Abstract
Purpose
Nicotine is a psychostimulant that is reported to be commonly supplemented by athletes. The purpose of the current study was to determine the effects of a rapidly absorbed form of nicotine on repeated bouts of anaerobic exercise, perception of exertion and a range of cardiovascular variables while monitoring side effect profiles.
Methods
Sixteen healthy, nicotine naïve male athletes (24.1 ± 5.3 years, 179.0 ± 8.8 cm, 81.7 ± 13.5 kg, BMI 25.5 ± 3.0, Body fat% 13.2 ± 5.1%) completed two repeated 30 s Wingate tests with 3 min rest between bouts following consumption of either a 5-mg oral-dispersible nicotine strip (NIC) or a flavour-matched placebo (PLA) in a randomised, double-blind, cross-over design. Before the Wingate test, resting heart rate and blood pressure were also measured prior to and following PLA and NIC ingestion.
Results
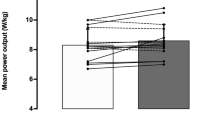
Peak and average power output were significantly greater following NIC administration compared to PLA (P < 0.01). Similarly, significant increases were also seen in heart rate and blood pressure following NIC administration compared to PLA (P < 0.01). No significant effect on pre-exercise side effect score, reaction time, rate of perceived exertion or post exercise blood lactate levels were observed (P > 0.05).
Conclusions
It was concluded that oral-dispersible nicotine strips increase repeated anaerobic performance, possibly through strong sympathetic stimulation, as evident by significant elevation of cardiovascular parameters.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- ICC:
-
Intra-class correlation coefficient
- NIC:
-
Nicotine
- PLAC:
-
Placebo
- REP:
-
Repeatability session
- RPE:
-
Rating of perceived exertion
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- SpO2 :
-
Saturated oxygen percentage
- SST:
-
Serum-separating tube
- WADA:
-
World Anti-Doping Agency
References
Andersson DC, Betzenhauser MJ, Reiken S, Umanskaya A, Shiomi T, Marks AR (2012) Stress-induced increase in skeletal muscle force requires protein kinase A phosphorylation of the ryanodine receptor. J Physiol 590(24):6381–6387
Argacha J-F, Adamopoulos D, Gujic M, Fontaine D, Amyai N, Berkenboom G, Van De Borne P (2008) Acute effects of passive smoking on peripheral vascular function. Hypertension 51(6):1506–1511
Bell DG, Jacobs I, Ellerington K (2001) Effect of caffeine and ephedrine ingestion on anaerobic exercise performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33(8):1399–1403
Borg G (1990) Psychophysical scaling with applications in physical work and the perception of exertion. Scand J Work Environ Health 16(Suppl 1):55–58
Crowe MJ, Leicht AS, Spinks WL (2006) Physiological and cognitive responses to caffeine during repeated, high-intensity exercise. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 16(5):528–544
Cryer PE, Haymond MW, Santiago JV, Shah SD (1976) Norepinephrine and epinephrine release and adrenergic mediation of smoking-associated hemodynamic and metabolic events. N Engl J Med 295(11):573–577
Davis JK, Green JM (2009) Caffeine and anaerobic performance. Sports Med 39(10):813–832. https://doi.org/10.2165/11317770-000000000-00000
Digard H, Proctor C, Kulasekaran A, Malmqvist U, Richter A (2013) Determination of nicotine absorption from multiple tobacco products and nicotine gum. Nicot Tob Res 15(1):255–261. https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/nts123
Du D, Nides M, Borders J, Selmani A, Waverczak W (2014) Comparison of nicotine oral soluble film and nicotine lozenge on efficacy in relief of smoking cue-provoked acute craving after a single dose of treatment in low dependence smokers. Psychopharmacol 231(22):4383–4391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3586-2
Fogt DL, Levi MA, Rickards CA, Stelly SP, Cooke WH (2016) Effects of acute vaporized nicotine in non-tobacco users at rest and during exercise. Int J Exerc Sci 9(5):607–615
Foulds J, Stapleton JA, Bell N, Swettenham J, Jarvis MJ, Russell MA (1997) Mood and physiological effects of subcutaneous nicotine in smokers and never-smokers. Drug Alcohol Dep 44(2):105–115
Gierczuk D, Bujak Z (2014) Reliability and accuracy of Batak Lite tests used for assessing coordination motor abilities in wrestlers. Pol J Sport Tour 21:72–76
Goto Y (2008) Limbic and cortical information processing in the nucleus accumbens. Trends Neurosci 31:552–558
Harte CB, Meston CM (2008) Acute effects of nicotine on physiological and subjective sexual arousal in nonsmoking men: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Sex Med 5(1):110–121
Hedelin R, Bjerle P, Henriksson-Larsen K (2001) Heart rate variability in athletes: relationship with central and peripheral performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33(8):1394–1398
Johnston R, Doma K, Crowe MJ (2017) Nicotine effects on exercise performance and physiological responses in nicotine naïve individuals: a systematic review. Clin Phys Funct Imag. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12443
Landers DM, Crews DJ, Boutcher SH, Skinner JS, Gustafsen S (1992) The effects of smokeless tobacco on performance and psychophysiological response. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24(8):895–903
Laughlin MH, Davis MJ, Secher NH, Lieshout JJ, Arce-Esquivel AA, Simmons GH, Bender SB, Padilla J, Bache RJ, Merkus D (2012) Peripheral circulation. Compr Physiol 2(1):321–447
Marclay F, Grata E, Perrenoud L, Saugy M (2011) A one-year monitoring of nicotine use in sport: frontier between potential performance enhancement and addiction issues. Forens Sci Int 213(1):73–84
medicines.org.au (2013) Product information. https://www.medicines.org.au. Accessed 10 May 2017
Menz HB, Latt MD, Tiedemann A, Mun San Kwan M, Lord SR (2004) Reliability of the GAITRite walkway system for the quantification of temporo-spatial parameters of gait in young and older people. Gait Posture 20(1):20–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0966-6362(03)00068-7
Morente-Sánchez J, Zandonai T, Mateo-March M, Sanabria D, Sánchez-Muñoz C, Chiamulera C, Zabala Díaz M (2015) Acute effect of Snus on physical performance and perceived cognitive load on amateur footballers. Scand J Med Sci Sports 25(4):e423–e431
Mündel T (2017) Nicotine: sporting friend or foe? A review of athlete use, performance consequences and other considerations. Sports Med 47:2497–2506
Mündel T, Jones DA (2006) Effect of transdermal nicotine administration on exercise endurance in men. Exp Physiol 91(4):705–713
Mündel T, Machal M, Cochrane DJ, Barnes MJ (2017) A randomised, placebo-controlled, crossover study investigating the effects of nicotine gum on strength, power and anaerobic performance in nicotine-naive, active males. Sports Med Open 3(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40798-016-0074-8
Pysný L, Petru D, Pysná J, Cihlár D (2015) The acute effect of nicotine intake on anaerobic exercise performance. J Phys Ed Sport 15(1):103
Sinclair C, Geiger J (2000) Caffeine use in sports: a pharmacological review. J Sports Med Phys Fit 40(1):71–79
Subramaniyan M, Dani JA (2015) Dopaminergic and cholinergic learning mechanisms in nicotine addiction. Ann NY Acad Sci 1349(1):46–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12871
Sureda X, Fernández E, López MJ, Nebot M (2013) Secondhand tobacco smoke exposure in open and semi-open settings: a systematic review. Environ Health Persp (Online) 121(7):766
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RJ and MC conceived the research and all authors designed the research. RJ and KD conducted the experiments. RJ, MC and KD analysed the data. RJ wrote the manuscript. All authors read, edited and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all the authors, the corresponding author states there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional Human Research Ethics Committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Communicated by I. Mark Olfert.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnston, R., Crowe, M. & Doma, K. Effect of nicotine on repeated bouts of anaerobic exercise in nicotine naïve individuals. Eur J Appl Physiol 118, 681–689 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3819-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3819-x