Abstract
Introduction
The objective of the study was to investigate how exposure to carbon disulfide (CS2) in a rayon-manufacturing plant has changed within two decades and whether it is possible to calculate valid data for the individual cumulative exposure.
Methods
The data for CS2 concentration in air and biological exposure monitoring (2-thio-1,3-thiaxolidine-4-carboxylic acid (TTCA) in urine) from two cross-sectional studies, performed in 1992 (n = 362) and 2009 (n = 212) in a German rayon-manufacturing plant, were compared to data obtained from company-internal measurements between the studies.
Results
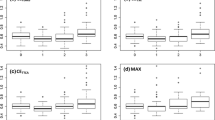
Using the data from the cross-sectional studies and company-internal data, cumulative external exposure and the cumulative internal exposure were calculated for each worker. External and internal CS2 exposure of the employees decreased from 1992 (medians 4.0 ppm and 1.63 mgTTCA/g creatinine) to 2009 (medians 2.5 ppm and 0.86 mg/g). However, company-internal CS2 data do not show a straight trend for this period. The annual medians of the company-internal measurement of external exposure to CS2 have varied between 2.7 and 8.4 ppm, in which median values exceeded 5 ppm generally since 2000. The annual medians for the company-internal biomonitoring assessment ranged between 1.2 and 2.8 mg/g creatinine. The cumulative CS2 exposure ranged from 8.5 to 869.5 ppm years for external exposure and between 1.30 and 176.2 mg/g creatinine years for the internal exposure. Significant correlations were found between the current air pollution and the internal exposure in 2009 but also between the cumulative external and internal CS2 exposure.
Conclusions
Current exposure data, usually collected in cross-sectional studies, rarely allow a reliable statement on the cumulative dose, because of higher exposure in the past and of fluctuating courses of exposure. On the other hand, company-internal exposure data may be affected by non-representative measurement strategies. Some verification of the reliability of cumulative exposure data may be possible by testing the correlation between cumulative exposure data of external assessment and biological monitoring.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bulat P, Daemen E, Van Rissighem M et al (2002) Comparison of occupational exposure to carbon disulphide in a viscose rayon factory before and after technical adjustments. Appl Occup Environ Hyg 17:34–38
Chan SJ, Shih TS, Chou TC et al (2003) Hearing loss in workers exposed to carbon disulfide and noise. Environ Health Perspect 111:1620–1624
Chan SJ, Chen CJ, Shih TS et al (2007) Risk for hypertension in workers exposed to carbon disulfide in the viscose rayon industry. Am J Ind Med 50:22–27
DGUV—Deutsche Gesetzliche Unfallversicherung (2001) Carbon disulphide. Analytical procedure no. 7725-2. IFA-Arbeitsmappe Messung von Gefahrstoffen. 26th edition, Erich Schmidt, Berlin (in German)
Drexler H, Göen T, Angerer J et al (1994) Carbon disulphide. I: External and internal exposure to carbon disulphide of workers in the viscose industry. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 65:359–365
Drexler H, Göen T, Angerer J (1995a) Carbon disulphide. II: Investigations on the uptake of CS2 and the excretion of its metabolite 2-thiothiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid after occupational exposure. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 67:5–10
Drexler H, Ulm K, Hubmann M et al (1995b) Carbon disulphide. III: Risk factors for coronary heart diseases in workers in the viscose industry. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 67:243–252
Drexler H, Ulm K, Hardt R et al (1996) Carbon disulphide. IV: Cardiovascular function in workers in the viscose industry. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 69:27–32
Eben A, Freudlsperger FP (1994) 2-Thioxothiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid (TTCA). In: Forschungsgemeinschaft D (ed) Analyses in biological materials, vol 4. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 207–221. doi:10.1002/3527600418.bi2093367e0004
Gelbke HP, Göen T, Mäurer M et al (2009) Review of health effects of carbon disulfide in viscose industry and a proposal for an occupational exposure limit. Crit Rev Toxicol 39(Suppl. 2):1–126
Ghitttori S, Maestri L, Contardi I et al (1998) Biological monitoring of workers exposed to carbon disulphide (CS2) in a viscose rayon fibers factory. Am J Ind Med 33:478–484
Göen T, Müller J, Angerer J et al (2002) Determination of carbon disulphide at the workplace by sampling on charcoal tubes—problems and solutions. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 63:659–663
Goldberg M, Hémon D (1993) Occupational epidemiology and assessment of exposure. Int J Epidemiol 22:S5–S9
Greim H (ed) (2005) Carbon disulfide. In: The MAK-Collection. Part I: MAK Value Documentations, vol 21. DFG, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, WILEY-VCH, Weinheim, pp 171–185. doi:10.1002/3527600418.mb7515e0021
Hernberg S, Partanen T, Nordman CH et al (1970) Coronary heart disease among workers exposed to carbon disulphide. Br J Ind Med 27:313–325
Kolanz ME, Madl AK, Kelsh MA et al (2001) A comparison and critique of historical and current exposure assessment methods for beryllium: implications for evaluating risk of chronic beryllium disease. Appl Occup Environ Hyg 16:593–614
Korinth G, Göen T, Ulm K et al (2003) Cardiovascular function of workers exposed to carbon disulfide. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 76:81–85
Kotseva K, Braeckman L, De Bacquer D et al (2001) Cardiovascular effects in viscose rayon workers exposed to carbon disulfide. Int J Occup Environ Health 7:7–13
Meuling WJ, Bragt PC, Braun CL (1990) Biological monitoring of carbon disulphide. Am J Ind Med 17:247–254
Omae K, Takebayashi T, Nomiyama T et al (1998) Cross sectional observation of the effects of carbon disulphide on arteriosclerosis in rayon manufacturing workers. Occup Environ Med 55:468–472
Price B, Berman TS, Rodriguez M et al (1987) A review of carbon disulfide exposure data and the association between carbon disulfide exposure and ischemic heart disease mortality. Reg Toxicol Pharmacol 26:119–128
Reinhardt F, Drexler H, Bickel A et al (1997a) Neurotoxicity of long-term low-level exposure to carbon disulfide: results of questionaire, clinical neurological examination and neuropsychological testing. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 69:332–338
Reinhardt F, Drexler H, Bickel A et al (1997b) Electrophysiological investigation of central, peripheral and autonomic nerve function in workers with long-term low-level exposure to carbon disulphide in the viscose industry. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 70:249–256
Ruijten MWMM, Sallé HJA, Verberk MM et al (1990) Special nerve functions and colour discrimination in workers with long term low level exposure to carbon disulphide. Br J Ind Med 47:589–595
Ruijten MWMM, Sallé HJA, Verberk MM (1993) Verification of effects on the nervous system of low level occupational exposure to CS2. Br J Ind Med 50:301–307
Schaller KH, Angerer J, Drexler H (2002) Quality assurance of biological monitoring in occupational and environmental medicine. J Chromatogr B 778:403–417
Seeber A, Bruckner T, Triebig G (2009) Occupational styrene exposure and neurobehavioural functions: a cohort study with repeated measurements. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 82:969–984
Sulsky SI, Hooven FH, Burch MT et al (2002) Critical review of the epidemiological literature on the potential cardiovascular effects of occupational carbon disulfide exposure. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 75:365–380
Tan X, Chen G, Peng X et al (2004) Cross-sectional study of cardiovascular effects of carbon disulfide among Chinese workers of a viscose factory. Int J Hyg Environ Health 206:217–225
Vanhoorne M, Grosjean R (1984) Exposure data in the viscose industry: Achilles’ heel of carbon disulphide epidemiology? G Ital Med Lav 6:95–99
Vanhoorne M, De Bacquer D, De Backer G (1992) Epidemiological study of the cardiovascular effects of carbon disulphide. Int J Epidemiol 21:745–752
Vanhoorne M, Ceulemans L, De Bacquer DA et al (1995) An epidemiological study of the effects of carbon disulphide on the peripheral nerves. Int J Occup Environ Health 1:295–302
Acknowledgments
The study was carried out with financial support from the Industrieverband Chemiefaser (IVC) and the Franz Koelsch Foundation. We would like to thank all participants that took part in the study and the management of the plants for their support. We also acknowledge Fritz Freudlsperger for assisting in planning and carrying out the study, Alfred Koenig for providing the company-internal records and information on circumstances of data collection, Barbara Bär for collecting anamnestic data, Nina Zonnur for collecting anamnestic data and carrying out TTCA analyses and Johannes Müller for carrying out CS2 air analyses.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests pertinent to the subject of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Göen, T., Schramm, A., Baumeister, T. et al. Current and historical individual data about exposure of workers in the rayon industry to carbon disulfide and their validity in calculating the cumulative dose. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 87, 675–683 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-013-0910-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-013-0910-9