Abstract
Purpose
To determine the vastus lateralis muscle temperature kinetics during and after passive heating, to exam the effect of sex on thermoregulatory responses, and the thermal safety and tolerance of the 42 °C hot-water immersion protocol.
Methods
Thirty participants (15 males, 15 females) underwent a 2 h 42 ºC hot-water immersion to the waist level. Vastus lateralis, rectal and skin temperature, thermal sensation, heart rate and blood pressure (BP) were measured during the passive heating and recovery period. Participant recovery was monitored until muscle temperature returned to baseline.
Results
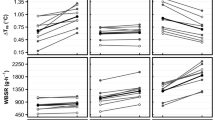
Vastus lateralis temperature increased to a maximal value of 39.0 ± 0.11 °C (P < 0.001), reaching a plateau after ~ 83.5 min of hot-water immersion and returning to baseline after ~ 115.8 min of recovery. Despite the anthropometric differences between males and females (e.g., height, body mass, body fat %, and fat thickness; P < 0.05), thermoregulatory responses showed no differences between sexes (P > 0.05). No change was found in systolic BP (~ 117 mmHg; P = 0.061). Peak rectal temperature (38.8 ± 0.14 °C; P < 0.001), heart rate (~ 100 bpm; P < 0.001), and diastolic BP (↓ ~ 13 mmHg; P < 0.001) during the hot-water immersion indicated the safety of the protocol. While skin temperature (~ 35.4 °C; P < 0.001) and thermal sensation (~ 5.95 AU; P < 0.001) confirmed protocol tolerance.
Conclusion
These data demonstrate lower-body 42 °C hot-water immersion to increase vastus lateralis temperature and plateau ~ 2.8 °C above baseline. This amplitude of muscle temperature change aligns with reported cellular adaptation and muscle growth. Thermal strain incurred from this protocol appears safe and tolerable, positioning it well for health-related prescription.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- %BF:
-
Body fat percentage
- ∆Max Temp:
-
Changes in muscle maximal temperature
- °C:
-
Celsius degrees
- µs:
-
Microseconds
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- AU:
-
Arbitrary unit
- BPM:
-
Beats per minute
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- df :
-
Degrees of freedom = [main effect, error]
- HIIT:
-
High-intensity interval training
- HPS:
-
Heat shock protein
- L s:
-
Litres per second
- MHz:
-
Megahertz
- RM:
-
Repetition maximum
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- T re :
-
Rectal temperature
- T VL :
-
Vastus lateralis muscle temperature
- T sk :
-
Skin temperature
- VI:
-
Vastus intermedius
- VL:
-
Vastus lateralis
- \(V{\text{O}}_{2\max }\) :
-
Maximum volume of oxygen consumption during exercise
- \(\eta_{{\text{p}}}^{2}\) :
-
Partial Eta squared
References
Becker JA, Stewart LK (2011) Heat-related illness. Am Fam Phys 83(11):1325–1330
Brazaitis M, Skurvydas A (2010) Heat acclimation does not reduce the impact of hyperthermia on central fatigue. Eur J Appl Physiol 109(4):771–778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1429-3
Brazaitis M, Skurvydas A, Vadopalas K, Daniusevičiūtė L, Senikienė Ž (2011) The effect of heating and cooling on time course of voluntary and electrically induced muscle force variation. Medicina 47(1):6
Broatch JR, Petersen A, Bishop DJ (2014) Postexercise cold water immersion benefits are not greater than the placebo effect. Med Sci Sports Exerc 46(11):2139–2147. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000000348
Brunt VE, Howard MJ, Francisco MA, Ely BR, Minson CT (2016) Passive heat therapy improves endothelial function, arterial stiffness and blood pressure in sedentary humans. J Physiol 594(18):5329–5342. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP272453
Buskirk ER, Thompson RH, Whedon GD (1963) Metabolic response to cold air in men and women in relation to total body fat content. J Appl Physiol 18(3):603–612. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1963.18.3.603
Castellani JW, Zambraski EJ, Sawka MN, Urso ML (2016) Does high muscle temperature accentuate skeletal muscle injury from eccentric exercise? Physiol Reports 4(9):e12777. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.12777
Cheung SS, Sleivert GG (2004) Lowering of skin temperature decreases isokinetic maximal force production independent of core temperature. Eur J Appl Physiol 91(5–6):723–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1062-0
Corbett J, Wright JA, Tipton M (2020) Sex differences in response to exercise heat-stress in the context of the military environment. BMJ Milit Health. https://doi.org/10.1136/jramc-2019-001253
Cramer MN, Jay O (2016) Biophysical aspects of human thermoregulation during heat stress. Auton Neurosci 196:3–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2016.03.001
Draper DO, Harris ST, Schulthies S, Durrant E, Knight KL, Ricard M (1998) Hot-Pack and 1-MHz ultrasound treatments have an additive effect on muscle temperature increase. J Athl Train 33(1):21–24
Faulkner SH, Jackson S, Fatania G, Leicht CA (2017) The effect of passive heating on heat shock protein 70 and interleukin-6: a possible treatment tool for metabolic diseases? Temperature 4(3):292–304. https://doi.org/10.1080/23328940.2017.1288688
Fox RH, Löfstedt BE, Woodward PM, Eriksson E, Werkstrom B (1969) Comparison of thermoregulatory function in men and women. J Appl Physiol 26(4):444–453. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1969.26.4.444
Frier BC, Locke M (2007) Heat stress inhibits skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Cell Stress Chaper 12(2):132. https://doi.org/10.1379/csc-233r.1
Gagge AP, Stolwijk JAJ, Hardy JD (1967) Comfort and thermal sensations and associated physiological responses at various ambient temperatures. Environ Res 1(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-9351(67)90002-3
Garramone JRR, Winters RM, Das DK, Deckers PJ (1994) Reduction of skeletal muscle injury through stress conditioning using the heat-shock response. Plasti Reconst Surg 93(6):1242–1247. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199405000-00021
Goto K, Honda M, Kobayashi T, Uehara K, Kojima A, Akema T, Yoshioka T (2004) Heat stress facilitates the recovery of atrophied soleus muscle in rat. Jpn J Physiol 54(3):285–293. https://doi.org/10.2170/jjphysiol.54.285
Goto K, Oda H, Kondo H, Igaki M, Suzuki A, Tsuchiya S, Naito H (2011) Responses of muscle mass, strength and gene transcripts to long-term heat stress in healthy human subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 111(1):17–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1617-1
Gregson W, Allan R, Holden S et al (2013) Postexercise cold-water immersion does not attenuate muscle glycogen resynthesis. Med Sci Sports Exerc 45(6):1174–1181. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3182814462
Guo Q, Miller D, An H, Wang H, Lopez J, Lough D, Kumar A (2016) Controlled heat stress promotes myofibrillogenesis during myogenesis. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166294
Habash RW, Bansal R, Krewski D, Alhafid HT (2006) Thermal therapy, part 1: an introduction to thermal therapy. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. https://doi.org/10.1615/critrevbiomedeng.v34.i6.20
Hafen PS, Preece CN, Sorensen JR, Hancock CR, Hyldahl RD (2018) Repeated exposure to heat stress induces mitochondrial adaptation in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 125(5):1447–1455. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00383.2018
Hafen PS, Abbott K, Bowden J, Lopiano R, Hancock CR, Hyldahl RD (2019) Daily heat treatment maintains mitochondrial function and attenuates atrophy in human skeletal muscle subjected to immobilization. J Appl Physiol 127(1):47–57. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01098.2018
Hardy JD, Du Bois EF (1940) Differences between men and women in their response to heat and cold. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 26(6):389. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.26.6.389
Harrison GG (1988) Skinfold thickness and measurement technique. Anthropometric standardization reference manual, pp 55–70
Havenith G, Coenen JM, Kistemaker L (1998) Kenney WL (1998) Relevance of individual characteristics for human heat stress response is dependent on exercise intensity and climate type. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 77(3):231–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050327
Heinonen I, Brothers RM, Kemppainen J, Knuuti J, Kalliokoski KK, Crandall CG (2011) Local heating, but not indirect whole-body heating, increases human skeletal muscle blood flow. J Appl Physiol 111(3):818–824. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00269.2011
Hertig BA (1963) Acclimatization of women during work in hot environments. Fed Proc 22:810–813
Hesketh K, Shepherd SO, Strauss JA et al (2019) Passive heat therapy in sedentary humans increases skeletal muscle capillarization and eNOS content but not mitochondrial density or GLUT4 content. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 317(1):114–123. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00816.2018
Hirunsai M, Srikuea R (2018) Differential effects of heat stress on fibre capillarisation in tenotomised soleus and plantaris muscles. Inter J Hyperther 34(4):432–441. https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2017.1350758
Hoekstra SP, Bishop NC, Faulkner SH, Bailey SJ, Leicht CA (2018) Acute and chronic effects of hot water immersion on inflammation and metabolism in sedentary, overweight adults. J Appl Physiol 125(12):2008–2018. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00407.2018
Hösl M, Böhm H, Eck J, Döderlein L, Arampatzis A (2018) Effects of backward-downhill treadmill training versus manual static plantarflexor stretching on muscle-joint pathology and function in children with spastic. Cerebral Palsy Gait Posture 65:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2018.07.171
Hunt AP, Minett GM, Gibson OR, Kerr GK, Stewart IB (2019) Could heat therapy be an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases? A narrative review. Front Physiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01556
ISO 9886 (2004) Ergonomics-Evaluation of thermal strain by physiological measurements. International Standardisation Organisation, Geneva
Iyoho AE, Ng LJ, MacFadden L (2017) Modeling of gender differences in thermoregulation. Mil Med 182(S1):295–303. https://doi.org/10.7205/MILMED-D-16-00213
Jackson AS, Pollock ML (1978) Generalized equations for predicting body density of men. Br J Nutr 40(3):497–504. https://doi.org/10.1079/bjn19780152
Jackson AS, Pollock ML, Ward A (1980) Generalized equations for predicting body density of women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 12(3):175–181
Jéquier E, Gygax PH, Pittet P, Vannotti A (1974) Increased thermal body insulation: relationship to the development of obesity. J Appl Physiol 36(6):674–678. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1974.36.6.674
Jones PR, Pearson J (1969) Anthropometric determination of leg fat and muscle plus bone volumes in young male and female adults. J Physiol 204(2):63P–66P
Keim SM, Guisto JA, Sullivan JBJ (2002) Environmental thermal stress. Ann Agric Environ Med 9(1):1–15
Kenny GP, Reardon FD, Zaleski W, Reardon ML, Haman F, Ducharme MB (2003) Muscle temperature transients before, during, and after exercise measured using an intramuscular multisensor probe. J Appl Physiol 94(6):2350–2357. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01107.2002
Kenny GP, Jay O, Zaleski WM, Reardon ML, Sigal RJ, Journeay WS, Reardon FD (2006) Postexercise hypotension causes a prolonged perturbation in esophageal and active muscle temperature recovery. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 291(3):R580–R588. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00918.2005
Kim K, Reid BA, Casey CA, Bender BE, Ro B, Song Q, Roseguini BT (2020) Effects of repeated local heat therapy on skeletal muscle structure and function in humans. J Appl Physiol 128(3):483–492. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00701.2019
Leicht CA, James LJ, Briscoe JH, Hoekstra SP (2019) Hot water immersion acutely increases postprandial glucose concentrations. Physiol Repor 7(20):e14223. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.14223
Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorell R (1988) Anthropometric standardization reference manual 177:3–8. Human kinetics books, Champaign
Mallette MM, Green LA, Gabriel DA, Cheung SS (2018) The effects of local forearm muscle cooling on motor unit properties. Eur J Appl Physiol 118(2):401–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3782-y
Mallette MM, Green LA, Hodges GJ, Fernley RE, Gabriel DA, Holmes MW, Cheung SS (2019) The effects of local muscle temperature on force variability. Eur J Appl Physiol 119(5):1225–1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04112-x
Mawhinney C, Low DA, Jones H, Green DJ, Costello JT, Gregson W (2017) Cold water mediates greater reductions in limb blood flow than whole body cryotherapy. Med Sci Sports Exerc 49(6):1252–1260. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000001223
McGorm H, Roberts LA, Coombes JS, Peake JM (2018) Turning up the heat: an evaluation of the evidence for heating to promote exercise recovery, muscle rehabilitation and adaptation. Sports Med 48(6):1311–1328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-018-0876-6
Mitchell JW, Galvez TL, Hengle J, Myers GE, Siebecker KL (1970) Thermal response of human legs during cooling. J Appl Physiol 29(6):859–865. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1970.29.6.859
Morimoto Y, Kondo Y, Kataoka H, Honda Y, Kozu R, Sakamoto JJ, Nakano T, Origuchi T, Yoshimura OM (2015) Heat treatment inhibits skeletal muscle atrophy of glucocorticoid-induced myopathy in rats. Physiol Res 64(6):897–905. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.932942
Morrison S, Sleivert GG, Cheung SS (2004) Passive hyperthermia reduces voluntary activation and isometric force production. Eur J Appl Physiol 91(5–6):729–736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1063-z
Morrison SA, Sleivert GG, Neary JP, Cheung SS (2009) Prefrontal cortex oxygenation is preserved and does not contribute to impaired neuromuscular activation during passive hyperthermia. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 34(1):66–74. https://doi.org/10.1139/H08-139
Morton JP, MacLaren DP, Cable NT et al (2006) Time course and differential responses of the major heat shock protein families in human skeletal muscle following acute nondamaging treadmill exercise. J Appl Physiol 101(1):176–182. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00046.2006
Morton JP, MacLaren DPM, Cable NT, Campbell IT, Evans L, Bongers T, Drust B (2007) Elevated core and muscle temperature to levels comparable to exercise do not increase heat shock protein content of skeletal muscle of physically active men. Acta Physiol 190(4):319–327. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-1716.2007.01711.x
Müller W, Lohman TG, Stewart AD, Maughan RJ, Meyerm NL, Sardinha LB, Ahammer H (2016) Subcutaneous fat patterning in athletes: selection of appropriate sites and standardisation of a novel ultrasound measurement technique: ad hoc working group on body composition, health and performance, under the auspices of the IOC Medical Commission. Br J Sports Med 50(1):45–54. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2015-095641
Naito H, Powers SK, Demirel HA, Sugiura T, Dodd SL, Aoki J (2000) Heat stress attenuates skeletal muscle atrophy in hindlimb-unweighted rats. J Appl Physiol 88(1):359–363. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.2000.88.1.359
Nosaka K, Sakamoto K, Newton M, Sacco P (2004) Influence of pre-exercise muscle temperature on responses to eccentric exercise. J Athl Train 39(2):132
Nosaka K, Muthalib M, Lavender A, Laursen PB (2007) Attenuation of muscle damage by preconditioning with muscle hyperthermia 1-day prior to eccentric exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 99(2):183–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-006-0331-5
Ogura Y, Naito H, Tsurukawa T, Ichinoseki-Sekine N, Saga N, Sugiura T, Katamoto S (2007) Microwave hyperthermia treatment increases heat shock proteins in human skeletal muscle. Br J Sports Med 41(7):453–455. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsm.2006.032938
Pallubinsky H, Schellen L, Kingma BRM, Dautzenberg B, van Baak MA, van Marken LWD (2017) Thermophysiological adaptations to passive mild heat acclimation. Temperature 4(2):176–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/23328940.2017.1303562
Papaioannou TG, Karamanou M, Protogerou AD, Tousoulis D (2016) Heat therapy: an ancient concept re-examined in the era of advanced biomedical technologies. J Physiol 594(23):7141. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP273136
Petrofsky JS, Lind AR (1975) The relationship of body fat content to deep muscle temperature and isometric endurance in man. Clin Sci Mol Med 48(5):405–412. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs0480405
Quaade F (1963) Insulation in leanness and obesity. Lancet 2(7305):429–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92172-x
Racinais S, Wilson MG, Gaoua N, Périard JD (2017a) Heat acclimation has a protective effect on the central but not peripheral nervous system. J Appl Physiol 123(4):816–824. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00430.2017
Racinais S, Wilson MG, Périard JD (2017b) Passive heat acclimation improves skeletal muscle contractility in humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 312(1):R101–R107. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00431.2016
Roberts LA, Nosaka K, Coombes JS, Peake JM (2014) Cold water immersion enhances recovery of submaximal muscle function after resistance exercise. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 307(8):R998–R1008. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00180.2014
Shibaguchi T, Sugiura T, Fujitsu T, Nomura T, Yoshihara T, Naito H, Ohira Y (2016) Effects of icing or heat stress on the induction of fibrosis and/or regeneration of injured rat soleus muscle. J Physiol Sci 66(4):345–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-015-0433-0
Siri WE (1961) Body composition from fluid spaces and density: analysis of methods. Nutrition 9(5):480–492
Skurvydas A, Kamandulis S, Stanislovaitis A, Streckis V, Mamkus G, Drazdauskas A (2008) Leg immersion in warm water, stretch-shortening exercise, and exercise-induced muscle damage. J Athl Train 43(6):592–599. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-43.6.592
Störchle P, Müller W, Sengeis M, Ahammer H, Fürhapter-Rieger A, Bachl N, Holasek S (2017) Standardized ultrasound measurement of subcutaneous fat patterning: high reliability and accuracy in groups ranging from lean to obese. Ultrasound Med Biol 43(2):427–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2016.09.014
Symons TB, Clasey JL, Gater DR, Yates JW (2004) Effects of deep heat as a preventative mechanism on delayed onset muscle soreness. J Strength Condi Res 18(1):155–161. https://doi.org/10.1519/1533-4287(2004)018<0155:eodhaa>2.0.co;2
Takeuchi K, Hatade T, Wakamiya S, Fujita N, Arakawa T, Miki A (2014) Heat stress promotes skeletal muscle regeneration after crush injury in rats. Acta Histoc 116(2):327–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2013.08.010
Tamura Y, Kitaoka Y, Matsunaga Y, Hoshino D, Hatta H (2015) Daily heat stress treatment rescues denervation-activated mitochondrial clearance and atrophy in skeletal muscle. J Physiol 593(12):2707–2720. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP270093
Thiebaud RS, Abe T, Loenneke JP, Fujita E, Akamine T (2019) Body fat percentage assessment by ultrasound subcutaneous fat thickness measurements in middle-aged and older adults. Clin Nutr 38(6):2659–2667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.11.017
Touchberry CD, Gupte AA, Bomhoff GL, Graham ZA, Geiger PC, Gallagher PM (2012) Acute heat stress prior to downhill running may enhance skeletal muscle remodeling. Cell Stress Chaper 17(6):693–705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-012-0343-5
Tsuchida W, Iwata M, Akimoto T, Matsuo S, Asai Y, Suzuki S (2017) Heat stress modulates both anabolic and catabolic signaling pathways preventing dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy in vitro. J Cell Physiol 232(3):650–664. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25609
Uehara K, Goto K, Kobayashi T, Kojima A, Akema T, Sugiura T, Aoki H (2004) Heat-stress enhances proliferative potential in rat soleus muscle. Jpn J Physiol 54(3):263–271. https://doi.org/10.2170/jjphysiol.54.263
Vaile J, Halson S, Gill N, Dawson B (2008) Effect of hydrotherapy on the signs and symptoms of delayed onset muscle soreness. Eur J Appl Physiol 102(4):447–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-007-0605-6
Vardiman JP, Moodie N, Siedlik JA, Kudrna RA, Graham Z, Gallagher P (2015) Short-wave diathermy pretreatment and inflammatory myokine response after high-intensity eccentric exercise. J Athl Train 50(6):612–620. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-50.1.12
Funding
Patrick Rodrigues has been supported by the International Postgraduate Research Scholarship (IPRS). No other sources of funding were utilized to assist this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors (PR, GST, LW, GMM) participated in the conception and design of the study. PR was responsible for the data collection, analysis and drafting of the manuscript. All authors were responsible for the interpretation of the data and revising it critically for important intellectual content. Moreover, all authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts or competing interest relevant to the content of this study.
Additional information
Communicated by George Havenith.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, P., Trajano, G.S., Wharton, L. et al. Muscle temperature kinetics and thermoregulatory responses to 42 °C hot-water immersion in healthy males and females. Eur J Appl Physiol 120, 2611–2624 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04482-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04482-7