–F1112
Dunn SR, Qi Z, Bottinger EP, Breyer MD, Sharma K (2004) Utility of endogenous creatinine clearance as a measure of renal function in mice. Kidney Int 65:1959–1967
El-Farhan N, Hampton D, Penney M (2013) Measurement of arginine vasopressin. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ) 1065:129–139
Gambaryan S, Hausler C, Markert T, Pohler D, Jarchau T, Walter U, Haase W, Kurtz A, Lohmann SM (1996) Expression of type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase in rat kidney is regulated by dehydration and correlated with renin gene expression. J Clin Investig 98:662–670
Guo L-J, Alli AA, Eaton DC, Bao H-F (2013) ENaC is regulated by natriuretic peptide receptor-dependent cGMP signaling. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 304:F930–F937
Hammond TG, Yusufi AN, Knox FG, Dousa TP (1985) Administration of atrial natriuretic factor inhibits sodium-coupled transport in proximal tubules. J Clin Investig 75:1983–1989
Harlow E, Harlow, Lane EHD (1988) Antibodies: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Harshfield GA, Dong Y, Kapuku GK, Zhu H, Hanevold CD (2009) Stress-induced sodium retention and hypertension: a review and hypothesis. Curr Hypertens Rep 11:29–34
Hiremath S, Akbari A, Shabana W, Fergusson DA, Knoll GA (2013) Prevention of contrast-induced acute kidney injury: is simple oral hydration similar to intravenous? A systematic review of the evidence. PloS ONE 8:e60009
Huang DY, Boini KM, Lang PA, Grahammer F, Duszenko M, Heller-Stilb B, Warskulat U, Haeussinger D, Lang F, Vallon V (2006) Impaired ability to increase water excretion in mice lacking the taurine transporter gene TAUT. Pflugers Arch 451:668–677
Jarchau T, Hausler C, Markert T, Pohler D, Vanderkerckhove J, De Jonge HR, Lohmann SM, Walter U (1994) Cloning, expression, and in situ localization of rat intestinal cGMP-dependent protein kinase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:9426–9430
Juilfs DM, Soderling S, Burns F, Beavo JA (1999) Cyclic GMP as substrate and regulator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs). Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 135:67–104
Klein JD (2010) Corin: an ANP protease that may regulate sodium reabsorption in nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 78:635–637
Klokkers J, Langehanenberg P, Kemper B, Kosmeier S, Gv B, Riethmuller C, Wunder F, Sindic A, Pavenstadt H, Schlatter E, Edemir B (2009) Atrial natriuretic peptide and nitric oxide signaling antagonizes vasopressin-mediated water permeability in inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 297:F693–F703
Kyhse-Andersen J (1984) Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polycrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods 10:203–209
Marples D, Knepper MA, Christensen EI, Nielsen S (1995) Redistribution of aquaporin-2 water channels induced by vasopressin in rat kidney inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol 269:C655–664
Martin FL, Stevens TL, Cataliotti A, Schirger JA, Borgeson DD, Redfield MM, Luchner A, Burnett JC Jr (2005) Natriuretic and antialdosterone actions of chronic oral NEP inhibition during progressive congestive heart failure. Kidney Int 67:1723–1730
Nakamura K, Hirano J, Itazawa S, Kubokawa M (2002) Protein kinase G activates inwardly rectifying K(+) channel in cultured human proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol 283:F784–791
Nedvetsky PI, Tamma G, Beulshausen S, Valenti G, Rosenthal W, Klussmann E, Beitz PDE (2009) Regulation of aquaporin-2 trafficking. Aquaporins. Springer, Berlin, pp 133–157
Nonoguchi H, Sands JM, Knepper MA (1989) ANF inhibits NaCl and fluid absorption in cortical collecting duct of rat kidney. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 256:F179–F186
Pech V, Thumova M, Dikalov SI, Hummler E, Rossier BC, Harrison DG, Wall SM (2013) Nitric oxide reduces Cl− absorption in the mouse cortical collecting duct through an ENaC-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 304:F1390–F1397
Pfeifer A, Aszodi A, Seidler U, Ruth P, Hofmann F, Fassler R (1996) Intestinal secretory defects and dwarfism in mice lacking cGMP-dependent protein kinase II. Science 274:2082–2086
Pfeifer A, Ruth P, Dostmann W, Sausbier M, Klatt P, Hofmann F (1999) Structure and function of cGMP-dependent protein kinases. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 135:105–149
Polzin D, Kaminski HJ, Kastner C, Wang W, Kramer S, Gambaryan S, Russwurm M, Peters H, Wu Q, Vandewalle A, Bachmann S, Theilig F (2010) Decreased renal corin expression contributes to sodium retention in proteinuric kidney diseases. Kidney Int 78:650–659
Rocha AS, Kudo LH (1990) Atrial peptide and cGMP effects on NaCl transport in inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 259:F258–F268
Sausbier M, Schubert R, Voigt V, Hirneiss C, Pfeifer A, Korth M, Kleppisch T, Ruth P, Hofmann F (2000) Mechanisms of NO/cGMP-dependent vasorelaxation. Circ Res 87:825–830
Silver MA (2006) The natriuretic peptide system: kidney and cardiovascular effects. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 15:14–21
Sonnenberg H, Cupples WA, Bold AJ, Veress AT (1982) Intrarenal localization of the natriuretic effect of cardiac atrial extract. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 60:1149–1152
Spiessberger B, Bernhard D, Herrmann S, Feil S, Werner C, Luppa PB, Hofmann F (2009) cGMP-dependent protein kinase II and aldosterone secretion. FEBS J 276:1007–1013
Uhler MD (1993) Cloning and expression of a novel cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase from mouse brain. J Biol Chem 268:13586–13591
Vaandrager AB, Bot AG, De Jonge HR (1997) Guanosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase II mediates heat-stable enterotoxin-provoked chloride secretion in rat intestine. Gastroenterology 112:437–443
Wagner C, Pfeifer A, Ruth P, Hofmann F, Kurtz A (1998) Role of cGMP-kinase II in the control of renin secretion and renin expression. J Clin Investig 102:1576–1582
Wang WH (2000) The cGMP-dependent protein kinase stimulates the basolateral 18-pS K channel of the rat CCD. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 278:C1212–1217
Winaver J, Burnett JC, Tyce GM, Dousa TP (1990) ANP inhibits Na(+)–H + antiport in proximal tubular brush border membrane: role of dopamine. Kidney Int 38:1133–1140
Xie L, Hoffert JD, Chou CL, Yu MJ, Pisitkun T, Knepper MA, Fenton RA (2010) Quantitative analysis of aquaporin-2 phosphorylation. Am J Physiol 298:F1018–1023
Acknowledgements
We thank Astrid Seefeld and Gertraud Wilberg for their excellent technical assistance. The work was supported by the Bavarian state, Sonderforschungsbereich SFB699, and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft DFG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schramm, A., Schinner, E., Huettner, J.P. et al. Function of cGMP-dependent protein kinase II in volume load-induced diuresis. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 466, 2009–2018 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1445-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1445-y