Abstract
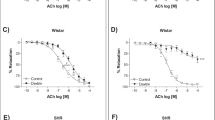
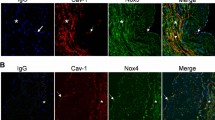
Diet-induced obesity induces changes in mechanisms that are essential for the regulation of normal artery function, and in particular the function of the vascular endothelium. Using a rodent model that reflects the characteristics of human dietary obesity, in the rat saphenous artery we have previously demonstrated that endothelium-dependent vasodilation shifts from an entirely nitric oxide (NO)-mediated mechanism to one involving upregulation of myoendothelial gap junctions and intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity and expression. This study investigates the changes in NO-mediated mechanisms that accompany this shift. In saphenous arteries from controls fed a normal chow diet, acetylcholine-mediated endothelium-dependent vasodilation was blocked by NO synthase and soluble guanylyl cyclase inhibitors, but in equivalent arteries from obese animals sensitivity to these agents was reduced. The expression of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) and caveolin-3 in rat saphenous arteries was unaffected by obesity, whilst that of caveolin-1 monomer and large oligomeric complexes of caveolins-1 and -2 were increased in membrane-enriched samples. The density of caveolae was increased at the membrane and cytoplasm of endothelial and smooth muscle cells of saphenous arteries from obese rats. Dissociation of eNOS from caveolin-1, as a prerequisite for activation of the enzyme, may be compromised and thereby impair NO-mediated vasodilation in the saphenous artery from diet-induced obese rats. Such altered signaling mechanisms in obesity-related vascular disease represent significant potential targets for therapeutic intervention.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Averna M, Stifanese R, De Tullio R, Passalacqua M, Salamino F, Pontremoli S, Melloni E (2008) Functional role of HSP90 complexes with endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS) and calpain on nitric oxide generation in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 283:29069–29076
Bauer PM, Fulton D, Boo YC, Sorescu GP, Kemp BE, Jo H, Sessa WC (2003) Compensatory phosphorylation and protein–protein interactions revealed by loss of function and gain of function mutants of multiple serine phosphorylation sites in endothelial nitric-oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 278:14841–14849
Blair A, Shaul PW, Yuhanna IS, Conrad PA, Smart EJ (1999) Oxidized low density lipoprotein displaces endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS) from plasmalemmal caveolae and impairs eNOS activation. J Biol Chem 274:32512–32519
Boscher CB, Nabi IR (2012) Caveolin-1: role in cell signalling. Adv Exp Med Biol 729:29–50
Boyd NL, Park H, Yi H, Boo YC, Sorescu GP, Sykes M, Jo H (2003) Chronic shear induces caveolae formation and alters ERK and Akt responses in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:H1113–H1122
Bullejos M, Bowles J, Koopman P (2002) Extensive vascularization of developing mouse ovaries revealed by caveolin-1 expression. Dev Dyn 225:95–99
Cenedella RJ, Neely AR, Sexton P (2006) Multiple forms of 22 kDa caveolin-1 alpha present in bovine lens cells could reflect variable palmitoylation. Exp Eye Res 82:229–235
Chadha PS, Haddock RE, Howitt L, Morris MJ, Murphy TV, Grayson TH, Sandow SL (2010) Obesity upregulates IKCa and myoendothelial gap junctions to maintain endothelial vasodilator function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 335:284–293
Chen CA, Druhan LJ, Varadharaj S, Chen YR, Zweier JL (2008) Phosphorylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase regulates superoxide generation from the enzyme. J Biol Chem 283:27038–27047
Chen Z, Bakhshi FR, Shajahan AN, Sharma T, Mao M, Trane A, Bernatchez P, van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Bonini MG, Skidgel RA, Malik AB, Minshall RD (2012) Nitric oxide-dependent Src activation and resultant caveolin-1 phosphorylation promote eNOS/caveolin-1 binding and eNOS inhibition. Mol Biol Cell 23:1388–1398
Collins BM, Davis MJ, Hancock JF, Parton RG (2012) Structure-based reassessment of the caveolin signaling model: do caveolae regulate signaling through caveolin-protein interactions? Dev Cell 23:11–20
Dart C (2010) Lipid microdomains and the regulation of ion channel function. J Physiol 588:3169–3178
Das K, Lewis RY, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP (1999) The membrane-spanning domains of caveolins-1 and -2 mediate the formation of caveolin hetero-oligomers. Implications for the assembly of caveolae membranes in vivo. J Biol Chem 274:18721–18728
Dong Y, Wu Y, Wu M, Wang S, Zhang J, Xie Z, Xu J, Song P, Wilson K, Zhao Z, Lyons T, Zou MH (2009) Activation of protease calpain by oxidized and glycated LDL increases the degradation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Cell Mol Med 13:2899–2910
Dudzinski DM, Igarashi J, Greif D, Michel T (2006) The regulation and pharmacology of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 46:235–276
Fang PK, Solomon KR, Zhuang L, Qi M, McKee M, Freeman MR, Yelick PC (2006) Caveolin-1alpha and -1beta perform nonredundant roles in early vertebrate development. Am J Pathol 169:2209–2222
Feron O, Dessy C, Moniotte S, Desager JP, Balligand JL (1999) Hypercholesterolemia decreases nitric oxide production by promoting the interaction of caveolin and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Clin Invest 103:897–905
Fleming I, Fisslthaler B, Dimmeler S, Kemp BE, Busse R (2001) Phosphorylation of Thr(495) regulates Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity. Circ Res 88:E68–E75
Fujimoto T, Kogo H, Nomura R, Une T (2000) Isoforms of caveolin-1 and caveolar structure. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 19):3509–3517
Garcia-Cardena G, Martasek P, Masters BS, Skidd PM, Couet J, Li S, Lisanti MP, Sessa WC (1997) Dissecting the interaction between nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and caveolin. Functional significance of the nos caveolin binding domain in vivo. J Biol Chem 272:25437–25440
Garcia-Cardena G, Fan R, Shah V, Sorrentino R, Cirino G, Papapetropoulos A, Sessa WC (1998) Dynamic activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by Hsp90. Nature 392:821–824
Gonzalez E, Kou R, Lin AJ, Golan DE, Michel T (2002) Subcellular targeting and agonist-induced site-specific phosphorylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 277:39554–39560
Greif DM, Sacks DB, Michel T (2004) Calmodulin phosphorylation and modulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1165–1170
Hansen MJ, Jovanovska V, Morris MJ (2004) Adaptive responses in hypothalamic neuropeptide Y in the face of prolonged high-fat feeding in the rat. J Neurochem 88:909–916
Hayer A, Stoeber M, Bissig C, Helenius A (2010) Biogenesis of caveolae: stepwise assembly of large caveolin and cavin complexes. Traffic 11:361–382
Hink U, Li H, Mollnau H, Oelze M, Matheis E, Hartmann M, Skatchkov M, Thaiss F, Stahl RA, Warnholtz A, Meinertz T, Griendling K, Harrison DG, Forstermann U, Munzel T (2001) Mechanisms underlying endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Circ Res 88:E14–E22
Howitt L, Sandow SL, Grayson TH, Ellis ZE, Morris MJ, Murphy TV (2011) Differential effects of diet-induced obesity on BKCaβ1-subunit expression and function in rat skeletal muscle arterioles and small cerebral arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H29–H40
Howitt L, Grayson TH, Morris MJ, Sandow SL, Murphy TV (2012) Dietary obesity increases NO and inhibits BKCa-mediated, endothelium-dependent dilation in rat cremaster muscle artery: association with caveolins and caveolae. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302:H2464–H2476
Jasmin JF, Malhotra S, Singh Dhallu M, Mercier I, Rosenbaum DM, Lisanti MP (2007) Caveolin-1 deficiency increases cerebral ischemic injury. Circ Res 100:721–729
Je HD, Gallant C, Leavis PC, Morgan KG (2004) Caveolin-1 regulates contractility in differentiated vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H91–H98
Ju H, Zou R, Venema VJ, Venema RC (1997) Direct interaction of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase and caveolin-1 inhibits synthase activity. J Biol Chem 272:18522–18525
Kogo H, Fujimoto T (2000) Caveolin-1 isoforms are encoded by distinct mRNAs. Identification Of mouse caveolin-1 mRNA variants caused by alternative transcription initiation and splicing. FEBS Lett 465:119–123
Kogo H, Aiba T, Fujimoto T (2004) Cell type-specific occurrence of caveolin-1alpha and -1beta in the lung caused by expression of distinct mRNAs. J Biol Chem 279:25574–25581
Kogo H, Ito SY, Moritoki Y, Kurahashi H, Fujimoto T (2006) Differential expression of caveolin-3 in mouse smooth muscle cells in vivo. Cell Tissue Res 324:291–300
Korda M, Kubant R, Patton S, Malinski T (2008) Leptin-induced endothelial dysfunction in obesity. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H1514–H1521
Lajoie P, Goetz JG, Dennis JW, Nabi IR (2009) Lattices, rafts, and scaffolds: domain regulation of receptor signaling at the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 185:381–385
Laufs U, Endres M, Stagliano N, Amin-Hanjani S, Chui DS, Yang SX, Simoncini T, Yamada M, Rabkin E, Allen PG, Huang PL, Bohm M, Schoen FJ, Moskowitz MA, Liao JK (2000) Neuroprotection mediated by changes in the endothelial actin cytoskeleton. J Clin Invest 106:15–24
Lee H, Volonte D, Galbiati F, Iyengar P, Lublin DM, Bregman DB, Wilson MT, Campos-Gonzalez R, Bouzahzah B, Pestell RG, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP (2000) Constitutive and growth factor-regulated phosphorylation of caveolin-1 occurs at the same site (Tyr-14) in vivo: identification of a c-Src/Cav-1/Grb7 signaling cassette. Mol Endocrinol 14:1750–1775
Levitan I, Volkov S, Subbaiah PV (2010) Oxidized LDL: diversity, patterns of recognition, and pathophysiology. Antiox Redox Sig 13:39–75
Li S, Seitz R, Lisanti MP (1996) Phosphorylation of caveolin by src tyrosine kinases. The alpha-isoform of caveolin is selectively phosphorylated by v-Src in vivo. J Biol Chem 271:3863–3868
Li S, Galbiati F, Volonte D, Sargiacomo M, Engelman JA, Das K, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP (1998) Mutational analysis of caveolin-induced vesicle formation. Expression of caveolin-1 recruits caveolin-2 to caveolae membranes. FEBS Lett 434:127–134
Li C, Ruan L, Sood SG, Papapetropoulos A, Fulton D, Venema RC (2007) Role of eNOS phosphorylation at Ser-116 in regulation of eNOS activity in endothelial cells. Vascul Pharmacol 47:257–264
Michel JB, Feron O, Sacks D, Michel T (1997) Reciprocal regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase by Ca2+-calmodulin and caveolin. J Biol Chem 272:15583–15586
Michell BJ, Chen Z, Tiganis T, Stapleton D, Katsis F, Power DA, Sim AT, Kemp BE (2001) Coordinated control of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation by protein kinase C and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 276:17625–17628
Mineo C, Shaul PW (2012) Regulation of eNOS in caveolae. Adv Exp Med Biol 729:51–62
Monier S, Parton RG, Vogel F, Behlke J, Henske A, Kurzchalia TV (1995) VIP21-caveolin, a membrane protein constituent of the caveolar coat, oligomerizes in vivo and in vitro. Mol Biol Cell 6:911–927
Mora R, Bonilha VL, Marmorstein A, Scherer PE, Brown D, Lisanti MP, Rodriguez-Boulan E (1999) Caveolin-2 localizes to the golgi complex but redistributes to plasma membrane, caveolae, and rafts when co-expressed with caveolin-1. J Biol Chem 274:25708–25717
Muniyappa R, Iantorno M, Quon MJ (2008) An integrated view of insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction. Endocrinol Metab 37:685–711
Nixon SJ, Wegner J, Ferguson C, Mery PF, Hancock JF, Currie PD, Key B, Westerfield M, Parton RG (2005) Zebrafish as a model for caveolin-associated muscle disease; caveolin-3 is required for myofibril organization and muscle cell patterning. Hum Mol Genet 14:1727–1743
Oh P, Schnitzer JE (2001) Segregation of heterotrimeric G proteins in cell surface microdomains. G(q) binds caveolin to concentrate in caveolae, whereas G(i) and G(s) target lipid rafts by default. Mol Biol Cell 12:685–698
Pani B, Singh BB (2009) Lipid rafts/caveolae as microdomains of calcium signaling. Cell Calcium 45:625–633
Park H, Go YM, St John PL, Maland MC, Lisanti MP, Abrahamson DR, Jo H (1998) Plasma membrane cholesterol is a key molecule in shear stress-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. J Biol Chem 273:32304–32311
Park H, Go YM, Darji R, Choi JW, Lisanti MP, Maland MC, Jo H (2000) Caveolin-1 regulates shear stress-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278:H1285–H1293
Patel HH, Murray F, Insel PA (2008) Caveolae as organizers of pharmacologically relevant signal transduction molecules. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 48:359–391
Ramirez MI, Pollack L, Millien G, Cao YX, Hinds A, Williams MC (2002) The alpha-isoform of caveolin-1 is a marker of vasculogenesis in early lung development. J Histochem Cytochem 50:33–42
Razani B, Combs TP, Wang XB, Frank PG, Park DS, Russell RG, Li M, Tang B, Jelicks LA, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP (2002a) Caveolin-1-deficient mice are lean, resistant to diet-induced obesity, and show hypertriglyceridemia with adipocyte abnormalities. J Biol Chem 277:8635–8647
Razani B, Park DS, Miyanaga Y, Ghatpande A, Cohen J, Wang XB, Scherer PE, Evans T, Lisanti MP (2002b) Molecular cloning and developmental expression of the caveolin gene family in the amphibian Xenopus laevis. Biochemistry 41:7914–7924
Razani B, Woodman SE, Lisanti MP (2002c) Caveolae: from cell biology to animal physiology. Pharmacol Rev 54:431–467
Rizzo V, McIntosh DP, Oh P, Schnitzer JE (1998a) In situ flow activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase in luminal caveolae of endothelium with rapid caveolin dissociation and calmodulin association. J Biol Chem 273:34724–34729
Rizzo V, Sung A, Oh P, Schnitzer JE (1998b) Rapid mechanotransduction in situ at the luminal cell surface of vascular endothelium and its caveolae. J Biol Chem 273:26323–26329
Rizzo V, Morton C, DePaola N, Schnitzer JE, Davies PF (2003) Recruitment of endothelial caveolae into mechanotransduction pathways by flow conditioning in vitro. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:H1720–H1729
Rybin VO, Grabham PW, Elouardighi H, Steinberg SF (2003) Caveolae-associated proteins in cardiomyocytes: caveolin-2 expression and interactions with caveolin-3. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:H325–H332
Saliez J, Bouzin C, Rath G, Ghisdal P, Desjardins F, Rezzani R, Rodella LF, Vriens J, Nilius B, Feron O, Balligand JL, Dessy C (2008) Role of caveolar compartmentation in endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-mediated relaxation: Ca2+ signals and gap junction function are regulated by caveolin in endothelial cells. Circulation 117:1065–1074
Sandow SL, Tare M, Coleman HA, Hill CE, Parkington HC (2002) Involvement of myoendothelial gap junctions in the actions of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor. Circ Res 90:1108–1113
Sandow SL, Goto K, Rummery N, Hill CE (2004) Developmental changes in myoendothelial gap junction mediated vasodilator activity in the rat saphenous artery. J Physiol 556:875–886
Sargiacomo M, Scherer PE, Tang Z, Kubler E, Song KS, Sanders MC, Lisanti MP (1995) Oligomeric structure of caveolin: implications for caveolae membrane organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:9407–9411
Sbaa E, Frerart F, Feron O (2005) The double regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by caveolae and caveolin: a paradox solved through the study of angiogenesis. Trends Cardiovasc Med 15:157–162
Scheiffele P, Verkade P, Fra AM, Virta H, Simons K, Ikonen E (1998) Caveolin-1 and -2 in the exocytic pathway of MDCK cells. J Cell Biol 140:795–806
Scherer PE, Tang Z, Chun M, Sargiacomo M, Lodish HF, Lisanti MP (1995) Caveolin isoforms differ in their N-terminal protein sequence and subcellular distribution. Identification and epitope mapping of an isoform-specific monoclonal antibody probe. J Biol Chem 270:16395–16401
Scherer PE, Okamoto T, Chun M, Nishimoto I, Lodish HF, Lisanti MP (1996) Identification, sequence, and expression of caveolin-2 defines a caveolin gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:131–135
Scherer PE, Lewis RY, Volonte D, Engelman JA, Galbiati F, Couet J, Kohtz DS, van Donselaar E, Peters P, Lisanti MP (1997) Cell-type and tissue-specific expression of caveolin-2. Caveolins 1 and 2 co-localize and form a stable hetero-oligomeric complex in vivo. J Biol Chem 272:29337–29346
Schlegel A, Arvan P, Lisanti MP (2001) Caveolin-1 binding to endoplasmic reticulum membranes and entry into the regulated secretory pathway are regulated by serine phosphorylation. Protein sorting at the level of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 276:4398–4408
Schulz E, Jansen T, Wenzel P, Daiber A, Munzel T (2008) Nitric oxide, tetrahydrobiopterin, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction in hypertension. Antiox Redox Sig 10:1115–1126
Shaul PW (2003) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase, caveolae and the development of atherosclerosis. J Physiol 547:21–33
Terasaka N, Yu S, Yvan-Charvet L, Wang N, Mzhavia N, Langlois R, Pagler T, Li R, Welch CL, Goldberg IJ, Tall AR (2008) ABCG1 and HDL protect against endothelial dysfunction in mice fed a high-cholesterol diet. J Clin Invest 118:3701–3713
Thomas SR, Chen K, Keaney JF Jr (2002) Hydrogen peroxide activates endothelial nitric-oxide synthase through coordinated phosphorylation and dephosphorylation via a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 277:6017–6024
Thum T, Fraccarollo D, Schultheiss M, Froese S, Galuppo P, Widder JD, Tsikas D, Ertl G, Bauersachs J (2007) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling impairs endothelial progenitor cell mobilization and function in diabetes. Diabetes 56:666–674
Thyberg J (2002) Caveolae and cholesterol distribution in vascular smooth muscle cells of different phenotypes. J Histochem Cytochem 50:185–195
Tran QK, Black DJ, Persechini A (2003) Intracellular coupling via limiting calmodulin. J Biol Chem 278:24247–24250
Velkoska E, Cole TJ, Morris MJ (2005) Early dietary intervention: long-term effects on blood pressure, brain neuropeptide Y, and adiposity markers. Am J Physiol 288:E1236–E1243
Wigg SJ, Tare M, Tonta MA, O’Brien RC, Meredith IT, Parkington HC (2001) Comparison of effects of diabetes mellitus on an EDHF-dependent and an EDHF-independent artery. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H232–H240
Williams TM, Lisanti MP (2004) The caveolin proteins. Genome Biol 5:214
Yeh DC, Duncan JA, Yamashita S, Michel T (1999) Depalmitoylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase by acyl-protein thioesterase 1 is potentiated by Ca2+-calmodulin. J Biol Chem 274:33148–33154
Youn JY, Gao L, Cai H (2012) The p47(phox)- and NADPH oxidase organiser 1 (NOXO1)-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) mediates endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) uncoupling and endothelial dysfunction in a streptozotocin-induced murine model of diabetes. Diabetologia 55:2069–2079
Yu S, Wong SL, Lau CW, Huang Y, Yu CM (2011) Oxidized LDL at low concentration promotes in vitro angiogenesis and activates nitric oxide synthase through PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 407:44–48
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (grant ID455243 to S.L.S. and M.J.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grayson, T.H., Chadha, P.S., Bertrand, P.P. et al. Increased caveolae density and caveolin-1 expression accompany impaired NO-mediated vasorelaxation in diet-induced obesity. Histochem Cell Biol 139, 309–321 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-1032-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-1032-2