Abstract
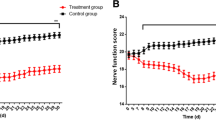
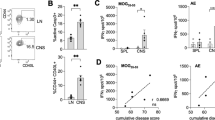
Mott cells are plasma cells that have multiple spherical Russell bodies packed in their cytoplasm. Russell bodies are dilated endoplasmic reticulum cisternae filled with aggregates of immunoglobulins that are neither secreted nor degraded. Mott cells were observed in our study by light and electron microscope in the lymph nodes of rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Mott cells were detected on hematoxylin and eosin (HE)-stained lymph node sections as vacuolated cells with eccentrically positioned nuclei and large number of faint blue spherical inclusions in the cytoplasm. Electron microscopic investigation revealed the presence of Russell bodies of the “medusa” form inside Mott cells in lymph node ultra-thin sections of EAE animals. Mott cells expressed the plasma cell marker CD138 and either kappa or lambda immunoglobulin light chains, indicating their origin from polyclonally activated B cells. Finally, Mott cells were associated with active EAE, as they were not found in the lymph nodes of EAE-resistant Albino Oxford rats. The presence of Russell bodies implies an excessive production of immunoglobulins in EAE, thus further emphasizing the role of B cells, and among them Mott cells, in the pathogenesis of this animal model of multiple sclerosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Apitz K (1937) Uber die bildung Russellscher korperchen in den plasmazellenmultipler myelome. Virchows Arch 300:113–129
Birmpili D, Charmarke Askar I, Bigaut K, Bagnard D (2022) The translatability of multiple sclerosis animal models for biomarkers discovery and their clinical use. Int J Mol Sci 23:11532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911532
Blom J, Mansa B, Wuk A (1976) Study of Russell bodies in human monoclonal plasma cells by means of immunofluorescence and electron microscopy. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A 84:335–349. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00124.x
Corcos D, Osborn MJ, Matheson LS, Santos F, Zou X, Smith JA, Morgan G, Hutchings A, Hamon M, Oxley D, Brüggemann M (2010) Immunoglobulin aggregation leading to Russell body formation is prevented by the antibody light chain. Blood 115:282–288. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-07-234864
Dahlman I, Jacobsson L, Glaser A, Lorentzen JC, Andersson M, Luthman H, Olsson T (1999) Genome-wide linkage analysis of chronic relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the rat identifies a major susceptibility locus on chromosome 9. J Immunol 162:2581–8
de Bruin NMWJ, Schmitz K, Schiffmann S, Tafferner N, Schmidt M, Jordan H, Häußler A, Tegeder I, Geisslinger G, Parnham MJ (2016) Multiple rodent models and behavioral measures reveal unexpected responses to FTY720 and DMF in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Behav Brain Res. 300:160–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.12.006
Decourt C, Galea HR, Sirac C, Cogne M (2004) Immunologic basis for the rare occurrence of true nonsecretory plasma cell dyscrasias. J Leukoc Biol 76:528–536. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0803382
Disanto G, Morahan JM, Barnett MH, Giovannoni G, Ramagopalan SV (2012) The evidence for a role of B cells in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 78:823–832. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e318249f6f0
Howell OW, Reeves CA, Nicholas R, Carassiti D, Radotra B, Gentleman SM, Serafini B, Aloisi F, Roncaroli F, Magliozzi R, Reynolds R (2011) Meningeal inflammation is widespread and linked to cortical pathology in multiple sclerosis. Brain 134:2755–2771. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr182
Kopito RR, Sitia R (2000) Aggresomes and Russell bodies: symptoms of cellular indigestion? EMBO Rep 1:225–231. https://doi.org/10.1093/embo-reports/kvd052
Kuerten S, Lehmann PV (2011) The immune pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: lessons learned for multiple sclerosis? J Interferon Cytokine Res 31:907–916. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2011.0072
Mahmoudi Aliabadi P, Al-Qaisi K, Jani PK, Honjo K, Klemm U, Lee KH, Baumgarth N, Radbruch A, Melchers F, Kubagawa H (2023) Enhanced Mott cell formation linked with IgM Fc receptor (FcμR) deficiency. Eur J Immunol 53(7):e2250315. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.202250315
Maldonado JE, Brown AL Jr, Bayrd ED, Pease GL (1966) Cytoplasmic and intranuclear electron-dense bodies in the myeloma cell. Arch Path 81:484–500
Mattioli L, Anelli T, Fagioli C, Tacchetti C, Sitia R, Valetti C (2006) ER storage diseases: a role for ERGIC-53 in controlling the formation and shape of Russell bodies. J Cell Sci 119:2532–2541. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02977
Maurano MT, Humbert R, Rynes E, Thurman RE, Haugen E, Wang H, Reynolds AP, Sandstrom R, Qu H, Brody J, Shafer A, Neri F, Lee K, Kutyavin T, Stehling-Sun S, Johnson AK, Canfield TK, Giste E, Diegel M, Bates D, Hansen RS, Neph S, Sabo PJ, Heimfeld S, Raubitschek A, Ziegler S, Cotsapas C, Sotoodehnia N, Glass I, Sunyaev SR, Kaul R, Stamatoyannopoulos JA (2012) Systematic localization of common disease-associated variation in regulatory DNA. Science 337:1190–1195. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222794
McLaughlin KA, Wucherpfennig KW (2008) B cells and autoantibodies in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and related inflammatory demyelinating diseases. Adv Immunol 98:121–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2776(08)00404-5
Mehta B, Goodman S, DiCarlo E, Jannat-Khah D, Gibbons JAB, Otero M, Donlin L, Pannellini T, Robinson WH, Sculco P, Figgie M, Rodriguez J, Kirschmann JM, Thompson J, Slater D, Frezza D, Xu Z, Wang F, Orange DE (2023) Machine learning identification of thresholds to discriminate osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis synovial inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther 25:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-023-03008-8
Mensah-Brown EP, Shahin A, Garey LJ, Lukic ML (2005) Neuroglial response after induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in susceptible and resistant rat strains. Cell Immunol 233:140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2005.04.023
Nicklas W, Baneux P, Boot R, Decelle T, Deeny AA, Fumanelli M, Illgen-Wilcke B (2002) Recommendations for the health monitoring of rodent and rabbit colonies in breeding and experimental units. Lab Anim 36:20–42. https://doi.org/10.1258/0023677021911740
Nylander A, Hafler DA (2012) Multiple sclerosis. J Clin Invest 122:1180–1188. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI58649
Pelc S, De Maertelaere E, Denolin-Reubens R (1981) CSF cytology of acute viral meningitis and meningoencephalitis. Eur Neurol 20:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1159/000115214
Rangachari M, Kuchroo VK (2013) Using EAE to better understand principles of immune function and autoimmune pathology. J Autoimmun 45:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2013.06.008
Ribourtout B, Zandecki M (2015) Plasma cell morphology in multiple myeloma and related disorders. Morphologie 99:38–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.morpho.2015.02.001
Robinson AP, Harp CT, Noronha A, Miller SD (2014) The experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of MS: utility for understanding disease pathophysiology and treatment. Handb Clin Neurol 122:173–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-52001-2.00008-X
Serafini B, Rosicarelli B, Magliozzi R, Stigliano E, Aloisi F (2004) Detection of ectopic B-cell follicles with germinal centers in the meninges of patients with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Brain Pathol 14:164–174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2004.tb00049.x
Stern J, Yaari G, Heiden JAV, Church G, Donahue WF, Hintzen RQ, Huttner AJ, Laman JD, Nagra RM, Nylander A, Pitt D, Ramanan S, Siddiqui BA, Vigneault F, Kleinstein SH, Hafler DA, O’Connor KC (2014) B cells populating the multiple sclerosis brain mature in the draining cervical lymph nodes. Sci Transl Med 6:248107. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3008879
Tosic J, Stanojevic Z, Vidicevic S, Isakovic A, Ciric D, Martinovic T, Kravic-Stevovic T, Bumbasirevic V, Paunovic V, Jovanovic S, Todorovic-Markovic B, Markovic Z, Danko M, Micusik M, Spitalsky Z, Trajkovic V (2019) Graphene quantum dots inhibit T cell-mediated neuroinflammation in rats. Neuropharmacology 146:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.11.030
Tsunoda I, Libbey JE, Kuang LQ, Terry EJ, Fujinami RS (2005) Massive apoptosis in lymphoid organs in animal models for primary and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Am J Pathol 167:1631–1646. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61247-3
Yanaba K, Bouaziz JD, Matsushita T, Magro CM, St Clair EW, Tedder TF (2008) B-lymphocyte contributions to human autoimmune disease. Immunol Rev 223:284–299. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00646.x
Zhang H, Jin Z, Cui R (2014) Russell body gastritis/duodenitis: a case series and description of immunoglobulin light chain restriction. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 38:e89-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinre.2014.05.008
Ziemssen T, Ziemssen F (2005) The role of the humoral immune system in multiple sclerosis (MS) and its animal model experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Autoimmun Rev 4:460–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2005.03.005
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the Ministry of Science of the Republic of Serbia (grant numbers 41025 and 175090) and Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts (grant number F-35).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each author’s contribution to the paper is quantified as following: TM, SV, and DC: were responsible for acquisition of data. DC, TM, VCM, and TKS: analyzed data. SV, JT, ZS, and SP: performed experiments on animals. TM, ND, and DC: processed the samples for light and electron microscopy. DC, TM, TKS, AI, VT, and VB: designed the study. TKS, VT, DC, SV, and TM: wrote the draft. DC: coordinated the study. All authors contributed to the interpretation of data and revision of the manuscript draft and approved the final version. DC is the guarantor of this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Martinovic, T., Vidicevic, S., Ciric, D. et al. The presence of Mott cells in the lymph nodes of rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Histochem Cell Biol 161, 287–295 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-023-02252-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-023-02252-y