Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of an acute high-intensity, long-duration passive stretching session of the plantar flexor muscles, on maximal dorsiflexion (DF) angle and passive stiffness at both ankle joint and gastrocnemius medialis (GM) muscle levels in children with unilateral cerebral palsy (CP).
Methods
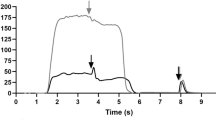
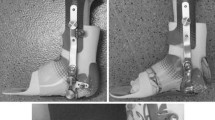
13 children [mean age: 10 years 6 months, gross motor function classification system (GMFCS): I] with unilateral CP underwent a 5 min passive stretching session at 80% of maximal DF angle. Changes in maximal DF angle, slack angle, passive ankle joint and GM muscle stiffness from PRE- to POST-intervention were determined during passive ankle mobilization performed on a dynamometer coupled with shear wave elastography measurements (i.e., ultrasound) of the GM muscle.
Results
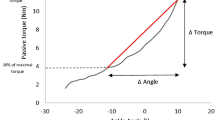
Maximal DF angle and maximal passive torque were increased by 6.3° (P < 0.001; + 50.4%; 95% CI 59.9, 49.9) and 4.2 Nm (P < 0.01; + 38.9%; 95% CI 47.7, 30.1), respectively. Passive ankle joint stiffness remained unchanged (P = 0.9; 0%; 95% CI 10.6, − 10.6). GM muscle shear modulus was unchanged at maximal DF angle (P = 0.1; + 34.5%; 95% CI 44.7, 24.7) and at maximal common torque (P = 0.5; − 4%; 95% CI − 3.7, − 4.3), while it was decreased at maximal common angle (P = 0.021; − 35%; 95% CI − 11.4, − 58.5). GM slack angle was shifted in a more dorsiflexed position (P = 0.02; + 20.3%; 95% CI 22.6, 18).
Conclusion
Increased maximal DF angle can be obtained in the paretic leg in children with unilateral CP after an acute bout of stretching using controlled parameters without changes in passive stiffness at joint and GM muscle levels.
Clinical trial number
NCT03714269.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AJPS:
-
Ankle joint passive stiffness
- AT:
-
Achilles tendon
- CP:
-
Cerebral palsy
- DF:
-
Dorsiflexion
- GM:
-
Gastrocnemius medialis
- GMFCS:
-
Gross motor function classification system
- SWE:
-
Shear wave elastography
- TD:
-
Typically developing
References
Akagi R, Takahashi H (2014) Effect of a 5-week static stretching program on hardness of the gastrocnemius muscle: static stretching program and muscle hardness. Scand J Med Sci Sports 24(6):950–957. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12111
Apostolopoulos N, Metsios GS, Flouris AD, Koutedakis Y, Wyon MA (2015) The relevance of stretch intensity and position—a systematic review. Front Psychol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01128
Barber LA, Read F, Stern JL, Lichtwark G, Boyd RN (2016) Medial gastrocnemius muscle volume in ambulant children with unilateral and bilateral cerebral palsy aged 2 to 9 years. Dev Med Child Neurol 58(11):1146–1152. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13132
Blazevich AJ (2006) Effects of physical training and detraining, immobilisation, growth and aging on human fascicle geometry. Sports Med 36(12):1003–1017
Blazevich AJ (2018) Adaptations in the passive mechanical properties of skeletal muscle to altered patterns of use. J Appl Physiol 126(5):1483–1491. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00700.2018
Boulard C, Gautheron V, Lapole T (2019) Reliability outcomes and inter-limb differences in ankle joint stiffness in children with unilateral cerebral palsy depend on the method of analysis. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 49:102353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2019.102353
Brandenburg JE, Eby SF, Song P, Kingsley-Berg S, Bamlet W, Sieck GC, An K-N (2016) Quantifying passive muscle stiffness in children with and without cerebral palsy using ultrasound shear wave elastography. Dev Med Child Neurol 58(12):1288–1294. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13179
Cao J, Xiao Y, Qiu W, Zhang Y, Dou Z, Ren J, Zheng R, Zheng H, Chen Z (2022) Reliability and diagnostic accuracy of corrected slack angle derived from 2D-SWE in quantitating muscle spasticity of stroke patients. J Neuroeng Rehabil 19(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-022-00995-8
Chen K, Yi-Ning W, Ren Y, Liu L, Gaebler-Spira D, Tankard K, Lee J, Song W, Wang M, Zhang L-Q (2016) Home-based versus laboratory-based robotic ankle training for children with cerebral palsy: a pilot randomized comparative trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 97(8):1237–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2016.01.029
Cobeljic G, Bumbasirevic M, Lesic A, Bajin Z (2009) The management of spastic equinus in cerebral palsy. Orthop Trauma 23(3):201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mporth.2009.05.003
Cohen J (1969) Statistical power analysis for the behavioural sciences. Academic Press, New York
Creze M, Nordez A, Soubeyrand M, Rocher L, Maître X, Bellin M-F (2018) Shear wave sonoelastography of skeletal muscle: basic principles, biomechanical concepts, clinical applications, and future perspectives. Skelet Radiol 47(4):457–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-017-2843-y
Eldridge F, Lavin N (2016) How effective is stretching in maintaining range of movement for children with cerebral palsy? A critical review. Int J Ther Rehabil 23(8):386–395. https://doi.org/10.12968/ijtr.2016.23.8.386
Fleiss JL (1981) The measurement of interrater agreement. Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions 2:22–23
Fowles JR, Sale DG, MacDougall JD (2000) Reduced strength after passive stretch of the human plantarflexors. J Appl Physiol 89(3):1179–1188. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.2000.89.3.1179
Freitas SR, Andrade RJ, Larcoupaille L, Mil-homens P, Nordez A (2015a) Muscle and joint responses during and after static stretching performed at different intensities. Eur J Appl Physiol 115(6):1263–1272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3104-1
Freitas S, Vaz J, Bruno P, Andrade R, Mil-Homens P (2015b) Stretching effects: high-intensity & moderate-duration vs. low-intensity & long-duration. Int J Sports Med 37(03):239–244. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1548946
Freitas SR, Vaz JR, Bruno PM, Valamatos MJ, Andrade RJ, Mil-Homens P (2015c) Are rest intervals between stretching repetitions effective to acutely increase range of motion? Int J Sports Physiol Perform 10(2):191–197. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijspp.2014-0192
Freitas SR, Vilarinho D, Vaz JR, Bruno PM, Costa PB, Mil-homens P (2015d) Responses to static stretching are dependent on stretch intensity and duration. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 35(6):478–484. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12186
Freitas SR, Andrade RJ, Nordez A, Mendes B, Mil-Homens P (2016) Acute muscle and joint mechanical responses following a high-intensity stretching protocol. Eur J Appl Physiol 116(8):1519–1526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3410-2
Gao F, Ren Y, Roth EJ, Harvey R, Zhang L-Q (2011) Effects of repeated ankle stretching on calf muscle–tendon and ankle biomechanical properties in stroke survivors. Clin Biomech 26(5):516–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2010.12.003
Gillett JG, Lichtwark GA, Boyd RN, Barber LA (2018) Functional capacity in adults with cerebral palsy: lower limb muscle strength matters. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 99(5):900-906.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2018.01.020
Harvey LA, Katalinic OM, Herbert RD, Moseley AM, Lannin NA, Schurr K (2017) Stretch for the treatment and prevention of contracture: an abridged republication of a cochrane systematic review. J Physiother 63(2):67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphys.2017.02.014
Hirata K, Miyamoto-Mikami E, Kanehisa H, Miyamoto N (2016) Muscle-specific acute changes in passive stiffness of human triceps surae after stretching. Eur J Appl Physiol 116(5):911–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3349-3
Hirata K, Kanehisa H, Miyamoto N (2017) Acute effect of static stretching on passive stiffness of the human gastrocnemius fascicle measured by ultrasound shear wave elastography. Eur J Appl Physiol 117(3):493–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3550-z
Hopkins GW (2000) Measures of reliability in sportsmedicine and science. Sports Med 30:1–15
Hösl M, Böhm H, Arampatzis A, Döderlein L (2015) Effects of ankle–foot braces on medial gastrocnemius morphometrics and gait in children with cerebral palsy. J Child Orthop 9(3):209–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-015-0664-x
Hug F, Lacourpaille L, Maïsetti O, Nordez A (2013) Slack length of gastrocnemius medialis and achilles tendon occurs at different ankle angles. J Biomech 46(14):2534–2538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2013.07.015
Hug F, Tucker K, Gennisson J-L, Tanter M, Nordez A (2015) Elastography for muscle biomechanics: toward the estimation of individual muscle force. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 43(3):125–133. https://doi.org/10.1249/JES.0000000000000049
Kalkman BM, Bar-On L, Cenni F, Maganaris CN, Bass A, Holmes G, Desloovere K, Barton GJ, O’Brien TD (2018a) Medial gastrocnemius muscle stiffness cannot explain the increased ankle joint range of motion following passive stretching in children with cerebral palsy. Exp Physiol 103(3):350–357. https://doi.org/10.1113/EP086738
Kalkman BM, Bar-On L, Cenni F, Maganaris CN, Bass A, Holmes G, Desloovere K, Barton GJ, O’Brien TD (2018b) Muscle and tendon lengthening behaviour of the medial gastrocnemius during ankle joint rotation in children with cerebral palsy. Exp Physiology 103(10):1367–1376. https://doi.org/10.1113/EP087053
Kalkman BM, Bar-On L, O’Brien TD, Maganaris CN (2020) Stretching interventions in children with cerebral palsy: why are they ineffective in improving muscle function and how can we better their outcome? Front Physiol 11:131. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00131
Lee SSM, Gaebler-Spira D, Zhang L-Q, Rymer WZ, Steele KM (2016) Use of shear wave ultrasound elastography to quantify muscle properties in cerebral palsy. Clin Biomech 31:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2015.10.006
Lorenzo M, Teresa ER, Caballero IM, Barragán AR, Lara SL (2017) Prolonged stretching of the ankle plantarflexors elicits muscle-tendon adaptations relevant to ankle gait kinetics in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Med Hypotheses 109:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2017.09.025
Maganaris CN (2003) Force-length characteristics of the in vivo human gastrocnemius muscle. Clin Anat 16(3):215–223. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.10064
Novak I, Morgan C, Fahey M, Finch-Edmondson M, Galea C, Hines A, Langdon K, Namara MM, Paton MCB, Popat H, Shore B, Khamis A, Stanton E, Finemore OP, Tricks A, te Velde A, Dark L, Morton N, Badawi N (2020) State of the evidence traffic lights 2019: systematic review of interventions for preventing and treating children with cerebral palsy. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 20(2):3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-020-1022-z
Olivier M, François Hug K, Bouillard AN (2012) Characterization of passive elastic properties of the human medial gastrocnemius muscle belly using supersonic shear imaging. J Biomech 45(6):978–984
Peeters N, Van Campenhout A, Hanssen B, Cenni F, Schless S-H, Van den Broeck C, Desloovere K, Bar-On L (2020) Joint and muscle assessments of the separate effects of botulinum neurotoxin-A and lower-leg casting in children with cerebral palsy. Front Neurol 11:210. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00210
Ryan ED, Beck TW, Herda TJ, Hull HR, Hartman MJ, Costa PB, Defreitas JM, Stout JR, Cramer JT (2008) The time course of musculotendinous stiffness responses following different durations of passive stretching. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 38(10):632–639. https://doi.org/10.2519/jospt.2008.2843
Sant L, Guillaume RG, Hug F, Nordez A (2019a) Influence of low muscle activation levels on the ankle torque and muscle shear modulus during plantar flexor stretching. J Biomech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2019.06.018
Sant L, Guillaume AN, Hug F, Andrade R, Lecharte T, McNair PJ, Gross R (2019b) Effects of stroke injury on the shear modulus of the lower leg muscle during passive dorsiflexion. J Appl Physiol 126(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00968.2017
Simon-Henri S, Cenni F, Bar-On L et al (2019) Medial gastrocnemius volume and echo-intensity after botulinum neurotoxin A interventions in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 61(7):783–790. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.14056
Theis N, Korff T, Kairon H, Mohagheghi AA (2013) Does acute passive stretching increase muscle length in children with cerebral palsy? Clin Biomech 28(9–10):1061–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2013.10.001
Theis N, Korff T, Mohagheghi AA (2015) Does long-term passive stretching alter muscle–tendon unit mechanics in children with spastic cerebral palsy? Clin Biomech 30(10):1071–1076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2015.09.004
Theis N, Mohagheghi AA, Korff T (2016) Mechanical and material properties of the plantarflexor muscles and Achilles tendon in children with spastic cerebral palsy and typically developing children. J Biomech 49(13):3004–3008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2016.07.020
Valentine J, Stannage K, Fabian V, Ellis K, Reid S, Pitcher C, Elliott C (2016) Muscle histopathology in children with spastic cerebral palsy receiving botulinum toxin type A: BoNTA and muscle histopathology. Muscle Nerve 53(3):407–414. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.24763
van den Noort JC, Bar-On L, Aertbeliën E, Bonikowski M, Braendvik SM, Broström EW, Buizer AI, Burridge JH, van Campenhout A, Dan B, Fleuren JF, Grunt S, Heinen F, Horemans HL, Jansen C, Kranzl A, Krautwurst BK, van der Krogt M, Lerma Lara S, Lidbeck CM, Lin JP, Martinez I, Meskers C, Metaxiotis D, Molenaers G, Patikas DA, Rémy-Néris O, Roeleveld K, Shortland AP, Sikkens J, Sloot L, Vermeulen RJ, Wimmer C, Schröder AS, Schless S, Becher JG, Desloovere K, Harlaar J (2017) European Consensus on the concepts and measurement of the pathophysiological neuromuscular responses to passive muscle stretch. Eur J Neurol 24(7):981-e38. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13322
Wiart L, Darrah J, Kembhavi G (2008) Stretching with children with cerebral palsy: what do we know and where are we going? Pediatr Phys Ther 20(2):173–78. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEP.0b013e3181728a8c
Yeh C-Y, Tsai K-H, Chen J-J (2005) Effects of prolonged muscle stretching with constant torque or constant angle on hypertonic calf muscles. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86(2):235–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2004.03.032
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Anders Gravholt and Callum Bronswtein for English reviewing.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CB conceived and designed research. CB conducted experiments. CB and TL analyzed data. CB and TL wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of University of Saint-Etienne (France). The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate and consent to publish
Written informed consent was obtained from the parents and children. Parents and children signed informed consent regarding publishing their data.
Additional information
Communicated by Olivier Seynnes.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Boulard, C., Gautheron, V. & Lapole, T. Acute passive stretching has no effect on gastrocnemius medialis stiffness in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Eur J Appl Physiol 123, 467–477 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-05046-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-05046-7