Abstract
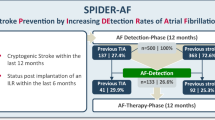
Atrial fibrillation (AF) leads to a high risk of recurrent stroke, and the insertable cardiac monitor (ICM), as a new kind of electrocardiographic monitoring device, has been proven to enhance the recognition rate of AF. The aim of this systematic review was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the ICM use in AF detection of patients with stroke. We pooled 1233 patients from three randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The detection rate of AF was superior in the ICM group to that in the control group at 6 months (risk ratio [RR], 4.63; P < 0.0001; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.17–9.90) and 12 months (RR, 5.04; P < 0.00001; 95% CI, 2.93 to 8.68). Patients in the ICM group had a higher rate of oral anticoagulant usage (RR, 2.76; P < 0.00001; 95% CI, 1.89–4.02). However, there was no difference in the time to first detection of AF within 12 months (mean difference, − 8.28; P = 0.82; 95% CI, − 77.84–61.28) or the rate of recurrent ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (RR, 0.88; P = 0.51; 95% CI, 0.60–1.28) between the ICM and control groups. In addition, the ICM group experienced more adverse events than the control group within 12 months (RR, 4.42; P = 0.002; 95% CI, 1.69–11.55). To conclude, the sensitivity of ICM is superior to that of conventional external cardiac monitoring. Reducing adverse reactions will be a new development direction of ICM.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Feigin VL et al (2021) Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Neurol 20(10):795–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(21)00252-0
Freedman B, Potpara TS, Lip GY (2016) Stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. Lancet 388(10046):806–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31257-0
Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Delling FN et al (2020) Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation 141(9):e139–e596. https://doi.org/10.1161/cir.0000000000000757
Kimura K, Minematsu K, Yamaguchi T (2005) Atrial fibrillation as a predictive factor for severe stroke and early death in 15,831 patients with acute ischaemic stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76(5):679–683. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2004.048827
(1993) Secondary prevention in non-rheumatic atrial fibrillation after transient ischaemic attack or minor stroke. EAFT (European Atrial Fibrillation Trial) Study Group. Lancet 342(8882):1255–1262
Camm AJ, Lip GY, De Caterina R, Savelieva I, Atar D, Hohnloser SH, Hindricks G (2012) 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Eur Heart J 33(21):2719–2747. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehs253
Cotter PE, Martin PJ, Ring L, Warburton EA, Belham M, Pugh PJ (2013) Incidence of atrial fibrillation detected by implantable loop recorders in unexplained stroke. Neurology 80(17):1546–1550. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31828f1828
Etgen T, Hochreiter M, Mundel M, Freudenberger T (2013) Insertable cardiac event recorder in detection of atrial fibrillation after cryptogenic stroke: an audit report. Stroke 44(7):2007–2009. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.001340
Douen AG, Pageau N, Medic S (2008) Serial electrocardiographic assessments significantly improve detection of atrial fibrillation 2.6-fold in patients with acute stroke. Stroke 39(2):480–482. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.492595
Jabaudon D, Sztajzel J, Sievert K, Landis T, Sztajzel R (2004) Usefulness of ambulatory 7-day ECG monitoring for the detection of atrial fibrillation and flutter after acute stroke and transient ischemic attack. Stroke 35(7):1647–1651. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000131269.69502.d9
Higgins P, MacFarlane PW, Dawson J, McInnes GT, Langhorne P, Lees KR (2013) Noninvasive cardiac event monitoring to detect atrial fibrillation after ischemic stroke: a randomized, controlled trial. Stroke 44(9):2525–2531. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.113.001927
Manina G, Agnelli G, Becattini C, Zingarini G, Paciaroni M (2014) 96 hours ECG monitoring for patients with ischemic cryptogenic stroke or transient ischaemic attack. Intern Emerg Med 9(1):65–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-012-0755-3
Burkowitz J, Merzenich C, Grassme K, Bruggenjurgen B (2016) Insertable cardiac monitors in the diagnosis of syncope and the detection of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol 23(12):1261–1272. https://doi.org/10.1177/2047487316632628
Kanters TA, Wolff C, Boyson D, Kouakam C, Dinh T, Hakkaart L, Rutten-Van Mölken MP (2016) Cost comparison of two implantable cardiac monitors in two different settings: Reveal XT in a catheterization laboratory vs. Reveal LINQ in a procedure room. Europace 18(6):919–924. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euv217
De Angelis MV, Di Stefano V, Franciotti R, Furia N, Di Girolamo E, Onofrj M, Faustino M (2020) Cryptogenic stroke and atrial fibrillation in a real-world population: the role of insertable cardiac monitors. Sci Rep 10(1):3230. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60180-6
Drak-Hernández Y, Toquero-Ramos J, Fernández JM, Pérez-Pereira E, Castro-Urda V, Fernández-Lozano I (2013) Effectiveness and safety of remote monitoring of patients with an implantable loop recorder. Rev Esp Cardiol (English ed) 66(12):943–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rec.2013.06.009
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ (Clin Res ed) 339:b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700
Sanna T, Diener HC, Passman RS, Di Lazzaro V, Bernstein RA, Morillo CA, Rymer MM, Thijs V, Rogers T, Beckers F et al (2014) Cryptogenic stroke and underlying atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 370(26):2478–2486. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1313600
Bernstein RA, Kamel H, Granger CB, Piccini JP, Sethi PP, Katz JM, Vives CA, Ziegler PD, Franco NC, Schwamm LH et al (2021) Effect of long-term continuous cardiac monitoring vs usual care on detection of atrial fibrillation in patients with stroke attributed to large- or small-vessel disease: the STROKE-AF randomized clinical trial. JAMA 325(21):2169–2177. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.6470
Buck BH, Hill MD, Quinn FR, Butcher KS, Menon BK, Gulamhusein S, Siddiqui M, Coutts SB, Jeerakathil T, Smith EE et al (2021) Effect of implantable vs prolonged external electrocardiographic monitoring on atrial fibrillation detection in patients with ischemic stroke: the per diem randomized clinical trial. JAMA 325(21):2160–2168. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.6128
Kulach A, Dewerenda M, Majewski M, Lasek-Bal A, Gasior Z (2021) Supraventricular Runs in 7-day holter monitoring are related to increased incidence of atrial fibrillation in a 3-year follow-up of cryptogenic stroke patients free from arrhythmia in a 24 h-holter. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8070081
Kishore A, Vail A, Majid A, Dawson J, Lees KR, Tyrrell PJ, Smith CJ (2014) Detection of atrial fibrillation after ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 45(2):520–526. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.113.003433
Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB (1991) Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke 22(8):983–988. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.22.8.983
Li L, Yiin GS, Geraghty OC, Schulz UG, Kuker W, Mehta Z, Rothwell PM (2015) Incidence, outcome, risk factors, and long-term prognosis of cryptogenic transient ischaemic attack and ischaemic stroke: a population-based study. Lancet Neurol 14(9):903–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(15)00132-5
Hart RG, Diener HC, Coutts SB, Easton JD, Granger CB, O’Donnell MJ, Sacco RL, Connolly SJ (2014) Embolic strokes of undetermined source: the case for a new clinical construct. Lancet Neurol 13(4):429–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(13)70310-7
Katz JM, Eng MS, Carrazco C, Patel AV, Jadonath R, Gribko M, Arora R, Libman RB (2018) Occult paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in non-cryptogenic ischemic stroke. J Neurol 265(10):2237–2242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-018-8982-9
Steffel J, Verhamme P, Potpara TS, Albaladejo P, Antz M, Desteghe L, Georg Haeusler K, Oldgren J, Reinecke H, Roldan-Schilling V et al (2018) The 2018 european heart rhythm association practical guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation: executive summary. Europace 20(8):1231–1242. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euy054
Healey JS, Connolly SJ, Gold MR, Israel CW, Van Gelder IC, Capucci A, Lau CP, Fain E, Yang S, Bailleul C et al (2012) Subclinical atrial fibrillation and the risk of stroke. N Engl J Med 366(2):120–129. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1105575
Seet RC, Friedman PA, Rabinstein AA (2011) Prolonged rhythm monitoring for the detection of occult paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in ischemic stroke of unknown cause. Circulation 124(4):477–486. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.111.029801
January CT, Wann LS, Calkins H, Chen LY, Cigarroa JE, Cleveland JC Jr, Ellinor PT, Ezekowitz MD, Field ME, Furie KL et al (2019) 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the american college of cardiology/american heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines and the heart rhythm society. J Am Coll Cardiol 74(1):104–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.011
Healey JS, Alings M, Ha A, Leong-Sit P, Birnie DH, de Graaf JJ, Freericks M, Verma A, Wang J, Leong D et al (2017) Subclinical atrial fibrillation in older patients. Circulation 136(14):1276–1283. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028845
Diederichsen SZ, Haugan KJ, Højberg S, Holst AG, Køber L, Pedersen KB, Graff C, Krieger D, Brandes A, Svendsen JH (2017) Complications after implantation of a new-generation insertable cardiac monitor: results from the LOOP study. Int J Cardiol 241:229–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.03.144
Funding
This work was supported by the Suzhou Health Talents Training Project (GSWS2019002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XT and ZLW was the principal investigator. XT and XW designed the study and developed the analysis plan. XW, XT and JZ analyzed the data and performed meta-analysis. TX and ZLW contributed in writing of the article. ZMS and YJQ revised the manuscript and polish the language. ZQC, ZW and GC supervised the project. All authors read and approved the final submitted paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
We confirm that we have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, X., Wang, Z., Wu, X. et al. The efficacy and safety of insertable cardiac monitor on atrial fibrillation detection in patients with ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol 269, 2338–2345 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10903-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10903-0