Abstract
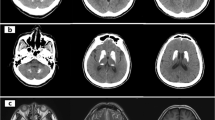
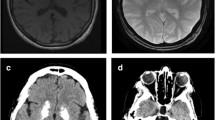
In this study we report clinical and imaging data from a multigenerational Serbian family with idiopathic basal ganglia calcification (IBGC) and exclusion of linkage to chromosome 14q, 2q37 and 8p21.1-q11.23. Fourteen out of 18 family members were personally examined and 11 of them were scanned with computed tomography (CT). CT scans revealed existence of symmetrical calcifications in six family members from three generations (four symptomatic and two asymptomatic). Age at onset of clinical symptoms varied between 22.0 and 55.4 years. The main clinical findings included parkinsonism, severe gait disturbances with freezing of gait, and dyskinesia. Hyperechogenicities identified by transcranial sonography corresponded well to the CT images of hyperintense calcifications in the same structures, whereas brain perfusion single photon emission computed tomography demonstrated predominant hypoperfusion in the frontal cortex and the basal ganglia. After exclusion of linkage to known loci, our pedigree with IBGC further demonstrates locus heterogeneity in this disorder. Analysis of clinically affected individuals supports observation that the clinical features of IBGC appear to be varied both within and between families. The age at onset of the clinical symptoms appeared to be decreasing in two observed transmissions, suggestive of possible genetic anticipation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellie E, Julien J, Ferrer X (1989) Familial idiopathic striopallidodentate calcifications. Neurology 39:381–385
Sobrido MJ, Geschwind DH (2002) Genetics of familial idiopathic basal ganglia calcification (FIBGC). In: Pulst S-M (ed) Genetics of movement disorders. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 443–448
Geschwind DH, Loginov M, Stern JM (1999) Identification of a locus on chromosome 14q for idiopathic basal ganglia calcification (Fahr disease). Am J Hum Genet 65:764–772
Volpato CB, De Grandi A, Buffone E, Facheris M, Gebert U, Schifferle G, Schonhuber R, Hicks A, Pramstaller PP (2009) 2q37 as a susceptibility locus for idiopathic basal ganglia calcification (IBGC) in a large South Tyrolean family. J Mol Neurosci 39:346–353
Dai X, Gao Y, Xu Z, Cui Z, Liu J, Li Y, Xu H, Liu M, Wang QK, Liu JY (2010) Identification of a novel genetic locus on chromosome 8p21.1–q11.23 for idiopathic basal ganglia calcification. Am J Med Genet Part B 153B:1305–1310
Cummings JL, Gosenfeld LF, Houlihan JP, McCaffrey T (1983) Neuropsychiatric disturbances associated with idiopathic calcification of the basal ganglia. Biol Psychiatry 18:591–601
Manyam BV, Walters AS, Narla KR (2001) Bilateral striatopallidodentate calcinosis: clinical characteristics of patients seen in registry. Mov Disord 16:258–264
Brodaty H, Mitchell P, Luscombe G, Kwok JJ, Badenhop RF, McKenzie R, Schofield PR (2002) Familial idiopathic basal ganglia calcification (Fahr’s disease) without neurological, cognitive and psychiatric symptoms is not linked to the IBGC1 locus on chromosome 14q. Hum Genet 110:8–14
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Hamilton M (1960) A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23:56–62
Mijajlović M, Dragašević N, Stefanova E, Petrović I, Svetel M, Kostić VS (2008) Transcranial sonography in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2. J Neurol 255:1164–1167
Svetel M, Ozelius LJ, Buckley A, Lohmann K, Brajkovic L, Klein C, Kostic VS (2009) Rapid-onset dystonia-parkinsonism: case report. J Neurol 257:472–474
Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM, Julier C, Ott J (1984) Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:3443–3446
Ottman R, Risch N, Hauser WA, Pedley TA, Lee JH, Barker-Cummings C, Lustenberger A, Nagle KJ, Lee KS, Scheuer ML, Neystat M, Susser M, Wilhelmsen KC (1995) Localization of a gene for partial epilepsy to chromosome 10q. Nat Genet 10:56–60
Bruggemann N, Schneider SA, Sander T, Klein C, Hagenah J (2010) Distinct basal ganglia hyperechogenicity in idiopathic basal ganglia calcification. Mov Disord 25:2661–2664
Konig P (1989) Psychopathological alterations in cases of symmetrical basal ganglia sclerosis. Biol Psychiatry 25:459–468
Lopez-Villegas D, Kulisevsky J, Deus J, Jungue C, Pujol J, Guardia E, Grau JM (1996) Neuropsychological alterations in patients with computed tomography-detected basal ganglia calcifications. Arch Neurol 53:251–256
Kobari M, Nogawa S, Sugimoto Y, Fukuuchi Y (1997) Familial idiopathic brain calcification with autosomal dominant inheritance. Neurology 48:645–649
Berg D, Godau J, Walter U (2008) Transcranial sonography in movement disorders. Lancet Neurol 7:1044–1055
Uygur GA, Liu Y, Hellman RS, Tikofsky RS, Collier BD (1995) Evaluation of regional cerebral blood flow in massive intracerebral calcifications. J Nucl Med 36:610–612
Saiki M, Saiki S, Sakai K, Matsunari I, Higashi K, Murata KY, Hattori N, Hirose G (2007) Neurological deficits are associated with increased brain calcinosis, hypoperfusion, and hypometabolism in idiopathic basal ganglia calcification. Mov Disord 22:1027–1030
Paschali A, Lakiotis V, Messinis L, Markaki E, Constantoyannis C, Ellul J, Vassilakos P (2009) Dopamine transporter SPECT/CT and perfusion brain SPECT imaging in idiopathic basal ganglia calcinosis. Clin Nucl Med 34:421–423
Benke T, Karner E, Seppo K, Delazer M, Marksteiner J, Donnemiller E (2004) Subacute dementia and imaging correlates in a case of Fahr’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:1163–1165
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by governmental, i.e. by a grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology (MST), Republic of Serbia (projects no. 175090). CK funded by the Volkswagen Foundation and the Hermann and Lilly Schilling Foundation. VSK had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Herein the authors claim that this study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Medical School University of Belgrade and have been thereafter performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down by the Declaration of Helsinki.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostić, V.S., Lukić-Ječmenica, M., Novaković, I. et al. Exclusion of linkage to chromosomes 14q, 2q37 and 8p21.1-q11.23 in a Serbian family with idiopathic basal ganglia calcification. J Neurol 258, 1637–1642 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-5985-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-5985-1