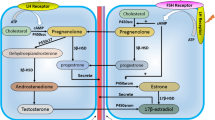
Abstract
The gonadal hormone 17β-estradiol is involved in numerous cellular processes. In many cases, 17β-estradiol actions are imitated by synthetic and natural chemicals in the environment. Their actions differ depending on the target tissue, the receptors involved and the molecular pathways activated. The plethora of estrogenic actions is triggered by different receptors and other specific structures that activate different signalling pathways. This amount of information may lead to a maze of effects triggered by endogenous and environmental estrogens that we intend to clarify in this review. Understanding the variety of estrogen receptors, their different locations and the signalling pathways activated by estrogenic ligands is fundamental for understanding the diversity of actions that estrogens have in different tissues and cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ábrahám IM, Han SK, Todman MG, Korach KS, Herbison AE (2003) Estrogen receptor β mediates rapid estrogen actions on gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons in vivo. J Neurosci 23:5771–5777
Ábrahám IM, Todman MG, Korach KS, Herbison AE (2004) Critical in vivo roles for classical estrogen receptors in rapid estrogen actions on intracellular signaling in mouse brain. Endocrinology 145:3955–3961
Aquila S, Sisci D, Gentile M, Middea E, Catalano S, Carpino A, Rago V, Ando S (2004) Estrogen receptor (ER)α and ERβ are both expressed in human ejaculated spermatozoa: evidence of their direct interaction with phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase/Akt pathway. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:1443–1451
Aronica SM, Kraus WL, Katzenellenbogen BS (1994) Estrogen action via the cAMP signaling pathways: stimulation of adenylate cyclase and cAMP-regulated gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8517–8521
Auricchio F, Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Di Domenico M (2003) Interactions of estrogen receptors with signal cascades molecules. In: Watson CS (ed.) The identities of membrane steroid receptors. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 77–83
Beato M, Klug J (2000) Steroids hormone receptors. An update. Hum Reprod Update 6:225–236
Benten WP, Stephan C, Lieberherr M, Wunderlich F (2001) Estradiol signaling via sequestrable surface receptors. Endocrinology 142:1669–1677
Brotons JA, Olea-Serrano MF, Villalobos M, Pedraza V, Olea N (1995) Xenoestrogens released from lacquer coatings in food cans. Environ Health Perspect 103:608–612
Bulayeva NN, Watson CS (2004) Xenoestrogen-induced ERK 1 and 2 activation via multiple membrane-initiated signalling pathways. Environ Health Perspect DOI 10.1289/ehp.7175
Canesi L, Lorusso LC, Ciacci C, Betti M, Zampini M, Gallo G (2004) Environmental estrogens can affect the function of mussel hemocytes through rapid modulation of kinase pathways. Gen Comp Endocrinol 138:58–69
Castoria G, Migliaccio A, Bilancio A, Di Domenico M, de Falco A, Lombardi M, Fiorentino R, Varricchio L, Barone MV, Auricchio F (2001) PI3-kinase in concert with Src promotes the S-phase entry of oestradiol-stimulated MCF-7 cells. EMBO J 21:6050–6059
Chambliss KL, Shaul PW (2002) Estrogen modulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Endocr Rev 23:665–686
Chambliss KL, Yuhanna, IS, Mineo C, Liu P, German Z, Sherman TS, Mendelsohn ME, Anderson RG, Shaul PW (2000) Estrogen receptor α and endothelial nitric oxide synthase are organised into a functional signaling module in caveolae. Circ Res 87:E44–E52
Christian HC, Morris JF (2002) Rapid actions of 17β-oestradiol on a subset of lactotrophs in the rat pituitary. J Physiol (Lond) 539:557–566
Coffer PJ, Jin J, Woodgett JR (1998) Protein kinase B (c-Akt): a multifunctional mediator of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation. Biochem J 335:1–13
Colborn T, vom Saal FS, Soto AM (1993) Developmental effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environ Health Perspect 101:378–384
Colborn T, Myers JP, Dubanowski D (1996) Our stolen future. Dutton, New York
Condliffe SB, Doolan CM, Harvey BJ (2001) 17β-Oestradiol acutely regulates Cl− secretion in rat distal colonic epithelium. J Physiol (Lond) 530:47–54
Couse JF, Korach KS (1999) Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr Rev 20:358–417
Deissederoth K, Heist EK, Tsien RW (1998) Translocation of calmodulin to the nucleus supports CREB phosphorylation in hippocampal neurons. Nature 392:198–202
Dick GM, Sanders KM (2001) (Xeno)estrogen sensitivity of smooth muscle BK channels conferred by the regulatory β1 subunit: a study of β1 knockout mice. J Biol Chem 276:44835–44840
Doolan CM, Harvey BJ (2003) A Gαs protein-coupled membrane receptor, distinct from the classical oestrogen receptor, transduces rapid effects from oestradiol on [Ca2+]i in female rat distal colon. Mol Cell Endocrinol 199:87–103
Filardo EJ, Quinn JA, Frackelton Jr, AR, Bland KI (2002) Estrogen-induced activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2 requires the G-protein-coupled receptor homologue, GPR30, and occurs via transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor-to-MAPK signalling axis. Mol Endocrinol 16:70–84
Flouriot G, Brand H, Denger S, Metivier R, Kos M, Reid G, Sonntag-Buck V, Gannon F (2000). Identification of a new isoform of the human estrogen receptor α (hERα) that is encoded by distinct transcripts and that is able to repress hERα activation function 1. EMBO J 19:4688–4700
Frigo DE, Burow ME, Mitchell KA, Chiang TC, McLachlan JA (2002) DDT and its metabolites alter gene expression in human uterine cell lines through estrogen receptor-independent mechanisms. Environ Health Perspect 110:1239–1245
Fulton D, Gratton JP, McCabe TJ, Fontana J, Fujio Y, Walsh K, Franke TF, Papapetropoulos A, Sessa WC (2001) Regulation of endothelium-derived nitric oxide production by the protein kinase Akt. Nature 399:597–601
Gu G, Rojo AA, Zee MC, Yu J, Simerly RB (1996) Hormonal regulation of CREB phosphorylation in the anteroventral periventricular nucleus. J Neurosci 16:3035–3044
Hall JM, Korach KS (2002) Analysis of molecular mechanism of human estrogen receptors alpha and beta reveals differential specificity in target promoter regulation by xenoestrogens. J Biol Chem 277:44455–44561
Hall JM, McDonnell DP, Korach KS (2002) Allosteric regulation of estrogen receptor structure, function, and coactivator recruitment by different estrogen response elements. Mol Endocrinol 16:469–486
Hawkins MB, Thomas P (2004) The unusual binding properties of the third distinct teleost estrogen receptor subtype ERβa are accompanied by high conserved amino acid changes in the ligand binding domain. Endocrinology 145:2968–2977
Hawkins MB, Thornton JW, Crews D, Skipper JK, Dotte A, Thomas P (2000) Identification of a third distinct estrogen receptor and reclassification of estrogen receptors in teleosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10751–10756
Haynes MP, Li L, Sinha D, Russell KS, Hisamoto K, Baron R, Collinge M, Sessa WC, Bender JR (2003). Src kinase mediates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent rapid endothelial nitric-oxide synthase activation by estrogen. J Biol Chem 278:2118–2123
Honda K, Sawada H, Kihara T, Urushitani M, Nakamizo T, Akaike A, Shimohama S (2000) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mediates neuroprotection by estrogen in culture cortical neurons. J Neurosci Res 60:321–327
Horigome T, Ogata F, Golding TS, Korach KS (1988) Estradiol-stimulated proteolytic cleavage of the estrogen receptor in mouse uterus. Endocrinology 123:2540–2548
Katzenellenbogen JA, O’Malley BW, Katzenellenbogen BS (1996) Tripartite steroid hormone receptor pharmacology: interaction with multiple effector sites as a basis for the cell and promoter-specific action of these hormones. Mol Endocrinol 10:119–131
Kelly M, Levin ER (2001) Rapid actions of plasma membrane estrogen receptors. Trends Endocrinol Metab 12:152–156
Kelly MJ, Qiu J, Wagner EJ, Rønnekleiv OK (2002) Rapid effects of estrogen on G protein-coupled receptor activation of potassium channels in the central nervous system (CNS). J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 1779:1–7
Kim HP, Lee JY, Jeong JK, Bae SW, Lee HK, Jo I (1999) Nongenomic stimulation of nitric oxide release by estrogen is mediated by estrogen receptor α localized in caveolae. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 263:257–262
Kuiper GG, Lemmen JG, Carlsson B, Corton JC, Safe SH, van der Saag PT, van der Burg G, Gustafsson JA (1998) Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor beta. Endocrinology 139:4252–4263
Lee HW, Eghbali-Webb M (1998) Estrogen enhances proliferative capacity of cardiac fibroblast by estrogen receptor- and mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathways. J Mol Cell Cardiol 30:1359–1368
Lee MH, Kim E, Kim TS (2004) Exposure to 4-tert-octylphenol, and environmentally persistent alkylphenol, enhances interleukin-4 production in T cells via NF-AT activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 197:19–28
Li L, Haynes P, Bender JR (2003) Plasma membrane localization and function of the estrogen receptor α variant (ER46) in human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4807–4812
Liu MM, Albanese C, Anderson CM, Hilty K, Webb P, Uht RM, Price RH, Pestell RG, Kushner PJ (2002) Opposing action of estrogen receptors alpha and beta on cyclin D1 gene expression. J Biol Chem 277:24353–24360
Lösel RM, Falkenstein E, Feuring M, Schultz A, Tillman HC, Rossol-Haseroth K, Wehling M (2003) Non-genomic steroid action: controversies, questions and answers. Physiol Rev 83:965–1016
Luconi M, Bonaccorsi L, Forti G, Baldi E (2001) Effects of estrogenic compounds on human spermatozoa: evidence for interaction with non-genomic receptor for estrogen on human sperm membrane. Mol Cell Endocrinol 10:39–45
Marin R, Guerra B, Hernández-Jiménez JG, Kang X-L, Fraser JD, López FJ, Alonso R (2003) Estradiol prevents amyloid-β peptide-induced cell death in a cholinergic cell line via modulation of a classical estrogen receptor. Neuroscience 121:917–926
McCabe TJ, Fulton D, Roman LJ, Sessa WC (2000) Enhanced electron flux and reduced calmodulin dissociation may explain “calcium-independent” eNOS activation by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 275:6123–6128
McLachlan JA (2001) Environmental signaling: what embryos and evolution teach us about endocrine disrupting chemicals. Endocr Rev 22:319–341
McKenna NJ, O’Malley BW (2002) Combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear receptors and coregulators. Cell 108:465–474
Mendelsohn ME (2000) Mechanism of estrogen action in the cardiovascular system. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 74:337–343
Migliaccio A, Di Domenico M, Castoria G, de Falco A, Bontempo P, Nola E, Auricchio F (1996) Tyrosine kinase/p21ras/MAP-kinase pathway activation by estradiol-receptor complex in MCF-7 cells. EMBO J 15:1292–1300
Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Di Domenico M, de Falco A, Bilanciom A, Lombardim M, Botterom D, Varricchio L, Nanayakkara M, Rotondi A, Auricchio F (2003) Sex steroid hormones act as growth factors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Endocrinol 83:31–35
Morales A, Díaz M, Ropero AB, Nadal A, Alonso R (2003) Estradiol modulates acetylcholine-induced Ca2+ signals in LHRH-releasing GT1-7 cells through a membrane binding site. Eur J Neurosci 18:2505–2514
Mueller SO, Simon S, Chae K, Metzler M, Korach KS (2004) Phytoestrogens and their human metabolites show distinct agonistic and antagonistic properties on estrogen receptor α (ERα) and ERβ in human cells. Toxicol Sci 80:14–25
Nadal A, Rovira JM, Laribi O, Leon-Quinto T, Andreu E, Ripoll C, Soria B (1998) Rapid insulinotropic effect of 17β-estradiol via a plasma membrane receptor. FASEB J 12:1341–1348
Nadal A, Ropero AB, Laribi O, Maillet M, Fuentes E, Soria B (2000) Nongenomic actions of estrogens and xenoestrogens by binding at a plasma membrane receptor unrelated to estrogen receptor α and estrogen receptor β. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11603–11608
Nadal A, Díaz M, Valverde MA (2001) The estrogen trinity: membrane, cytosolic and nuclear effects. Physiology 16:251–255
Nadal A, Ropero AB, Fuentes E, Soria B (2001) The plasma membrane estrogen receptor: nuclear or unclear? Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:597–599
Nadal A, Ropero AB, Fuentes E, Soria B, Ripoll C (2004) Estrogen and xenoestrogen actions on endocrine pancreas: from ion channel modulation to activation of nuclear function. Steroids 69:531–536
Nakazawa K, Ohno Y (2003) Block by phytoestrogens of recombinant human neuronal nicotinic receptors. J Pharmacol Sci 93:118–121
Negishi I, Ishii Y, Kyuwa S, Kuroda Y, Yoshikawa Y (2003) Inhibition of staurosporine-induced neuronal cell death by bisphenol A and nonylphenol in primary cultured rat hippocampal and cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett 353:99–102
Noguchi S, Nakatsuka M, Asagiri K, Habara T, Takata M, Konishi H, Kudo T (2002) Bisphenol A stimulates NO synthesis through a non-genomic estrogen receptor-mediated mechanism in mouse endothelial cells. Toxicol Lett 135:95–101
Olea N, Pulgar R, Perez P, Olea-Serrano F, Rivas A, Novillo-Fertrell A, Pedraza V, Soto AM, Sonnenschein C (1996) Estrogenicity of resin-based composites and sealants used in dentistry. Environ Health Perspect 104:298–305
Pilz RB, Casteel DE (2003) Regulation of gene expression by cyclic GMP. Circ Res 93:1034–1046
Qiu J, Bosch MA, Tobias SC, Grandy DK, Scanlan TS, Rønnekleiv OK, Kelly MJ (2003) Rapid signaling of estrogen in hypothalamic neurons involves a novel G-protein-coupled receptor that activates protein kinase C. J Neurosci 23:9529–9540
Quesada I, Fuentes E, Viso-León MC, Soria B, Ripoll C, Nadal A (2002) Low doses of the endocrine disruptor bisphenol-A and the native hormone 17β-estradiol rapidly activate transcription factor CREB. FASEB J 16:1671–1673. DOI 10.1096/fjo01-02-0313fje
Razandi M, Pedram A, Greene GL, Levin ER (1999) Cell membrane and nuclear estrogen receptors derive from a single transcript: Studies of ERα and ERβ expressed in CHO cells. Mol Endocrinol 13:307–319
Razandi M, Pedram A, Merchenthaler I, Greene GL, Levin ER (2004) Plasma membrane estrogen receptors exist and functions as dimers. Mol Endocrinol Doi 10.1210/me.2004-0115
Ropero AB, Fuentes E, Rovira JM, Ripoll C, Soria B, Nadal A (1999) Non-genomic actions of 17β-oestradiol in mouse pancreatic β-cells are mediated by a cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J Physiol (Lond) 521:397–407
Ropero AB, Soria B, Nadal A (2002) A nonclassical estrogen membrane receptor triggers rapid differential actions in the endocrine pancreas. Mol Endocrinol 16:497–505
Rorsman P, Eliasson L, Renström E, Gromada J, Barg S, Göpel S (2000) The cell physiology of biphasic insulin secretion. Physiology 15:72–77
Ruelhmann DO, Steinert JR, Valverde MA, Jacob R, Mann GE (1998) Environmental estrogenic pollutants induce acute vascular relaxation by inhibiting L-type Ca2+ channels in smooth muscle cells. FASEB J 12:613–619
Samadi A, Carlson G, Gueorgiev A, Cenedella RJ (2002) Rapid, non-genomic actions of progesterone and estradiol on steady-state calcium and resting calcium influx in lens epithelial cells. Pflugers Arch 444:700–709
Simoncini T, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Brazil DP, Ley K, Chin WW, Liao JK (2000) Interaction of oestrogen receptor with the regulatory subunit of phosphatidyl-3-OH-kinase. Nature 407:538–541
Singer CA, Figueroa-Masot XA, Batchelor RH, Dorsa DM (1999) The mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway mediates estrogen neuroprotection after glutamate toxicity in primary cortical neurons. J Neurosci 19:2455–2463
Soto AM, Chung KL, Sonnenschein C (1994) The pesticides endosulfan, toxaphene, and dieldrin have estrogenic effects on human estrogen-sensitive cells. Environ Health Perspect 102:380–383
Sylvia VL, Boyan BD, Dean DD, Schwarts Z (2000) The membrane effects of 17β-estradiol on chondrocyte phenotypic expression are mediated by activation of protein kinase C through phospholipase C and G-proteins. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 73:211–224
Sylvia VL, Walton J, Lopez D, Dean DD, Boyan BD, Schwartz Z (2001) 17beta-estradiol-BSA conjugates and 17beta-estradiol regulate growth plate chondrocytes by common membrane associated mechanisms involving PKC dependent and independent signal transduction. J Cell Biochem 81:413–429
Toran-Allerand CD (2004) A plethora of estrogen receptors in the brain: where will it end? Endocrinology 145:1069–1074
Toran-Allerand CD, Guan X, MacLusky NJ, Horvath TL, Diano S, Singh M, Connolly ES, Nethrapalli IS, Tinnikov AA (2002) ER-X: a novel plasma membrane-associated, putative estrogen receptor that is regulated during development and after ischemic brain injury. J Neurosci 22:8391–8401
Valverde MA, Rojas P, Amigo J, Cosmelli D, Orio P, Bahamonde MI, Mann GE, Vergara C, Latorre R (1999) Acute activation of maxi-K channels (hSlo) by estradiol bind the beta subunit. Science 285:1929–1931
Viso-León MC, Ripoll C, Nadal A (2004) Oestradiol rapidly inhibits Ca2+ signals in ciliary neurons through classical oestrogen receptors in cytoplasm. Pflugers Arch 449:33–41
Watson CS, Gametchu B (2003) Proteins of multiple classes may participate in nongenomic steroid actions. Exp Biol Med 228:1272–1281
Watson CS, Campbell CH, Gametchu B (1999) Membrane oestrogen receptors on rat pituitary tumour cells: immuno-identification and responses to oestradiol and xenoestrogens. Exp Physiol 84:1013–1022
Watters JJ, Campbell JS, Cunningham MJ, Krebs EG, Dorsa DM (1997) Rapid membrane effects of steroids in neuroblastoma cells: effects of estrogen on mitogen activated protein kinase signalling cascade and c-fos immediate early gene transcription. Endocrinology 138:4030–4033
Webb P, Lopez GN, Uht RM, Kushner PJ (1995) Tamoxifen activation of the estrogen receptor/AP-1 pathway: potential origin for the cell-specific estrogen-like effects of antiestrogens. Mol Endocrinol 9:443–456
87 Wisdom R (1999) AP-1: one switch for many signals. Exp Cell Res 253:180–185
Yang SH, Liu R, Perez EJ, Wen Y, Stevens SM, Valencia T, Brun-Zinkernagel AM, Prokai L, Will Y, Dykens J, Koulen P, Simpkins JW (2004) Mitochondrial localization of estrogen receptor β. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA101:4130–4135
Yoneda T, Hiroi T, Osada M, Asada A, Funae Y (2003) Non-genomic modulation of dopamine release by bisphenol-A in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 87:1499–1508
Zalko D, Soto AM, Dolo L, Dorio C, Rathahao E, Debrauwer L, Faure R, Cravedi JP (2003) Biotransformation of bisphenol A in mammalian model: answer and new questions raised by low-dose metabolic fate studies in pregnant CD1 mice. Environ Health Perspect 111:309–319
Zhou Y, Watters JJ, Dorsa DM (1996) Estrogen rapidly induces the phosphorylation of the cAMP response element binding protein in rat brain. Endocrinology 137:2163–2166
Acknowledgements
The authors’ laboratory is funded by grants from Instituto de Salud Carlos III RCMN (C03/08) and (03/0178), and Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (BFI2002-01469). PAM has a studentship from Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia. We thank Dr. Mario Díaz for helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadal, A., Alonso-Magdalena, P., Ripoll, C. et al. Disentangling the molecular mechanisms of action of endogenous and environmental estrogens. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 449, 335–343 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-004-1343-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-004-1343-9