Abstract
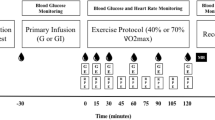
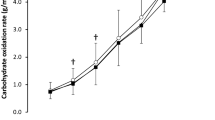
In order to test the hypothesis that salbutamol would change substrate oxidation during submaximal exercise, eight recreationally trained men twice performed 1 h at 60% VO2 peak after ingestion of placebo or 4 mg of salbutamol. Gas exchange was monitored and blood samples were collected during exercise for GH, ACTH, insulin, and blood glucose and lactate determination. With salbutamol versus placebo, there was no significant difference in total energy expenditure and substrate oxidation, but the substrate oxidation balance was significantly modified after 40 min of exercise. ACTH was significantly decreased with salbutamol during the last 10 min of exercise, whereas no difference was found between the two treatments in the other hormonal and metabolic parameters. The theory that the ergogenic effect of salbutamol results from a change in substrate oxidation has little support during relatively short term endurance exercise, but it is conceivable that longer exercise duration can generate positive findings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Damluji S, Perry L, Tomlin S, Bouloux P, Grossman A, Rees LH, Besser GM (1987) Alpha-adrenergic stimulation of corticotropin secretion by a specific central mechanism in man. Neuroendocrinology 45:68–76
Arlettaz A, Portier H, Lecoq A-M, Labsy Z, De Ceaurriz J, Collomp K (2008) Effects of acute prednisolone intake on substrate utilization during submaximal exercise. Int J Sports Med 29:21–26
Carter SL, Rennie C, Tarnopolsky MA (2001) Substrate utilization during endurance exercise in men and women after endurance training. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 280:E898–E907
Collomp K, Candau R, Collomp R, Carra J, Lasne F, Préfaut C, De Ceaurriz J (2000a) Effects of acute ingestion of salbutamol during submaximal exercise. Int J Sports Med 21:480–484
Collomp K, Candau R, Lasne F, Labsy Z, Ch Préfaut, De Ceaurriz J (2000b) Effects of short-term oral salbutamol administration on exercise endurance and metabolism. J Appl Physiol 89:430–436
Collomp K, Candau R, Millet G, Mucci P, Borrani F, Préfaut C, De Ceaurriz J (2002) Effects of salbutamol and caffeine ingestion on exercise metabolism and performance. Int J Sports Med 23:549–554
Collomp K, Le Panse B, Portier H, Lecoq AM, Jaffre C, Richard O, Benhamou L, Courteix D, De Ceaurriz J (2005) Effects of acute salbutamol intake during a Wingate test. Int J Sports Med 26:513–517
Giustina A, Malerba M, Bresciani E, Desenzani P, Licini M, Zaltieri G, Grassi V (1995) Effect of two β2-agonist drugs, salbutamol and broxaterol, on the growth hormone response to exercise in adult patients with asthmatic bronchitis. J Endocrinol Invest 18:847–852
Green HJ, Jones S, Ball-Burnett M, Farrance B, Ranney D (1995) Adaptations in muscle metabolism to prolonged voluntary exercise and training. J Appl Physiol 78:138–145
Hoeks J, Van Baak M, Hesselink M, Hul G, Vidal H, Saris W, Schrauwen P (2003) Effect of β1- and β2-adrenergic stimulation on energy expenditure, substrate oxidation, and UCP3 expression in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:E775–E782
Le Panse B, Collomp K, Portier H, Lecoq AM, Jaffre C, Beaupied H, Richard O, Benhamou L, De Ceaurriz J, Courteix D (2005) Effects of short-term salbutamol ingestion during a Wingate test. Int J Sports Med 26:518–523
Le Panse B, Arlettaz A, Portier H, Lecoq AM, De Ceaurriz J, Collomp K (2006) Short term salbutamol ingestion and supramaximal exercise in healthy women. Br J Sports Med 40:627–631
Le Panse B, Arlettaz A, Portier H, Lecoq AM, De Ceaurriz J, Collomp K (2007) Effects of acute salbutamol intake during supramaximal exercise in women. Br J Sports Med 41:430–434
Perronet F, Massicotte D (1991) Table of nonprotein respiratory quotient: an update. Can J Sport Sci 16:23–29
Rolf Smith S, Kendall M (1984) Metabolic responses to β2 stimulants. J R Coll Chest Physiol 18:190–194
Sahlin K (1990) Muscle glucose metabolism during exercise. Ann Med 22:85–89
Schiffelers S, Brouwer E, Saris W, Van Baak M (1998) Inhibition of lipolysis reduces beta1-adrenoceptor-mediated thermogenesis in man. Metabolism 47:1462–1467
Schiffelers S, Saris W, Boomsma F, Van Baak M (2001) Beta(1)- and beta(2)-adrenoceptor-mediated thermogenesis and lipid utilization in obese and lean men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:2191–2199
Schiffelers S, Van Harmelen V, De Grauw H, Saris W, Van Baak M (1999) Dobutamine as selective β1-adrenoceptor agonist in in vivo studies on human thermogenesis and lipid utilization. J Appl Physiol 87:977–981
Stisen A, Stougaard O, Langfort J, Helge J, Sahlin K, Madsen K (2006) Maximal fat oxidation rates in endurance trained and untrained women. Eur J Appl Physiol 98:497–506
Van Baak M, Mayer L, Kempinski R, Hartgens F (2000) Effect of salbutamol on muscle strength and endurance performance in nonasthmatic men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:1300–1306
Van Baak M, de Hon O, Hartgens F, Kuipers H (2004) Inhaled salbutamol and endurance cycling performance in non-asthmatic athletes. Int J Sports Med 25:533–538
Wager J, Fredholm B, Lunell N, Persson B (1982) Metabolic and circulatory effects of intravenous and oral salbutamol in late pregnancy in diabetic and non-diabetic women. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl 108:41–46
Werle E, Strobel G, Weicker H (1990) Decrease in rat cardiac beta1- and beta2-adrenoceptors by training and endurance exercise. Life Sci 46:9–17
Acknowledgments
The authors wish also to express their gratitude to the subjects for their dedicated performance. In addition we likewise thank the CHR of Orléans, Nathalie Crépin, Sandra Ferary, Patrick Guenon, Nicole Chevrier and Dr M. Ferry for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arlettaz, A., Le Panse, B., Portier, H. et al. Salbutamol intake and substrate oxidation during submaximal exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 105, 207–213 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0891-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0891-7