Abstract
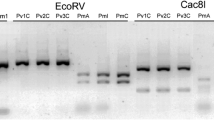
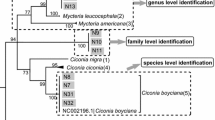
Species identification was carried out by nucleotide sequence analysis of the cytochrome b (cytb) gene. The aim of the study was to identify biological specimens from diverse vertebrate animals by extracting and amplifying DNA from 44 different animal species covering the 5 major vertebrate groups (i.e. mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fishes). The sequences derived were used to identify the biological origin of the samples by aligning to cytb gene sequence entries in nucleotide databases using the program BLAST. All sequences were submitted to the GenBank including new species which were not observed in the databases. The applicability of this method to the forensic field is demonstrated by simulated casework conditions where different types of samples including problematic specimens such as hair, bone samples, bristles and feathers were investigated to identify the species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 February 1999 / Accepted: 17 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parson, W., Pegoraro, K., Niederstätter, H. et al. Species identification by means of the cytochrome b gene. Int J Leg Med 114, 23–28 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004140000134
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004140000134