Abstract
Purpose
To determine the blood and urine concentrations of a number of metals and organic substances in workers at a hazardous waste incinerator (HWI) in Catalonia, Spain, 8 years after regular operations in the facility. To compare these concentrations with the baseline (1999) levels and with those obtained in previous (2000 and 2005) surveys.
Methods
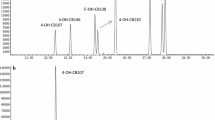
The employees were divided into three groups according to their specific workplaces. Plasma analyses of hexachlorobenzene (HCB), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs 28, 52, 101, 138, 153 and 180) and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs), as well as urinary analyses of 2,4- and 2,5-dichlorophenol (DCP), 2,4,5- and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (TCP), pentachlorophenol (PCP) and 1-hydroxypyrene (1-HP) were carried out. Blood concentrations of manganese and mercury, and urinary levels of nickel were also determined.
Results
For organic compounds in plasma, the comparison of the current levels with those of previous surveys did not show any significant increase for any of the compounds analyzed. In contrast, plasma levels of PCBs 28, 52 and 101 were significantly lower than the respective baseline concentrations, while especially notable was the significant reduction in the levels of PCDD/Fs in plasma of plant workers, which decreased from 26.7 pg I-TEQ/g lipid in the baseline survey to the current 2.5 pg I-TEQ/g lipid.
Conclusion
According to the results of the present study, there are no evident signs of occupational exposure to a number of metals and organic substances in the workers of the HWI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agramunt MC, Domingo A, Domingo JL, Corbella J (2003) Monitoring internal exposure to metals and organic substances in workers at a hazardous waste incinerator after 3 years of operation. Toxicol Lett 146:83–91. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2003.09.003
Agramunt MC, Domingo JL, Bocio A, Nadal M, Müller L (2004) Biological monitoring of organic substances in workers of a hazardous waste incinerator. Organohalogen Compd 66:2445–2450
Agramunt MC, Schuhmacher M, Hernandez JM, Domingo JL (2005) Levels of dioxins and furans in plasma of nonoccupationally exposed subjects living near a hazardous waste incinerator. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 15:29–34. doi:10.1038/sj.jea.7500339
Angerer J, Heinzow B, Reimann DO, Knorz W, Lehnert G (1992) Internal exposure to organic substances in a municipal waste incinerator. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 64:265–273. doi:10.1007/BF00378285
Bakoğlu M, Karademir A, Ayberk S (2004) An evaluation of the occupational health risks to workers in a hazardous waste incinerator. J Occup Health 46:156–164. doi:10.1539/joh.46.156
Bocio A, Domingo JL (2005) Daily intake of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDD/PCDFs) in foodstuffs consumed in Tarragona, Spain: a review of recent studies (2001–2003) on human PCDD/PCDF exposure through the diet. Environ Res 97:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2004.01.012
Bolt HM, Thier R (2006) Biological monitoring and biological limit values (BLV): the strategy of the European Union. Toxicol Lett 162:119–124. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2005.09.015
Brzeźnicki S, Jakubowski M, Czerski B (1997) Elimination of 1-hydroxypyrene after human volunteer exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 70:257–260. doi:10.1007/s004200050216
Charbotel B, Hours M, Perdrix A, Anzivino-Viricel L, Bergeret A (2005) Respiratory function among waste incinerator workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 78:65–70. doi:10.1007/s00420-004-0557-7
Chen HL, Liao PC, Su HJ, Guo YL, Chen CH, Lee CC (2005) Profile of PCDD/F levels in serum of general Taiwanese between different gender, age and smoking status. Sci Total Environ 337:31–43. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.06.021
Clark NA, Teschke K, Rideout K, Copès R (2007) Trace element levels in adults from the west coast of Canada and associations with age, gender, diet, activities, and levels of other trace elements. Chemosphere 70:155–164. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.06.038
Domingo JL (2002) Human health risks of dioxins for populations living near modern municipal solid waste incinerators. Rev Environ Health 17:135–147
Domingo JL, Schuhmacher M, Granero S, Llobet JM (1999) PCDDs and PCDFs in food samples from Catalonia, Spain. An assessment of dietary intake. Chemosphere 38:3517–3528. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00581-5
Domingo JL, Schuhmacher M, Agramunt MC, Müller L, Neugebauer F (2001) Levels of metals and organic substances in blood and urine of workers at a new hazardous waste incinerator. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 74:263–269. doi:10.1007/s004200000217
Farzin L, Amiri M, Shams H, Faghih MAA, Moassesi ME (2007) Blood levels of lead, cadmium, and mercury in residents of Tehran. Biol Trace Elem Res 123:14–26. doi:10.1007/s12011-008-8106-y
Ferré-Huguet N, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2006) Environmental impact and human health risks of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the vicinity of a new hazardous waste incinerator: a case study. Environ Sci Technol 40:61–66. doi:10.1021/es051630+
Hardt J, Angerer J (2003) Biological monitoring of workers after the application of insecticidal pyrethroids. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 76:492–498
Hours M, Anzivino-Viricel L, Maitre A, Perdrix A, Perrodin Y, Charbotel B et al (2003) Morbidity among municipal waste incinerator workers: a cross-sectional study. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 76:467–472. doi:10.1007/s00420-003-0430-0
Hu SW, Chang-Chien GP, Chan CC (2004) PCDD/Fs levels in indoor environments and blood of workers of three municipal waste incinerators in Taiwan. Chemosphere 55:611–620. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.10.057
Ichiba M, Ogawa Y, Mohri I, Kondoh T, Horita M, Matsumoto A et al (2007) Analysis of urinary metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in incineration workers. J Occup Health 49:159–164. doi:10.1539/joh.49.159
Jongeneelen FJ (2001) Benchmark guideline for urinary 1-hydroxypyrene as biomarker of occupational exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Ann Occup Hyg 45:3–13
Jongeneelen F, Anzion RBM (1991) 1-Hydroxypyrene. In: Angerer J, Schaller KH (eds) Analyses of hazardous substances in biological material, vol 3. Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, VCH, Germany, pp 151–169
Jönsson LS, Broberg K, Axmon A, Bergendorf U, Littorin M, Jönsson BA (2008) Levels of 1-hydroxypyrene, symptoms and immunologic markers in vulcanization workers in the southern Sweden rubber industries. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 82:131–137. doi:10.1007/s00420-008-0310-8
Kim Y, Yang SH, Kim M, Shih DC (2001) PCDD and PCDF exposure in workers and controls living near an industrial waste incinerator. Chemosphere 43:985–987. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00459-8
Kim BH, Ikonomou MG, Lee SJ, Kim HS, Chang YS (2005a) Concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans, and polychlorinated biphenyls in human blood samples from Korea. Sci Total Environ 336:45–56. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.05.030
Kim BH, Lee SJ, Mun SJ, Chang YS (2005b) A case study of dioxin monitoring in and around an industrial waste incinerator in Korea. Chemosphere 58:1589–1599. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.041
Kumagai S, Koda S (2005) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran concentrations in serum samples of workers at an infectious waste incineration plant in Japan. J Occup Environ Hyg 2:120–125. doi:10.1080/15459620590913146
Kumagai S, Oda H, Tabuchi T, Akasaka S, Kosaka H, Yoshida J et al (2004) Relationships between dioxin concentrations in deposited dust and those in serum of workers at municipal waste incineration plants. Sangyo Eiseigaku Zasshi 46:1–9. doi:10.1539/sangyoeisei.46.1 in Japanese
Lee CC, Chen HL, Su HJ, Guo YL, Liao PC (2005) Evaluation of PCDD/Fs patterns emitted from incinerator via direct ambient sampling and indirect serum levels assessment of Taiwanese. Chemosphere 59:1465–1474. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.075
Leem JH, Hong YC, Lee KH, Kwon HJ, Chang YS, Jang JY (2003) Health survey on workers and residents near the municipal waste and industrial waste incinerators in Korea. Ind Health 41:181–188. doi:10.2486/indhealth.41.181
Llobet JM, Granero S, Schuhmacher M, Corbella J, Domingo JL (1998) Biological monitoring of environmental pollution and human exposure to metals in Tarragona, Spain. III. Blood levels. Trace Elem Electrolytes 15:76–80
Mari M, Borrajo MA, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2007) Monitoring PCDD/Fs and other organic substances in workers of a hazardous waste incinerator: a case study. Chemosphere 67:574–581. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.09.069
Martí-Cid R, Bocio A, Domingo JL (2008) Dietary exposure to PCDD/PCDFs by individuals living near a hazardous waste incinerator in Catalonia, Spain: temporal trend. Chemosphere 70:1588–1595. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.08.017
Masuda Y, Haraguchi K, Kono S, Tsuji H, Päpke O (2005) Concentrations of dioxins and related compounds in the blood of Fukuoka residents. Chemosphere 58:329–344. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.06.016
Moon CS, Chang YS, Kim BH, Shin D, Ikeda M (2005) Evaluation of serum dioxin congeners among residents near continuously burning municipal solid waste incinerators in Korea. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 78:205–210. doi:10.1007/s00420-005-0603-0
Park S, Kim SJ, Kim KS, Lee DS, Kim JG (2004) Influence of an industrial waste incinerator as assessed by the levels and congener patterns of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans. Environ Sci Technol 38:3820–3826. doi:10.1021/es049976s
Pirard C, Eppe G, Massart AC, Fierens S, De Pauw E, Focant JF (2005) Environmental and human impact of an old-timer incinerator in terms of dioxin and PCB level: a case study. Environ Sci Technol 39:4721–4728. doi:10.1021/es0481981
Reis MF, Sampaio C, Brantes A, Aniceto P, Melim M, Cardoso L et al (2007) Human exposure to heavy metals in the vicinity of Portuguese solid waste incinerators—Part 1: Biomonitoring of Pb, Cd and Hg in blood of the general population. Int J Hyg Environ Health 210:439–446. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2007.01.023
Richter S, Johnke B (2004) Status of PCDD/F-emission control in Germany on the basis of the current legislation and strategies for further action. Chemosphere 54:1299–1302. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00247-9
Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2006) Long-term study of environmental levels of dioxins and furans in the vicinity of a municipal solid waste incinerator. Environ Int 32:397–404. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2005.09.002
Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Lindström G, Wingfors H (1999a) Dioxin and dibenzofuran concentrations in blood of a general population from Tarragona, Spain. Chemosphere 38:1123–1133. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00363-4
Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Kiviranta H, Vartiainen T (1999b) PCDD/F concentrations in milk of nonoccupationally exposed women living in southern Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere 38:995–1004. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00359-2
Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Lindström G, Wingfors H (1999c) Dioxin and dibenzofuran concentrations in adipose tissue of a general population from Tarragona, Spain. Chemosphere 38:2475–2487. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00454-8
Schuhmacher M, Agramunt MC, Rodriguez-Larena MC, Díaz-Ferrero J, Domingo JL (2002a) Baseline levels of PCDD/Fs in soil and herbage samples collected in the vicinity of a new hazardous waste incinerator in Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere 46:1343–1350. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00249-1
Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Agramunt MC, Bocio A, Müller L (2002b) Biological monitoring of metals and organic substances in hazardous-waste incineration workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 75:500–506. doi:10.1007/s00420-002-0340-6
Selden AS, Westberg H, Hanberg A, Nygren Y (1997) Congener-speficic monitoring of PCB and hexachlorobenzene in hazardous waste incineration workers. Organohalogen Compd 33:398–401
Shih SI, Wang YF, Chang JE, Jang JS, Kuo FL, Wang LC et al (2006a) Comparisons of levels of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans in the surrounding environment and workplace of two municipal solid waste incinerators. J Hazard Mater 137:1817–1830. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.022
Shih TS, Chen HL, Wu YL, Lin YC, Lee CC (2006b) Exposure assessment of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) in temporary municipal-waste-incinerator maintenance workers before and after annual maintenance. Chemosphere 64:1444–1449. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.01.014
Snary C (2002) Health risk assessment for planned waste incinerators: getting the right science and the science right. Risk Anal 22:1095–1105. doi:10.1111/1539-6924.00275
Wrbitzky R, Göen T, Letzel S, Frank F, Angerer J (1995) Internal exposure of waste incineration workers to organic and inorganic substances. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 68:13–21. doi:10.1007/BF01831628
Yoshida J, Kumagai S, Tabuchi T, Kosaka H, Akasaka S, Kasai H et al (2006) Negative association between serum dioxin level and oxidative DNA damage markers in municipal waste incinerator workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 79:115–122. doi:10.1007/s00420-005-0035-x
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by GRECAT SA, Constantí, Catalonia, Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mari, M., Schuhmacher, M. & Domingo, J.L. Levels of metals and organic substances in workers at a hazardous waste incinerator: a follow-up study. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 82, 519–528 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-008-0350-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-008-0350-0