Abstract
Purpose
To demonstrate the efficacy and safety of ranibizumab 0.5 mg pro re nata (PRN) versus laser photocoagulation for the treatment of Chinese patients with visual impairment due to diabetic macular edema (DME).
Methods
REFINE was a phase III, 12-month, double-masked, multicenter, laser-controlled study in patients (aged ≥ 18 years) with DME. Patients were randomized 4:1 to receive either ranibizumab 0.5 mg or laser dosing regimen. Efficacy was evaluated as mean average change in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) from Months 1 to 12 versus baseline (primary endpoint), anatomical outcomes, treatment exposure, and safety were also assessed.
Results
Ranibizumab was statistically superior (p < 0.001) to laser treatment, with a mean average BCVA gain of 6.8 letters (ranibizumab) over 12 months versus 1.1 letters (laser). At Month 12, mean BCVA gain was 7.8 letters (ranibizumab) and 2.5 letters (laser) from baseline. Patients in the ranibizumab arm received a mean number of 7.9 intravitreal injections, whereas those in the laser arm received a mean of 2.1 treatments. There were no new safety signals.
Conclusion
Ranibizumab 0.5 mg PRN demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful treatment effect versus laser and was well tolerated in Chinese patients with visual impairment due to DME over 12 months.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of visual impairment and blindness in the global population aged 20–74 years [1, 2] and is an increasing concern with the rising prevalence of diabetes [3]. Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a common manifestation of DR and a cause of serious central visual loss and impairment in diabetic patients if left untreated [4]. Timely intervention in patients with diabetes can help to prevent vision deterioration and lower the risk of blindness due to DME.
This is particularly relevant for China, as at least 50% of its population (aged ≥ 18 years) have been shown to have pre-diabetes based on a 2010 nationwide survey [5]. In another nationally representative cross-sectional survey conducted in 2013 in mainland China, it reported 35.7% of population aged ≥ 18 years with pre-diabetes [6]. For patients with a confirmed diagnosis of diabetes, two epidemiological studies in 2642 to 7577 patients conducted in China in 2010 and 2011 have reported a high prevalence of DR (9.4% to 43.1% of patients, respectively) and its associated risks including longer duration of diabetes, higher plasma concentration of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), higher postprandial blood glucose concentrations, and higher systolic blood pressure [7,8,9]. In a cross-sectional study of 17,985 patients in Beijing, the prevalence of DR was reported to be 8.1% [10].
Macular edema is a vision threatening complication of DR. In the Beijing Eye Study, which included 4439 patients with diabetes mellitus aged > 40 years, the overall prevalence of macular edema was 5.2% [11]. An epidemiologic study in the Shanghai city region in China identified 829 patients > 15 years old with diabetes, of whom 36 (4.34%) had macular edema [12].
Laser photocoagulation is currently considered the standard of care for visual impairment due to DME in China, which stabilizes rather than improves vision in these patients [13]. Furthermore, 13% of laser-treated eyes remain unresponsive to treatment and are at risk of progressive vision loss [13]. Therefore, there is a need for a treatment that not only halts progressive vision loss but also has a quick effect on improving visual acuity (VA) in Chinese patients with DME.
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels are elevated in the vitreous of eyes with DR; therefore, anti-VEGFs are an alternative treatment for patients with DME [14, 15]. Ranibizumab 0.5 mg was the first anti-VEGF approved for the treatment of visual impairment due to DME in Europe (2011) based on the data from the RESOLVE [16] and RESTORE [17] studies. These studies enrolled predominantly Caucasian patients and demonstrated significant and continuous improvement in VA over 12 months compared with sham or laser in patients with visual impairment due to DME. Currently in China, ranibizumab 0.5 mg is only approved for the treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration [18].
Here, we present the 12-month findings of the REFINE study that was conducted to provide additional data on the efficacy and safety of ranibizumab 0.5 mg compared with laser photocoagulation in Chinese patients with visual impairment due to DME.
Methods
Study design
REFINE was a phase III, 12-month, multicenter (28 sites) laser-controlled study conducted in mainland Chinese patients with visual impairment due to DME from November 2014 to January 2017. To minimize potential bias, the study had a parallel, randomized, double-masked design. Written informed consent was obtained from each patient before randomization.
The study was conducted according to the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and the study protocol was reviewed by the Ethics Committee for each center. The study is registered at clinicaltrials.gov with identifier NCT02259088.
Patient population
The study population consisted of Chinese male and female patients aged ≥ 18 years with either type I or type II diabetes mellitus (according to the American Diabetes Association or World Health Organization guidelines [19]) and HbA1c ≤ 10.0% at screening. Patients were included in the study with visual impairment due to focal or diffuse DME in at least one eye with a best-corrected VA (BCVA) score between 78 and 39 letters (inclusively, approximately 20/32 to 20/160 Snellen equivalent) as measured by Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS)-like charts at four meters. If both eyes were eligible, the eye with the worse VA at screening or baseline visits was selected as the study eye, unless the eye with the better VA was deemed to be more appropriate for study by the investigator based on medical reasons.
Patients with any type of systemic disease including those who had received treatment for it or any medical condition (controlled or uncontrolled) that could be expected to progress, recur, or change to an extent that it might influence the assessment of the clinical status of the patient to a significant degree or put the patient at special risk; uncontrolled systolic blood pressure of > 160 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure of > 100 mmHg; and laser (panretinal, focal, grid) photocoagulation within 3 months prior to baseline visit (study eye) were excluded from the study. Detailed inclusion and exclusion criteria are provided in the A1.
Randomization and treatment
Patients were randomized 4:1 into two treatment arms to receive either ranibizumab 0.5 mg (pro re nata [PRN] dosing regimen) or laser photocoagulation (as needed according to ETDRS guidelines) (Fig. 1). A randomization list was produced by the interactive response technology (IRT) provider by using a validated system that automated the random assignment of patient numbers to randomization numbers.
In the REFINE study, the treatment regimen was based on the EU Summary of Product Characteristics 2011 (three monthly injections followed by PRN as per VA stabilization criterion) [20].
Ranibizumab arm
All patients received three initial monthly ranibizumab 0.5-mg injections (on Day 1, Month 1, and Month 2), and sham laser photocoagulation on Day 1, followed by monthly ranibizumab based on a PRN dosing regimen until stable VA was achieved.
Stable VA was defined over three consecutive monthly assessments post-baseline, with study treatment given at each visit. If stable VA was achieved (at Month 3 or any later time point), treatment was stopped. Treatment with ranibizumab was resumed upon any loss of VA due to disease activity and continued until stable VA was reached again for three consecutive monthly assessments. Thus, after reinitiation of ranibizumab injections, a minimum of two successive monthly treatments were required.
Laser arm
Patients received active laser photocoagulation on Day 1 (with option to split into two sessions with maximum of 4-week interval in between), and sham ranibizumab injection on Day 1, Month 1, and Month 2.
If stable VA was achieved, sham injections were discontinued. Monthly treatment with sham injections was resumed upon any loss of VA due to disease activity and continued until stable VA was reached again for three consecutive monthly assessments.
After Day 1, active laser photocoagulation was given as needed as per the ETDRS guidelines at intervals of no less than 3 months. Patients could receive a maximum of four laser photocoagulation throughout the study.
Rescue medication
In case of lack of efficacy of the study treatment and when the investigator deemed it in the best interests of the patient to receive alternative treatment for DME in the study eye, the patient was asked to discontinue the study and was treated outside of the study protocol.
Treatment masking
In order to fulfill masking requirements, the site personnel consisted of a VA assessor, an evaluating investigator responsible for all other assessments and treatment decisions, and a treating investigator. Both the VA assessor and the evaluating investigator were masked to the treatment assignment, while treating investigator was unmasked and performed the treatment according to the assigned randomized treatment arm (A2).
Study objectives
The primary objective was to demonstrate superior efficacy of ranibizumab 0.5 mg monotherapy (PRN regimen driven by VA stability) compared with laser photocoagulation for the treatment of visual impairment due to DME in Chinese patients, as assessed by the mean average change in BCVA from Month 1 to Month 12 compared with baseline.
Secondary objectives were to evaluate the following: mean change in BCVA from baseline at Month 12; mean change in central subfield thickness (CSFT) from baseline at Month 12; proportion of patients with BCVA gain of ≥ 10 and ≥ 15 letters and loss of < 10 and < 15 letters from baseline at Month 12; proportion of patients with BCVA ≥ 73 letters (approximate 20/40 Snellen chart equivalent) at Month 12; treatment exposure, number of retreatments, and retreatment patterns; and safety as assessed by ocular and non-ocular adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs (SAEs) over 12 months.
Other exploratory objectives were to evaluate the effect of treatment on DR as assessed by proportion of patients with changes on the ETDRS-diabetic retinopathy severity score (DRSS) on a 10-point scale (defined in A3), and proportion of patients progressing from non-proliferative DR (NPDR [ETDRS-DRSS on 10-point scale < 7 at baseline]) to proliferative DR (PDR [ETDRS-DRSS on 10-point scale ≥ 7]).
Efficacy and safety assessments
Study assessments were performed at screening (Visit 1), at baseline (Visit 2), and at monthly visits (every 30 days from baseline) until Month 12.
Efficacy assessments
Best-corrected visual acuity
BCVA was assessed in both eyes at screening, baseline, Months 6 and 12, and in the study eye at all other visits. The measurements were performed in a sitting position using ETDRS-like VA testing charts at a testing distance of four meters.
Optical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography was performed in both eyes at screening, Months 6 and 12, and in the study eye at all other visits to monitor disease activity, specifically CSFT. Images were also analyzed by a central reading center (CRC) which was masked to treatment.
Fluorescein angiography and color fundus photography
FA was performed in conjunction with color fundus photography in both eyes at the screening, Month 6, and Month 12 visits to determine eligibility and monitor disease activity. In addition, the images were analyzed by a CRC to assess the presence and the type of DME, the area of leakage, and severity of DR by using the ETDRS severity scale for the study eye.
Treatment exposure and compliance
Patients were assigned to one of the two treatment arms by means of the IRT system.
Any deviations from the protocol or the administration of the active/sham ranibizumab injections as well as active/sham laser treatments were described on the dosage and administration record of the electronic Case Report Form.
Safety assessments
Safety was assessed by monitoring and recording all AEs and SAEs, conducting slit lamp and fundus examinations before dosing in both eyes at all visits and tonometry to assess intraocular pressure (IOP). IOP measurements (pre-injection and post-injection) were presented descriptively (absolute values and change from baseline) by monthly visit for the study eye, and in the subset of patients with IOP ≥ 30 mmHg.
Statistical analysis
A sample size of 380 patients was required (ranibizumab 304 and laser 76) to ensure that at least 300 patients received ranibizumab. Under this sample size, a statistical power of nearly 100% was expected with a significance level of 0.025.
For the primary analysis, the following one-sided hypothesis was tested at a one-sided alpha level of 0.025. The statistical hypothesis testing was based on a Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel (CMH) row mean score statistics using a stratified CMH test with original BCVA values as scores and with stratification according to DME type (focal, diffuse, honeycomb, and petaloid) and baseline BCVA score (≤ 60 letters versus > 60 letters). A three-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) model with treatment, baseline BCVA category, and DME type as factors were applied to generate least square (LS) means and two-sided 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
The primary analysis was performed on the full analysis set (FAS) with missing values imputed by the mean value last observation carried forward (MV-LOCF) method. The FAS comprised all patients in the randomized set (which consisted of all randomized patients) to whom the study treatment had been assigned. Following the intent-to-treat principle, patients were analyzed according to the treatment to which they were assigned at randomization.
Missing values of other efficacy variables were imputed by standard LOCF method. For proportion of patients with a ≥ two-step in ETDRS-DRSS, an additional analysis was also performed on subgroup of patients with moderately severe NPDR or worse (ETDRS-DRSS on 10-point scale ≥ 5) at baseline.
Patient disposition was summarized by treatment by using the randomized set. Descriptive statistics were provided for patient demographics, baseline diabetes, and ocular characteristics for all randomized patients by treatment arm.
Descriptive statistics were provided for exposure to the study treatment by using the safety set. The safety set consisted of all patients who received at least one application of study treatment and had at least one post-baseline safety assessment. Patients were analyzed according to treatment received. The statement that a patient had no AEs also constituted a safety assessment. The numbers of ranibizumab, laser, and sham treatments in the study eye were presented by treatment arm in frequency tables by visit and cumulatively over 12 months. Patients who received both active ranibizumab and active laser were analyzed under the ranibizumab arm in the safety analysis.
Results
Patient disposition, baseline demographics, disease, and ocular characteristics
A total of 384 patients were randomized; 307 to the ranibizumab 0.5 mg arm and 77 to the laser arm. The majority (n = 342; 89.1%) of patients completed the 12-month study period (90.9% in the ranibizumab arm; 81.8% in the laser arm; Fig. 2). The two most frequent reasons for premature study discontinuation in the ranibizumab and laser arms were patients’/guardians’ decision to withdraw consent (2.6% and 10.4%, respectively) and AEs (2.0% and 5.2%, respectively; Fig. 2). Overall, 10.2% of patients (n = 39) had at least one protocol deviation (ranibizumab 10.4% and laser 9.1%). The most common protocol deviations with an impact on analysis were related to the eligibility criteria (3.6%) such as a change in diabetes medication within 3 months prior to enrollment (1.6%).
Patient baseline demographic, disease, and ocular characteristics were comparable between the treatment arms (Table 1). All patients were Chinese with a mean (± standard deviation [SD]) age of 58.7 (8.79) years; 53.6% were female. The majority of patients (99.0%) had type II diabetes and mean (SD) HbA1c of 7.41 (1.14)%. Focal DME was the most frequent type of DME present at baseline (34.9%). The baseline mean (SD) VA was 59.3 (10.32) letters, and 96.9% of patients had an IOP of ≤ 21 mmHg; mean CSFT (SD) was similar in both treatment arms (ranibizumab 473.4 [166.13] μm; laser 475.0 [161.52] μm), and more patients had visible cysts in the ranibizumab arm (99%) (Table 1).
At baseline, a total of 290 (75.5%) patients had moderate non-proliferative DR or better (NPDR, DRSS < 4), while 94 (24.5%) patients had moderately/severe NPDR or worse (DRSS scores > 5) based on CRC assessment. DR severity was balanced between treatment groups.
Prior to the study, 58.3% of patients in the ranibizumab arm and 67.5% in the laser arm received laser treatment in the study eye, mostly for DR (62.3% of all patients with prior laser therapy) and DME (36.8%).
Efficacy and anatomical outcomes
Best-corrected visual acuity
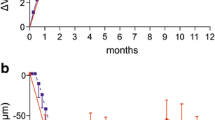
The mean (SD) average change in BCVA from Month 1 to Month 12 compared with baseline was 6.8 (6.58) letters in the ranibizumab arm and 1.1 (7.73) letters in the laser arm. The difference in LS means between the two treatment arms was 5.8 letters (95% CI 4.1, 7.5) and statistically significant (p < 0.001).
The mean change in BCVA from baseline at Month 12 was 7.8 (8.72) letters in the ranibizumab arm and 2.5 (8.78) letters in the laser arm (Fig. 3). The difference in LS means between the two arms was 5.4 letters (95% CI 3.2, 7.6).
Mean change in BCVA from baseline to Month 12 (full analysis set; LOCF). The full analysis set included all patients to whom treatment regimen was assigned. BCVA best-corrected visual acuity, ETDRS Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study, LOCF last observation carried forward, SE standard error, PRN pro re nata
A larger proportion of patients in the ranibizumab arm gained ≥ 10 and ≥ 15 BCVA letters at Month 12 compared to the laser arm (A4). Similarly, the proportion of patients with a loss of < 10 and < 15 letters was numerically higher in the ranibizumab arm compared with the laser arm (A4). The proportion of patients with a BCVA of ≥ 73 letters at Month 12 was numerically greater in the ranibizumab arm compared to the laser arm (36% versus 21.3%; A4).
A total of 35.8% of patients in the ranibizumab arm and 22.4% of patients in the laser arm reported an improvement by one or more steps in the ETDRS-DRSS 10-point scale from baseline to Month 12. At Month 12, 13.0% and 10.4% of patients had an improvement of a ≥ two-step change in the ETDRS-DRSS 10-point scale from baseline in the ranibizumab and laser arms, respectively. Out of the 69 patients in the ranibizumab arm with moderately severe NPDR or worse (DRSS ≥ 5) at baseline as determined by the CRC, 37 (53.6%) experienced a ≥ two-step improvement in the ETDRS-DRSS 10-point scale from baseline, compared to 7 (36.8%) of patients in the laser arm.
The proportion of patients who progressed from NPDR to PDR from baseline was 2.4% and 3.0% in the ranibizumab and laser arms, respectively.
Anatomical outcomes
A rapid and clinically relevant decrease in CSFT was observed from baseline during the first 3 months and was maintained up to Month 12 in the ranibizumab arm. At Month 12, the mean (SD) change in CSFT was higher in the ranibizumab arm than in the laser arm (− 146.5 [157.61] μm versus − 85.9 [166.60] μm). The difference in LS mean change between the two arms (ranibizumab 0.5-mg minus laser) was 72.5 μm (95% CI − 111.6, − 33.5 μm) and statistically significant (p < 0.001) (Fig. 4).
Treatment exposure
The mean (SD) number of active study treatments received in the study eye was 7.9 (2.82) in the ranibizumab arm and 2.1(1.08) in the laser arm (Table 2).
The mean (SD) number of ranibizumab re-treatments, i.e., treatments administered from Month 3 to Month 12 after the first treatment interruption due to VA stabilization, was 1.6 (0.64) as shown in Table 3 with 32.6% of patients not requiring any further injections. The mean (SD) treatment-free interval for the ranibizumab arm was 3.0 (2.50) months, with a mean (SD) maximum treatment-free interval of 3.2 (2.52) months (Table 3). The proportion of patients in the ranibizumab arm with a maximum treatment-free interval of ≥ 3 months was 39.0%.
Safety outcomes
Overall, 25.4% and 57.3% of patients reported ocular AEs and non-ocular AEs in the study eye, respectively.
Ocular AEs
In total, 27.4% of patients in the ranibizumab arm and 17.3% of patients in the laser arm reported ocular AEs of the study eye. The most frequently reported ocular AEs was IOP increased (ranibizumab 5.2%), followed by vitreous hemorrhage (ranibizumab 1.6%; laser 5.3%), conjunctival hemorrhage (ranibizumab 3.6%; laser 1.3%), and dry eye (ranibizumab 3.6%; laser 1.3%) as shown in Table 4. No cases of endophthalmitis were reported.
The most commonly reported ocular AEs in the study eye that were suspected to be related to the study drug and/or injection procedure in the ranibizumab arm were conjunctival hemorrhage (3.6%) and IOP increased (3.3%) (A5).
Non-ocular AEs
Similarly, 57.0% of patients in the ranibizumab arm and 58.7% of patients in the laser arm experienced non-ocular AEs. The most frequently reported non-ocular AEs were hypertension (ranibizumab 6.2%; laser 13.3%) and nasopharyngitis (ranibizumab 6.5%; laser 9.3%) followed by upper respiratory tract infection (ranibizumab 8.5%; laser 2.7%) and cough (ranibizumab 5.9%; laser 2.7%; Table 4). None of the non-ocular AEs were suspected to be related to the study drug.
Overall, a similar proportion of patients experienced SAEs in both treatment arms (ranibizumab 18.9% and laser 21.3%).
Ocular SAEs
Cataract was reported in 0.3% of patients in the ranibizumab arm and vitreous hemorrhage in 1.3% of patients in the laser arm (Table 5).
Non-ocular SAEs
The non-ocular SAEs were reported in 16.3% of patients in the ranibizumab arm and 14.7% of patients in the laser arm. Two deaths were reported in the ranibizumab arm (one with sudden death and one due to pneumonia) which were considered not related to the study treatment and/or injection procedure (Table 5).
Discussion
REFINE is the first study conducted in the mainland Chinese population to assess the efficacy and safety data on ranibizumab 0.5 mg compared with laser photocoagulation, the current standard of care, in patients with visual impairment due to DME. In this study, ranibizumab 0.5 mg dosed PRN (driven by VA stability) demonstrated superior efficacy over laser photocoagulation in improving BCVA from baseline to Month 1 to Month 12 compared with baseline. The difference in LS means between both treatment arms was statistically significant (p < 0.001) and clinically meaningful. This improvement in BCVA was rapid during the first 3 months and was maintained throughout Month 12 in patients treated with ranibizumab 0.5 mg, while there was no meaningful improvement in BCVA in patients treated with laser. Anatomical outcomes further supported these functional improvements where the reduction in CSFT was higher in patients treated with ranibizumab than those treated with laser. More patients gained ≥ 10 and ≥ 15 letters in the ranibizumab arm than in the laser arm. With regard to the DR severity as assessed by the CRC, results demonstrated that more patients improved in the ranibizumab arm compared with the laser arm. This effect was more prominent in the group of patients with moderately severe NPDR or worse at baseline, where more than half of patients in the ranibizumab arm improved by 2 or more steps on the ETDRS-DRSS 10-point scale.
The findings of REFINE are consistent with the previous pivotal studies such as RESOLVE16 and RESTORE17. The mean change in BCVA letter score from baseline at Month 12 among REFINE, RESOLVE15, and RESTORE16 studies was similar in the ranibizumab arm (7.8, 10.3, 6.8 letters, respectively) and the laser arm (2.5, − 1.4, 0.9 letters, respectively). A comparable proportion of patients gained ≥ 10 letters as well as ≥ 15 letters in the ranibizumab arm from baseline at Month 12 in REFINE, RESOLVE16, and RESTORE17 (gain of ≥ 10 letters 40.6%, 60.8%, 37.4%, respectively; and gain of ≥ 15 letters 18.5%, 32.4%, 22.6%, respectively). At Month 12, the mean number of ranibizumab injections was also similar among the REFINE, RESOLVE16, and RESTORE17 studies (7.9, 10.2, and 7.0, respectively).
Ranibizumab 0.5 mg was well-tolerated in the Chinese patients with visual impairment due to DME. Overall, the ocular and non-ocular AEs reported in the study eye were comparable between treatment arms, and no new AEs related to ranibizumab safety concerns were identified. The safety signals were consistent with the well-established safety profile of ranibizumab in previous DME studies [15, 16, 21].
Due to the nature of this study, there was no ethnical diversity and the study population was limited to mainland China. The REFINE study is the first to represent a large Chinese patient population with visual impairment due to DME. This study was adequately powered and therefore yielded highly significant results. The study was well-controlled and the central reading center ensured consistent interpretation of the anatomical outcomes.
In conclusion, given the clinical benefit achieved in the ranibizumab arm and the well-established safety profile of ranibizumab, the REFINE study results support the use of ranibizumab 0.5 mg PRN in Chinese patients with visual impairment due to DME.
References
Cheung N, Mitchell P, Wong TY (2010) Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet 376:124–136
Mohamed Q, Gillies MC, Wong TY (2007) JAMA 298:902–916
Prokofyeva E, Zrenner E (2012) Epidemiology of major eye diseases leading to blindness in Europe: a literature review. Ophthalmic Res 47:171–188
Williams R, Airey M, Baxter H et al (2004) Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy and macular oedema: a systematic review. Eye (Lond) 18:963–983
Chan JC, Zhang Y, Ning G (2014) Diabetes in China: a societal solution for a personal challenge. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2:969–979
Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M et al (2017) Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013. JAMA 317:2515–2523
Pang C, Jia L, Jiang S et al (2012) Determination of diabetic retinopathy prevalence and associated risk factors in Chinese diabetic and pre-diabetic subjects: Shanghai diabetic complications study. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 28:276–283
Wang FH, Liang YB, Peng XY et al (2011) Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in a rural Chinese population with type 2 diabetes: the Handan eye study. Acta Ophthalmol 89:e336–e343
Xu J, Wei WB, Yuan MX et al (2012) Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic retinopathy: the Beijing communities diabetes study 6. Retina 32:322–329
Cui J, Ren JP, Chen DN et al (2017) Prevalence and associated factors of diabetic retinopathy in Beijing, China: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 7:e015473
Xie XW, Xu L, Jonas JB et al (2009) Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy among subjects with known diabetes in China: the Beijing eye study. Eur J Ophthalmol 19:91–99
Wang N, Xu X, Zou H et al (2008) The status of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema in patients with type 2 diabetes: a survey from Beixinjing district of Shanghai city in China. Ophthalmologica 222:32–36
Network DRCR (2008) A randomized trial comparing intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide and focal/grid photocoagulation for diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology 115:1447–1449
Endo M, Yanagisawa K, Tsuchida K et al (2001) Increased levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and advanced glycation end products in aqueous humor of patients with diabetic retinopathy. Horm Metab Res 33:317–322
Funatsu H, Yamashita H, Noma H et al (2005) Aqueous humor levels of cytokines are related to vitreous levels and progression of diabetic retinopathy in diabetic patients. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 243:3–8
Massin P, Bandello F, Garweg JG et al (2010) Safety and efficacy of ranibizumab in diabetic macular edema (RESOLVE study): a 12-month, randomized, controlled, double-masked, multicenter phase II study. Diabetes Care 33:2399–2405
Mitchell P, Bandello F, Schmidt-Erfurth U et al (2011) The RESTORE study: ranibizumab monotherapy or combined with laser versus laser monotherapy for diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology 118:615–625
Zhao J, Li X, Tang S et al (2014) EXTEND II: an open-label phase III multicentre study to evaluate efficacy and safety of ranibizumab in Chinese patients with subfoveal choroidal neovascularization secondary to age-related macular degeneration. BioDrugs 28:527–536
Rodriguez BL, Abbott RD, Fujimoto W et al (2002) The American Diabetes Association and World Health Organization classifications for diabetes. Diabetes Care 25:951–955
Lucentis EU label (2011) Available from http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Assessment_Report_-_Variation/human/000715/WC500101009.pdf
Ishibashi T, Li X, Koh A et al (2015) The REVEAL study ranibizumab monotherapy or combined with laser versus laser monotherapy in Asian patients with diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology 122:1402–1415
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Rhutika Desai and Najeeb Ashraf (Scientific Services Practice-Product Lifecycle Services, Novartis Global Service Center, Hyderabad, India) for their medical writing and editorial assistance towards the development of this manuscript.
We also thank other study investigators: Dr. Feng Zhang, Prof. Fangtian Dong, Prof. Zhizhong Ma, Dr. Liu Zhang, Prof. Yanling Wang, Prof. Dachuan Liu, Prof. Lin Lu, Dr. WeiQi Chen, Prof. Junjun Zhang, Prof. Jian Ye, Prof. Zhao Peiquan, Prof. Xiaodong Sun, Dr. Zhifeng Wu, Dr. Ye Shen, Prof. Dr. Miaoquin Wu, Prof. Dr. Yanping Song, Prof. Ming Chang Zhang, Prof. Xioling Lu, Dr. Yusheng Wang, Prof. Tang Luosheng, Prof. Dr. Haifeng Xu, Prof. Dr. Dawei Sun, and Prof. Jinglin Yi.
REFINE Study Group.
Center No. 1101:
Dr. Xiaoxin Li (PI), Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing, Beijing 100044, China.
-
Chunan Li (Other), Dr. Huijun Qi (Sub Inv), Dr. Ye Tao (Other), Yan Li (Other), Yujing Bai (Sub Inv), Dr. Hong Yin (Sub Inv), Guodong Liu (Other), Li Han (Other), Tong Qian (Sub Inv), Lvzhen Huang (Sub Inv), Dr. Heng Miao (Sub Inv), Dr. Mingwei Zhao (Sub Inv), Dr. Jing Hou (Sub Inv), Dr. Yong Cheng (Sub Inv), Jianhong Liang (Sub Inv), Xuan Shi (Sub Inv), Jinfeng Qu (Sub Inv), Wenzhen Yu (Sub Inv), Yong Tao (Sub Inv), Yi Chen (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1102:
Prof. Feng Zhang (PI), Beijing Tongren Hosptial, Beijing, Beijing 100176, China.
-
Dr. Xuehui Shi (Sub Inv), Dr. Liqin Gao (Sub Inv), Dr. Ning Ding (Sub Inv), Dr. Lihong Yang (Sub Inv), Dr. Shiqiang Zhao (Sub Inv), Dr. Qiong Yang (Sub Inv), Ms. Rong Shen (Other), Ying Xiong (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1103:
Prof. Fangtian Dong (PI), Peking Union Medical College, Hospital Beijing, Beijing 100730, China.
-
Xiao Zhang (Sub Inv), Di Gong (Sub Inv), Dr. Yi Qu (Other), Dr. Fangfang Dai (Other), Dr. Feng He (Sub Inv), Dr. Xiaoxu Han (Sub Inv), Dr. Rongping Dai (Sub Inv), Dr. Hong Du (Other), Dr. Weihong Yu (Sub Inv), Donghui Li (Other), Dr. Zhikun Yang (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1104:
Prof. Zhizhong Ma (PI), Peking University third hospital, Beijing, Beijing 100191, China.
-
Min Zhang (Other), Dr. Hongliang Dou (Sub Inv), Xiuhong Chen (Nurse), Ying Chu (Other), Jing Ren (Other), Fang Qian (Other), Dr. Fan Yang (Sub Inv), Dr. Lin Zhao (Sub Inv), Aihua Ding (Other), Dr. Tong Guo (Sub Inv), Xinrong Lu (Sub Inv), Dr. Yuling Liu (Sub Inv), Xin Wang (Other).
Center No. 1105:
Prof Liu Yang (PI), Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, Beijing 100034, China.
-
Dr. Jun Li (Sub Inv), Dr. Ruilin Zhu (Sub Inv), Dr. Jianchen Hao (Sub Inv), Dr. Lijun Qiao (Sub Inv), Dr. Chunying Guo (Sub Inv), Dr. Jing Zhang (Sub Inv), Dr. Hongping Nie (Sub Inv), Dr. Xiaopeng Gu (Sub Inv), Dr. Lixiao Du (Sub Inv), Dr. Yadi Zhang (Sub Inv), Dr. Wenbo Zhang (Sub Inv), Dr. Shijie Zhang (Sub Inv), Dr. Jianchen Hao (Sub Inv), Dr. Liang Zhao (Sub Inv), Jingmei Shi (Nurse), Dr. Hailong Wu (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1106:
Prof. Hong Dai (PI), Beijing Hospital, Beijing, Beijing 100730, China.
-
Dr. Jianfeng Huang (Sub Inv), Dr. Jing Zhao (Sub Inv), Dr. Lei Hu (Sub Inv), Dr. Xiaobing Yu (Sub Inv), Dr. Yingyi Lu (Sub Inv), Dr. Nuan Peng (Other), Dr. Xiaoya Gu (Sub Inv), Dr. Li Long (Other), Dr. Zian Shi (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1107:
Dr. Yanling Wang (PI), Friendship Hospital, Beijing, Beijing 100050, China.
-
Dr. Lu Zhao (Sub Inv), Dr. Xiaolei Zhang (Sub Inv), Dr. Yanli Hou (Sub Inv), Dr. Yinxiang Huang (Sub Inv), Ms. Mingming Li (Other), Ms. Fan Zhang (Other), Dr. Hui Hong (Sub Inv), Dr. Kang Wang (Sub Inv), Dr. Simeng Tang (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1108:
Prof. Dachuan Liu (PI), Xuan Wu Hospital Capital Medical, University Beijing, Beijing 100053, China.
-
Bian Junjie (Sub Inv), Zhang lei (Sub Inv), Weijia Dai (Sub Inv), Yang Huiqing (Other), Hao Ning (Other), Xizhe Wang (Sub Inv), Liyan Zhao (Other).
Center No. 1109:
Prof. Xiaorong Li (PI), Tianjin Medical University Eye Hospital, Tianjin, Tianjin 300020, China.
-
Ms. Shaorui Wang (Other), Dr. Linni Wang (Sub Inv), Dr. Jindong Han (Sub Inv), Ms. Lu Chen (Other), Ms. Jinghua Ma (Other), Ms. He Ma (Other), Dr. Zhiqing Li (Sub Inv), Ms. Tingting Wang (Other), Dr. Rongguo Yu (Sub Inv), Ms. Xiaojun Dong (Other), Ms. Ying Li (Sub Inv), Mr. Junlin Guo (Other), Ms. Yahan Hu (Other), Mr. Xueyong Sheng (Other), Shuang Li (Other).
Center No. 1110:
Prof. Mei Han (PI), Tianjin Eye Hospital, Tianjin, Tianjin 300070, China.
-
Dr. Chunxia Cong (Sub Inv), Dr. Li Li (Sub Inv), Dr. Ying Han (Sub Inv), Prof. Yanshan Xu (Sub Inv), Nannan MA (Other), Dr. Shiyong Xie (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1111:
Prof. Lin Lu (PI), Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University Guangzhou, Guangdong 510060, China.
-
Ms. Andina Hu (Other), Dr. Ping Lian (Sub Inv), Dr. Wei Ma (Sub Inv), Mr. Guangxing Su (Other), Ms. Miner Yuan (Sub Inv), Ms. Wangying Lai (Nurse), Ms. Xiaofang Li (Other), Guangxian Chen (Other), Xiling Yu (Sub Inv), Ms. Guiying Mai (Other), Junying Zhong (Other), Ms. Xing Chen (Nurse), Dr. Bingqian Liu (Sub Inv), Ms. Yuhong Liu (Other), Xiujuan Zhao (Sub Inv), Ms. Qinmei Mo (Nurse), Ms. Jiangmei Cheng (Nurse), Dr. Hui Yang (Sub Inv), Ms. Qiufen Yang (Other), Dr. Xiaojing Zhong (Sub Inv), Dr. Chenjin Jin (Sub Inv), Mr. Feng Wen (Other), Caiqing He (Other), Ms. Qiuhua Xie (Other), Ms. Ping Huang (Nurse), Xiaoxi Mai (Other).
Center No. 1112:
Dr. Jingxiang Zhong (PI), First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University Guangzhou Guangdong 510632, China.
-
Ms. Xiaoming Zhang (Other), Dr. Xiaoyong Liu (Sub Inv), Dr. Ting Zhang (Sub Inv), Ms. Liqiong Zhang (Other), Dr. Guifang Wang (Sub Inv), Ms. Xiaojuan He (Other), Dr. Jing Meng (Sub Inv), Dr. Rijia Zhang (Sub Inv), Ms. Yuan Tian (Other).
Center No. 1113:
Prof. Weiqi Chen (PI), Shantou international eye center of Shantou University, Shantou, Guangdong 515041, China.
-
Shirong Chen (Other), Dr. Bingrong Huang (Other), Dr. Guihua Zhang (Sub Inv), Dr. Anlin Zhang (Other), Dr. Xinyu Liu (Other), Kangkeng Zheng (Sub Inv), Lingling Zhou (Other), Dr. Haoyu Chen (Sub Inv), Dr. Kun Peng (Sub Inv), Dr. Zhaotao Zhou (Other), Dr. Dusheng Lin (Sub Inv), Huichun Huang (Sub Inv), Dr. Xiaoang Lin (Other).
Center No. 1114:
Prof. Junjun Zhang (PI), West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu Sichuan 610041, China.
-
Prof. Meixia Zhang (Sub Inv), Helian Zhu (Nurse), Xi Huang (Sub Inv), Dr. Mei Xin (Sub Inv), Mr. Zhibing Zeng (Other), Mr. Dan Meng (Other), Ms. Ye Wu (Other), Dr. Qianying Wu (Sub Inv), Dr. Lin Ma (Sub Inv), Zhifeng Lai (Other), Dr. Sheng Gao (Sub Inv), Xiaoyue Wang (Other), Juqin Ren (Other), Guoxian Qiu (Nurse).
Center No. 1116:
Prof. Jian Ye (PI), 3rd Hospital, Third Military Medical Univ.(Daping Hos.), Chongqing, Chongqing 400042, China.
-
Dr. Hongxia Liao (Sub Inv), Ying Tang (Other), Ms. Lusha Tao (Other), Dr. Shaozhang Liu (Sub Inv), Ms. Li Yue (Other), Ms. Sijia Feng (Other), Ms. Jie Xu (Other), Ms. Yan Dong (Other), Nian Tan (Sub Inv), Dr. Yanli Chen (Sub Inv), Dr. Shaoqiong Chen (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1117:
Prof Peiquan Zhao (PI), Shanghai XinHua Hospital Shanghai, Shanghai 200092, China.
-
Zhaoyang Wang (Sub Inv), Yang Dong (Other), Xiaofei Man (Other), Xunda Ji (Sub Inv), Dr. Tian Tian (Other), Dr. Huazhang Feng (Other), Dr. Xin Li (Other), Qiujing Huang (Other), Dr. Shiyuan Wang (Other), Kebo Cai (Sub Inv), Dr. Qi Zhang (Sub Inv), Yian Li (Other), Dr. Haiying Jin (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1118:
Prof. Xiaodong Sun (PI), Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai, Shanghai 200080, China.
-
Kairong Zheng (Nurse), Jingyang Feng (Sub Inv), Liang Ye (Other), Alice Shih (Sub Inv), Xiaoxiao Liu (Other), Zhengyuan Cai (Other), Ying Wu (Other), Ying Fan (Sub Inv), Ping He (Other), Liping Xie (Nurse), Jian Sun (Other), Zhongju Duan (Nurse), Tingting Zhao (Sub Inv), Dr. Weijun Wang (Sub Inv), Lu Cheng (Other), Pang Yao (Other).
Center No. 1121:
Zhifeng Wu (PI), Wuxi No. 2 People’s Hospital, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China.
-
Dr. Huiyan Xu (Sub Inv), Jie Zhang (Sub Inv), Dr. Dongyuan Zhu (Other), Dr. Xiaomei Meng (Other), Dr. Yuting Fu (Other), Dr. Tiantian Chen (Other), Dr. Shui Lu (Other), Wenjun Zou (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1122:
Ye Shen (PI), The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310003, China.
-
Jianping Tong (Sub Inv), Chengying Yu (Sub Inv), Hong Lu (Sub Inv), Qin Wu (Other), Wenting Fan (Other), Baishuang Huang (Other), Xiaoen Wang (Other), Nan Hong (Other).
Center No. 1123:
Miaoqin Wu (PI), Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China.
-
Xiaoxia Li (Sub Inv), Qingqing Zheng (Sub Inv), Yurong Chen (Other), Hong Xu (Other), Hui Liu (Sub Inv), Zhe Liu (Sub Inv), Ting Shen (Sub Inv), Hong Guo (Other), Luyi Zhang (Sub Inv), Xinchang Chi (Sub Inv), Hailan Zhao (Other), Jie Yu (Other), Lan Zhang (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1124:
Prof. Yanping Song (PI), Wuhan General Hospital of Guangzhou Military, Wuhan, Hubei 430070, China.
-
Dr. Qin Ding (Sub Inv), Ms. Jinlan Qiu (Other), Yan Liu (Nurse), Yangting Dong (Nurse), Dr. Feng Chang (Sub Inv), Dr. Zhongshan Chen (Sub Inv), Ms. Yunhui Chen (Nurse), Dr. Ming Yan (Sub Inv), Dr. Zhen Huang (Sub Inv), Zhijian Huang (Sub Inv), Ms. Lina Ma (Nurse), Qian Du (Nurse).
Center No. 1125:
Mingchang Zhang (PI), Wuhan Union Hospital, Wuhan, Hubei 430022, China.
-
Dr. Pengcheng Li (Sub Inv), Wenhui Yan (Nurse), Dr. Hai Zheng (Other), Dr. Kangkang Xu (Sub Inv), Dr. Jing Fang (Other), Dr. Jingjing Wei (Nurse), Junjie Yang (Sub Inv), Dr. Shuangyan Sheng (Sub Inv), Qiong Ao (Nurse).
Center No. 1126:
Prof. Xiaoling Liu (PI), The affiliated eye hospital to Wenzhou Medical University Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325027, China.
-
Lina Ge (Sub Inv), Tingye Zhou (Other), Qianqian Zhu (Other), Dr. Bing Lin (Sub Inv), Yingdong Luo (Other), Ying Huang (Sub Inv), Leilei Zeng (Other), Dr. Weiwei Zheng (Other), Miaojun Yan (Other), Dr. Zuhua Sun (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1127:
Prof. Yusheng Wang (PI), The First Affiliated Hospital of The Fourth Military Medical Xi’an, Shanxi 710032, China.
-
Peng Zhang (Sub Inv), Dr. Haiyan Wang (Sub Inv), Jinting Zhu (Sub Inv), Xiaoni Yu (Sub Inv), Dr. Manhong Li (Sub Inv), Qihua Wang (Sub Inv), Juan Li (Sub Inv), Wenle Bai (Sub Inv), Huiyuan Hou (Sub Inv), Zifeng Zhang (Sub Inv), Jin He (Other), Dongjie Sun (Sub Inv), Xiaojin Song (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1128:
Luosheng Tang (PI), The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410011, China.
-
Fei Zhao (Other), Kun Zhang (Other), Pingbo Ouyang (Sub Inv), Jun Zeng (Sub Inv), Jia Liu (Sub Inv), Wei Wei (Sub Inv), Jiao Tian (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1129:
Prof. Haifeng Xu (PI), Qingdao Eye Hospital, Qingdao, Shandong, China.
-
Dr. Jun Li (Sub Inv), Jing Xu (Nurse), Min Wang (Sub Inv), Dr. Depeng Shi (Sub Inv), Peipei Wu (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1130:
Prof. Dawei Sun (PI), The 2nd Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang 150086, China.
-
Ms. Liping Shi (Sub Inv), Dr. Bo Jiang (Sub Inv), Dr. Fang Cheng (Sub Inv), Dr. Danhua Jia (Sub Inv), Dr. Zhongyu Zhang (Sub Inv), Dr. Xuemei Zhou (Sub Inv), Dr. Wulian Song (Sub Inv), Dr. Ling Shen (Sub Inv),Dr. Pan Fan (Sub Inv).
Center No. 1131:
Jinglin Yi (PI), Affiliated Eye Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330019, China.
-
Haijun Yang (Sub Inv), Yanping Zuo (Other), Jiao Zeng (Other), Yan Liu (Other), Hongyan Du (Sub Inv), Li Yu (Other), Xian Liu (Other), Shenghui Wan (Other), Si Zhu (Other), Qiulin Li (Other), Wenjia Dong (Sub Inv).
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Xiaoxin Li: Has no financial disclosures.
Hong Dai: Has no financial disclosures.
Xiaorong Li: Has no financial disclosure.
Mei Han: Has no financial disclosures.
Jun Li, Andrea Suhner: Employees of Novartis Pharma AG, Basel Switzerland.
Renxin Lin: Employee of Novartis Pharma Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China.
Sebastian Wolf: Consultant for Alcon, Allergan, Bayer Healthcare, Heidelberg Engineering, Novartis, Optos, Roche, and Zeiss.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were conducted according to the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and the study protocol was reviewed by the Ethics Committee for each center.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
Supplemental Digital Content 1: Listing all the inclusion and exclusion criteria in detail. AMD, age-related macular degeneration; BCVA, best-corrected visual acuity; DME, diabetic macular edema; DR, diabetic retinopathy; ETDRS, Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study; VA, visual acuity; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor (DOCX 18.8 kb)
ESM 2
Supplemental Digital Content 2: Masking details. VA, visual acuity (DOCX 14.9 kb)
ESM 3
Supplemental Digital Content 3: Definitions of ETDRS-DRSS: a 10-point scale and ≥ 2 step change and ≥ 3 step change in ETDRS-DRSS on the 10-point scale. a. ETDRS-DRSS: a 10-point scale. b. A ≥ 2 step change and ≥ 3 step change in ETDRS-DRSS on the 10-point scale ETDRS-DRSS (10-point scale) change in steps from baseline to Month 12, was defined as: Change in steps from baseline to Month 12 = ETDRS-DRSS (10-point scale) at Month 12 – ETDRS-DRSS (10-point scale) at baseline. ETDRS, Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (DOCX 14 kb)
ESM 4
Supplemental Digital Content 4: Proportion of patients with categorical BCVA change from baseline to the end of study (full analysis set; LOCF). The full analysis set included all patients to whom treatment regimen was assigned. BCVA, best-corrected visual acuity; ETDRS, Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study; LOCF, last observation carried forward; PRN, pro re nata (PNG 168 kb)
ESM 5
Supplemental Digital Content 5: Ocular (study eye) and non-ocular adverse events suspected to be related to study drug and/or ocular injection or leading to permanent study drug discontinuation, by preferred term (safety set). The safety set included all patients who received at least one application of study treatment and has at least one post-baseline safety assessment. A patient with multiple occurrences of an AE under one treatment is counted only once in the AE category. AEs with start date on or after the date of first administration of study treatment in the study eye are counted. Preferred terms are sorted by descending order of incidence in the ranibizumab 0.5 mg arm. Percentages are based on the number of patients in the safety set in the specific treatment arm. Coded with MedDRA version 19.1. AE, adverse event; MedDRA, medical dictionary for regulatory activities; PRN, pro re nata (DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Dai, H., Li, X. et al. Efficacy and safety of ranibizumab 0.5 mg in Chinese patients with visual impairment due to diabetic macular edema: results from the 12-month REFINE study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 257, 529–541 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-018-04213-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-018-04213-x