Abstract
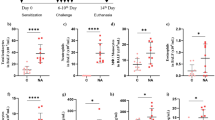
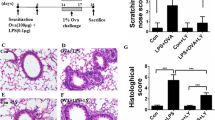
Extracellular ATP promotes an indirect contraction of airway smooth muscle via the secondary release of thromboxane A2 (TXA2) from airway epithelium. Our aim was to evaluate if common contractile agonists modify this response to ATP. Tracheas from sensitized guinea pigs were used to evaluate ATP-induced contractions before and after a transient contraction produced by histamine, carbachol, or serotonin. Epithelial mRNA for COX-1 and COX-2 was measured by RT-PCR and their expression assessed by immunohistochemistry. Compared with the initial response, ATP-induced contraction was potentiated by pretreatment with histamine, carbachol, or serotonin. Either suramin (antagonist of P2X and P2Y receptors) plus RB2 (antagonist of P2Y receptors) or indomethacin (inhibitor of COX-1 and COX-2) annulled the ATP-induced contraction, suggesting that it was mediated by P2Y receptor stimulation and TXA2 production. When COX-2 was inhibited by SC-58125 or thromboxane receptors were antagonized by SQ-29548, just the potentiation was abolished, leaving the basal response intact. Airway epithelial cells showed increased COX-2 mRNA after stimulation with histamine or carbachol, but not serotonin, while COX-1 mRNA was unaffected. Immunochemistry corroborated this upregulation of COX-2. In conclusion, we showed for the first time that histamine and carbachol cause hyperresponsiveness to ATP by upregulating COX-2 in airway epithelium, which likely increases TXA2 production. Serotonin-mediated hyperresponsiveness seems to be independent of COX-2 upregulation, but nonetheless is TXA2 dependent. Because acetylcholine, histamine, and serotonin can be present during asthmatic exacerbations, their potential interactions with ATP might be relevant in its pathophysiology.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham F, Sacerdoti F, De Leon R, Gentile T, Canellada A (2012) Angiotensin II activates the calcineurin/NFAT signaling pathway and induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression in rat endometrial stromal cells. PLoS One 7(5):e37750
Advenier C, Bidet D, Floch-Saint-Aubin A, Renier A (1982) Contribution of prostaglandins and thromboxanes to the adenosine and ATP-induced contraction of guinea-pig isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol 77(1):39–44
Basoglu OK, Pelleg A, Essilfie-Quaye S, Brindicci C, Barnes PJ, Kharitonov SA (2005) Effects of aerosolized adenosine 5′-triphosphate vs adenosine 5′-monophosphate on dyspnea and airway caliber in healthy nonsmokers and patients with asthma. Chest 128(4):1905–1909
Bergner A, Sanderson MJ (2002) ATP stimulates Ca2+ oscillations and contraction in airway smooth muscle cells of mouse lung slices. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 283(6):L1271–L1279
Burnstock G (2007) Physiology and pathophysiology of purinergic neurotransmission. Physiol Rev 87(2):659–797
Burnstock G, Brouns I, Adriaensen D, Timmermans JP (2012) Purinergic signaling in the airways. Pharmacol Rev 64(4):834–868
Carbajal V, Vargas MH, Flores-Soto E, Martinez-Cordero E, Bazan-Perkins B, Montano LM (2005) LTD4 induces hyperresponsiveness to histamine in bovine airway smooth muscle: role of SR-ATPase Ca2+ pump and tyrosine kinase. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288(1):L84–L92
Clark EA, Hill SJ (1996) Sensitivity of histamine H3 receptor agonist-stimulated [35S]GTP gamma[S] binding to pertussis toxin. Eur J Pharmacol 296(2):223–225
Coulson FR, Fryer AD (2003) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and airway diseases. Pharmacol Ther 98(1):59–69
Chávez J, Vargas MH, Rebollar-Ayala DC, Díaz-Hernández V, Cruz-Valderrama JE, Flores-Soto E, Flores-García M, Jiménez-Vargas NN, Barajas-López C, Montaño LM (2013) Inhibition of extracellular nucleotides hydrolysis intensifies the allergic bronchospasm. A novel protective role of ectonucleotidases. Allergy. doi:10.1111/all.12113
Chen BC, Yu CC, Lei HC, Chang MS, Hsu MJ, Huang CL, Chen MC, Sheu JR, Chen TF, Chen TL, Inoue H, Lin CH (2004) Bradykinin B2 receptor mediates NF-kappaB activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression via the Ras/Raf-1/ERK pathway in human airway epithelial cells. J Immunol 173(8):5219–5228
Fedan JS, Belt JJ, Yuan LX, Frazer DG (1993) Contractile effects of nucleotides in guinea pig isolated, perfused trachea: involvement of respiratory epithelium, prostanoids and Na+ and Cl− channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264(1):210–216
Flores-Soto E, Carbajal V, Reyes-Garcia J, Garcia-Hernandez LM, Figueroa A, Checa M, Barajas-Lopez C, Montano LM (2011) In airways ATP refills sarcoplasmic reticulum via P2X smooth muscle receptors and induces contraction through P2Y epithelial receptors. Pflugers Arch 461(2):261–275
Gever JR, Cockayne DA, Dillon MP, Burnstock G, Ford AP (2006) Pharmacology of P2X channels. Pflugers Arch 452(5):513–537
Govindaraju V, Martin JG, Maghni K, Ferraro P, Michoud MC (2005) The effects of extracellular purines and pyrimidines on human airway smooth muscle cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315(2):941–948
Hattori M, Gouaux E (2012) Molecular mechanism of ATP binding and ion channel activation in P2X receptors. Nature 485(7397):207–212
Idzko M, Hammad H, van Nimwegen M, Kool M, Willart MA, Muskens F, Hoogsteden HC, Luttmann W, Ferrari D, Di Virgilio F, Virchow JC Jr, Lambrecht BN (2007) Extracellular ATP triggers and maintains asthmatic airway inflammation by activating dendritic cells. Nat Med 13(8):913–919
Jarjour NN, Calhoun WJ, Schwartz LB, Busse WW (1991) Elevated bronchoalveolar lavage fluid histamine levels in allergic asthmatics are associated with increased airway obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis 144(1):83–87
Liu MC, Bleecker ER, Lichtenstein LM, Kagey-Sobotka A, Niv Y, McLemore TL, Permutt S, Proud D, Hubbard WC (1990) Evidence for elevated levels of histamine, prostaglandin D2, and other bronchoconstricting prostaglandins in the airways of subjects with mild asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 142(1):126–132
Liu T, Laidlaw TM, Feng C, Xing W, Shen S, Milne GL, Boyce JA (2012) Prostaglandin E2 deficiency uncovers a dominant role for thromboxane A2 in house dust mite-induced allergic pulmonary inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(31):12692–12697
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Makwana R, Gozzard N, Spina D, Page C (2012) TNF-alpha-induces airway hyperresponsiveness to cholinergic stimulation in guinea pig airways. Br J Pharmacol 165(6):1978–1991
Minette PA, Lammers JW, Dixon CM, McCusker MT, Barnes PJ (1989) A muscarinic agonist inhibits reflex bronchoconstriction in normal but not in asthmatic subjects. J Appl Physiol 67(6):2461–2465
Miralpeix M, Camacho M, Lopez-Belmonte J, Canalias F, Beleta J, Palacios JM, Vila L (1997) Selective induction of cyclo-oxygenase-2 activity in the permanent human endothelial cell line HUV-EC-C: biochemical and pharmacological characterization. Br J Pharmacol 121(2):171–180
Mounkaila B, Marthan R, Roux E (2005) Biphasic effect of extracellular ATP on human and rat airways is due to multiple P2 purinoceptor activation. Respir Res 6143
Muller T, Myrtek D, Bayer H, Sorichter S, Schneider K, Zissel G, Norgauer J, Idzko M (2006) Functional characterization of histamine receptor subtypes in a human bronchial epithelial cell line. Int J Mol Med 18(5):925–931
Nagaoka M, Nara M, Tamada T, Kume H, Oguma T, Kikuchi T, Zaini J, Moriya T, Ichinose M, Tamura G, Hattori T (2009) Regulation of adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP)-gated P2X4 receptors on tracheal smooth muscle cells. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 166(1):61–67
Newton R, Kuitert LM, Bergmann M, Adcock IM, Barnes PJ (1997) Evidence for involvement of NF-kappaB in the transcriptional control of COX-2 gene expression by IL-1beta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 237(1):28–32
Pan ZK, Ye RD, Christiansen SC, Jagels MA, Bokoch GM, Zuraw BL (1998) Role of the Rho GTPase in bradykinin-stimulated nuclear factor-kappaB activation and IL-1beta gene expression in cultured human epithelial cells. J Immunol 160(6):3038–3045
Pellegrino R, Wilson O, Jenouri G, Rodarte JR (1996) Lung mechanics during induced bronchoconstriction. J Appl Physiol 81(2):964–975
Segura P, Vargas MH, Cordoba-Rodriguez G, Chavez J, Arreola JL, Campos-Bedolla P, Ruiz V, Garcia-Hernandez LM, Mendez C, Montano LM (2010) Role of 5-HT2A, 5-HT4 and 5-HT7 receptors in the antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in guinea-pigs. Clin Exp Allergy 40(2):327–338
Shichijo M, Arimura A, Hirano Y, Yasui K, Suzuki N, Deguchi M, Abraham WM (2009) A prostaglandin D2 receptor antagonist modifies experimental asthma in sheep. Clin Exp Allergy 39(9):1404–1414
Swayne GT, Maguire J, Dolan J, Raval P, Dane G, Greener M, Owen DA (1988) Evidence for homogeneity of thromboxane A2 receptor using structurally different antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 152(3):311–319
Van Crombruggen K, Van Nassauw L, Timmermans JP, Lefebvre RA (2007) Inhibitory purinergic P2 receptor characterisation in rat distal colon. Neuropharmacology 53(2):257–271
von Kugelgen I (2006) Pharmacological profiles of cloned mammalian P2Y-receptor subtypes. Pharmacol Ther 110(3):415–432
Wildman SS, Unwin RJ, King BF (2003) Extended pharmacological profiles of rat P2Y2 and rat P2Y4 receptors and their sensitivity to extracellular H+ and Zn2+ ions. Br J Pharmacol 140(7):1177–1186
Yang CM, Chien CS, Hsiao LD, Luo SF, Wang CC (2002) Interleukin-1beta-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression is mediated through activation of p42/44 and p38 MAPKS, and NF-kappaB pathways in canine tracheal smooth muscle cells. Cell Signal 14(11):899–911
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by a grant from CONACYT (81409) and DGAPA-UNAM (IN201810-3 and IN200613) to Dr. Luis M. Montaño.
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest are declared by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montaño, L.M., Carbajal, V., Vargas, M.H. et al. Histamine, carbachol, and serotonin induce hyperresponsiveness to ATP in guinea pig tracheas: involvement of COX-2 pathway. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 465, 1171–1179 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1253-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1253-9