Abstract
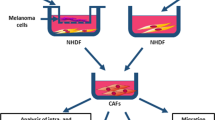
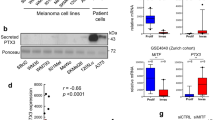
Tumour microenvironment plays a critical role in cell invasion and metastasis. To investigate the role of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in melanoma cell invasiveness, we used 3D spheroid invasion assay. The effect of conditioned media from normal fibroblasts and CAFs cultivated alone or co-cultivated with melanoma cells on BLM or A2058 melanoma spheroid invasion was analysed. We found that conditioned media from CAFs and CAFs co-cultured with melanoma cells, especially, promote invasion and migration, without significant effect on melanoma cell proliferation. We further analysed the expression of pro-invasive cytokines IL-8 and IL-6 in media and found that melanoma cells are dominant producers of IL-8 and fibroblasts are dominant producers of IL-6 in 2D monocultures, while co-cultivation of CAFs with melanoma cells induces production/secretion of IL-6 and IL-8 into the media. The analyses of IL-6 levels in 3D cultures and human melanoma samples, however, revealed that at least in some cases IL-6 is also produced directly by melanoma cells. Analysis of the role of IL-6 and IL-8 in CAF-induced melanoma invasion, using neutralising antibodies, revealed that simultaneous blocking of IL-6 and IL-8 is sufficient to fully inhibit CAF-induced human melanoma cell invasiveness. In summary, these experiments indicate the important role of CAFs and IL-8 and IL-6 cytokines in melanoma cell invasiveness.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aladowicz E, Ferro L, Vitali GC, Venditti E, Fornasari L, Lanfrancone L (2013) Molecular networks in melanoma invasion and metastasis. Future Oncol 9(5):713–726
Braeuer RR, Zigler M, Villares GJ, Dobroff AS, Bar-Eli M (2011) Transcriptional control of melanoma metastasis: the importance of the tumour microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol 21(2):83–88
Cirri P, Chiarugi P (2012) Cancer-associated-fibroblasts and tumour cells: a diabolic liaison driving cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31(1–2):195–208
Comito G, Giannoni E, Di Gennaro P, Segura CP, Gerlini G, Chiarugi P (2012) Stromal fibroblasts synergize with hypoxic oxidative stress to enhance melanoma aggressiveness. Cancer Lett 324(1):31–41
Fedorenko IV, Wargo JA, Flaherty KT, Messina JL, Smalley KS (2015) BRAF inhibition generates a host-tumor niche that mediates therapeutic escape. J Invest Dermatol 135(12):3115–3124
Fofaria NM, Frederick DT, Sullivan RJ, Flaherty KT, Srivastava SK (2015) Overexpression of Mcl-1 confers resistance to BRAFV600E inhibitors alone and in combination with MEK1/2 inhibitors in melanoma. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.5755
Frantz C, Stewart KM, Weaver VM (2010) The extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci 123(Pt 24):4195–4200
Gaggioli C, Hooper S, Hidalgo-Carcedo C, Grosse R, Marshall JF, Harrington K et al (2007) Fibroblast-led collective invasion of carcinoma cells with differing roles for RhoGTPases in leading and following cells. Nat Cell Biol 9(12):1392–1400
Gallagher PG, Bao Y, Prorock A, Zigrino P, Nischt R, Politi V et al (2005) Gene expression profiling reveals crosstalk between melanoma and fibroblasts: implications for host-tumor interactions in metastasis. Cancer Res 65(10):4134–4146
Harper J, Sainson RC (2014) Regulation of the anti-tumour immune response by cancer-associated fibroblasts. Semin Cancer Biol 25:69–77
Huang S, Mills L, Mian B, Tellez C, McCarty M, Yang XD et al (2002) Fully humanized neutralizing antibodies to interleukin-8 (ABX-IL8) inhibit angiogenesis, tumour growth, and metastasis of human melanoma. Am J Pathol 161(1):125–134
Kalluri R, Zeisberg M (2006) Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6(5):392–401
Kim GY, Lee JW, Ryu HC, Wei JD, Seong CM, Kim JH (2010) Proinflammatory cytokine IL-1beta stimulates IL-8 synthesis in mast cells via a leukotriene B4 receptor 2-linked pathway, contributing to angiogenesis. J Immunol 184(7):3946–3954
Kodet O, Lacina L, Krejčí E, Dvořánková B, Grim M, Štork J et al (2015) Melanoma cells influence the differentiation pattern of human epidermal keratinocytes. Mol Cancer 5(14):1
Kolář M, Szabo P, Dvořánková B, Lacina L, Gabius HJ, Strnad H et al (2012) Upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and CXCL-1 production in dermal fibroblasts by normal/malignant epithelial cells in vitro: immunohistochemical and transcriptomic analyses. Biol Cell 104(12):738–751
Kucera R, Topolcan O, Treskova I, Kinkorova J, Windrichova J, Fuchsova R et al (2015) Evaluation of IL-2, IL-6, IL-8 and IL-10 in malignant melanoma diagnostics. Anticancer Res 35(6):3537–3541
Li L, Dragulev B, Zigrino P, Mauch C, Fox JW (2009) The invasive potential of human melanoma cell lines correlates with their ability to alter fibroblast gene expression in vitro and the stromal microenvironment in vivo. Int J Cancer 125(8):1796–1804
Linnskog R, Jönsson G, Axelsson L, Prasad CP, Andersson T (2014) Interleukin-6 drives melanoma cell motility through p38a-MAPK-dependent up-regulation of WNT5A expression. Mol Oncol 8(8):1365–1378
Martin TA, Ye L, Sanders AJ, Lane J, Jiang WG (2000) Cancer invasion and metastasis: molecular and cellular perspective. In: Jandial R (ed) Madame Curie Bioscience Database [Internet]. Landes Bioscience, Austin
Na YR, Lee JS, Lee SJ, Seok SH (2013) Interleukin-6-induced twist and N-cadherin enhance melanoma cell metastasis. Melanoma Res 23(6):434–443
Navab R, Strumpf D, To C, Pasko E, Kim KS, Park CJ et al (2016) Integrin α11β1 regulates cancer stromal stiffness and promotes tumourigenicity and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 35(15):1899–1908
Okamura S, Fujiwara H, Yoneda M, Furutani A, Todo M, Ikai A et al (2013) Overexpression of IL-6 by gene transfer stimulates IL-8-mediated invasiveness of KYSE170 esophageal carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res 33(4):1483–1489
Okochi M, Matsumara T, Yamamoto S, Nakayama E, Jimbow K, Honda H (2013) Cell behavior observation and gene expression analysis of melanoma associated with stromal fibroblasts in a three-dimensional magnetic cell culture array. Biotechnol Prog 29(1):135–142
Östman A, Augsten M (2009) Cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumour growth—bystanders turning into key players. Curr Opin Genet Dev 19(1):67–73
Osuala KO, Sameni M, Shah S, Aggarwal N, Simonait ML, Franco OE et al (2015) Il-6 signaling between ductal carcinoma in situ cells and carcinoma-associated fibroblasts mediates tumour cell growth and migration. BMC Cancer 13(15):584
Pérez-Lorenzo R, Zheng B (2012) Targeted inhibition of BRAF kinase: opportunities and challenges for therapeutics in melanoma. Biosci Rep 32(1):25–33
Petersen OW, Rønnov-Jessen L, Howlett AR, Bissell MJ (1992) Interaction with basement membrane serves to rapidly distinguish growth and differentiation pattern of normal and malignant human breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(19):9064–9068
Sanmamed MF, Carranza-Rua O, Alfaro C, Oñate C, Martín-Algarra S, Perez G et al (2014) Serum interleukin-8 reflects tumor burden and treatment response across malignancies of multiple tissue origins. Clin Cancer Res 20(22):5697–5707
Sasser AK, Sullivan NJ, Studebaker AW, Hendey LF, Axel AE, Hall BM (2007) Interleukin-6 is a potent growth factor for ER-alpha-positive human breast cancer. FASEB J 21(13):3763–3770
Shi H, Wu Y, Wang Y, Zhou M, Yan S, Chen Z et al (2015) Liquiritigenin potentiates the inhibitory effects of cisplatin on invasion and metastasis via downregulation MMP-2/9 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in B16F10 melanoma cells and mice model. Nutr Cancer 67(5):761–770
Shimoda M, Mellody KT, Orimo A (2010) Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts are a rate-limiting determinant for tumour progression. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21(1):19–25
Su F, Viros A, Milagre C, Trunzer K, Bollag G, Spleiss O et al (2012) RAS mutations in cutaneous squamous-cell carcinomas in patients treated with BRAF inhibitors. N Engl J Med 366(3):207–215
Trylcova J, Busek P, Smetana K Jr, Balaziova E, Dvorankova B, Mifkova A et al (2015) Effect of cancer-associated fibroblasts on the migration of glioma cells in vitro. Tumour Biol 36(8):5873–5879
van Kempen LC, Rijntjes J, Mamor-Cornelissen I, Vincent-Naulleau S, Gerritsen MJ, Ruiter DJ et al (2008) Type I collagen expression contributes to angiogenesis and the development of deeply invasive cutaneous melanoma. Int J Cancer 122(5):1019–1029
Vinci M, Gowan S, Boxall F, Patterson L, Zimmermann M, Court W et al (2012) Advances in establishment and analysis of three-dimensional tumor spheroid-based functional assays for target validation and drug evaluation. BMC Biol 22(10):29
Vultur A, Villanueva J, Krepler C, Rajan G, Chen Q, Xiao M et al (2014) MEK inhibition affects STAT3 signaling and invasion in human melanoma cell lines. Oncogene 33(14):1850–1861
Weinstein D, Leininger J, Hamby C, Safai B (2014) Diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in melanoma. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 7(6):13–24
Weiswald LB, Bellet D, Dangles-Marie V (2015) Spherical cancer models in tumor biology. Neoplasia 17(1):1–15
Westphal JR, Hullenaar RV, Peek R, Willems RW, Crickard K, Crickard U et al (2000) Angiogenic balance in human melanoma: expression of VEGF, bFGF, IL-8, PDGF and angiostatin in relation to vascular density of xenografts in vivo. Int J Cancer 86:768–776
Whipple CA, Brinckerhoff CE (2014) BRAF(V600E) melanoma cells secrete factors that activate stromal fibroblasts and enhance tumourigenicity. Br J Cancer 111(8):1625–1633
Wiercinska E, Naber HP, Pardali E, van der Pluijm G, van Dam H, ten Dijke P (2011) The TGF-β/Smad pathway induces breast cancer cell invasion through the up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 in a spheroid invasion model system. Breast Cancer Res Treat 128(3):657–666
Wu S, Singh S, Varney ML, Kindle S, Singh RK (2012) Modulation of CXCL-8 expression in human melanoma cells regulates tumor growth, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. Cancer Med 1(3):306–317
Yao X, Huang J, Zhong H, Shen N, Faggioni R, Fung M, Yao Y (2014) Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol Ther 141(2):125–139
Yin M, Soikkeli J, Jahkola T, Virolainen S, Saksela O, Hölttä E (2012) TGF-β signaling, activated stromal fibroblasts, and cysteine cathepsins B and L drive the invasive growth of human melanoma cells. Am J Pathol 181(6):2202–2216
Zhou L, Yang K, Andl T, Wickett RR, Zhang Y (2015) Perspective of targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts in melanoma. J Cancer 6(8):717–726
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Marie Charvátová, Marie Jindráková and Radana Kavková for excellent technical assistance. This publication is a result of the project implementation: “The equipment for metabolomic and cell analyses”, Registration Number CZ.1.05/2.1.00/19.0400, supported by Research and Development for Innovations Operational Programme (RDIOP) co-financed by European regional development fund and the state budget of the Czech Republic. Salary of Dr Mateu was covered by project GLYCOPHARM. This study was also supported by the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (Project Nos. 304/02/1333 and 16-05534S), the Charles University (project of Specific University Research and PRVOUK-27, UNCE 204013, Grant Agency of Charles University Grant 629312), the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of CR within the National Sustainability Program II (Project BIOCEV-FAR Reg. No. LQ1604), the project BIOCEV (CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0109) and the Kellner Family Foundation Principal Investigator grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
Blocking IL-6 and IL-8 in conditioned media fully inhibits CAF-induced invasion. WM3629 (a) and WM3670 (b) melanoma spheroids were embedded in collagen, and incubated with conditioned media (top panel) and conditioned media supplemented with IL-6 and IL-8 blocking antibody (bottom panel) at a concentration of 200 ng/ml, each. The graphs (c, d) show relative invasion after 48 hours. CC HFP3 and CC Mel Fib is conditioned media from co-culture of melanoma cells with normal fibroblasts and CAFs, respectively. These results are representative of three independent experiments. Scale bar 400 µm. *p < 0.05 (TIFF 3623 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jobe, N.P., Rösel, D., Dvořánková, B. et al. Simultaneous blocking of IL-6 and IL-8 is sufficient to fully inhibit CAF-induced human melanoma cell invasiveness. Histochem Cell Biol 146, 205–217 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1433-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1433-8