Abstract
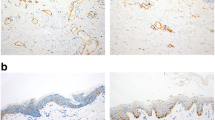
Immunohistochemical study combined with morphometry was carried out to examine the expression of oxygen-regulated protein 150 (ORP150) using 58 human skin wounds of different ages (group I, 0–12 h; II, 1–5 days; III, 7–14 days; and IV, 17–21 days). In human wound specimens aged 4–12 h, neutrophils recruited at the wound showed no positive signals for ORP150. With the increase in wound age of ≥7 days, granulation tissue and angiogenesis were observed, with the migration of macrophages and fibroblasts with ORP150-positive reactions. In semi-quantitative analysis, the average of ORP150-positive ratios in group III was highest. In group III, all samples had an ORP150-positive ratio of >40%, and 17 samples showed >50%. In group IV, three out of ten samples showed a positive ratio of 40–45% and the remaining seven cases less than 40%. Collectively, with regard to the practical applicability with forensic safety, these observations suggest that an ORP150-positive ratio of >50% strongly indicates a wound age of 7–14 days.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raekallio J (1972) Determination of the age of wounds by histochemical and biochemical methods. Forensic Sci Int 1:3–16
Laiho K (1998) Myeloperoxidase activity in skin lesions. I. Influence of the loss of blood, depth of excoriation and thickness of the skin. Int J Legal Med 111:6–9
Laiho K (1998) Myeloperoxidase activity in skin lesions. II. Influence of alcohol and some medicines. Int J Legal Med 111:10–12
Eisenmenger W, Nerlich A, Glück G (1988) Die Bedeutung des Kollagens bei Wundaltersbestimmung. Z Rechtsmed 100:79–100
Oehmichen M (1990) Die Wundheilung. Springer, Berlin, pp 5–67
Oehmichen M, Cröpelin A (1995) Temporal course of intravital and postmortem proliferation of epidermal cells after injury—an immunohistochemical study using bromodeoxyuridine in rats. Int J Legal Med 107:257–262
Betz P (1994) Histological and enzyme histochemical parameters for the age estimation of human skin wounds. Int J Legal Med 107:60–68
Betz P, Eisenmenger W (1996) Morphometrical analysis of hemosiderin deposits in relation to wound age. Int J Legal Med 108:262–264
Dressler J, Busuttil A, Koch R, Harrison DJ (2001) Sequence of melanocyte migration into human scar tissue. Int J Legal Med 115:61–63
Kondo T (2007) Timing of skin wounds. Legal Med 9:109–114
Martin P (1997) Wound healing—aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 276:75–81
Singer AJ, Clark RA (1999) Cutaneous wound healing. N Engl J Med 341:738–746
Ishida Y, Kondo T, Takayasu T, Iwakura Y, Mukaida N (2004) The essential involvement of cross-talk between IFN-g and TGF-b in the skin wound-healing process. J Immunol 172:1848–1855
Lin ZQ, Kondo T, Ishida Y, Takayasu T, Mukaida N (2003) Essential involvement of IL-6 in the skin wound-healing process as evidenced by delayed wound healing in IL-6-deficient mice. J Leukoc Biol 73:713–721
Mori R, Kondo T, Ohshima T, Ishida Y, Mukaida N (2002) Accelerated wound healing in tumor necrosis factor receptor p55-deficient mice with reduced leukocyte infiltration. FASEB J 16:963–974
Ishida Y, Kondo T, Kimura A, Matsushima K, Mukaida N (2006) Absence of IL-1 receptor antagonist impaired wound healing along with aberrant NF-κB activation and a reciprocal suppression of TGF-β signal pathway. J Immunol 176:5598–5606
Ishida Y, Gao JL, Murphy PM (2008) Chemokine receptor CX3CR1 mediates skin wound healing by promoting macrophage and fibroblast accumulation and function. J Immunol 180:569–579
Betz P, Nerlich A, Wilske J, Tübel J, Wiest I, Penning R, Eisenmenger W (1992) Immunohistochemical localization of fibronectin as a tool for the age determination of human skin wounds. Int J Legal Med 105:21–26
Betz P, Nerlich A, Wilske J, Tübel J, Penning R, Eisenmenger W (1993) Analysis of the immunohistochemical localization of collagen type III and V for the time-estimation of human skin wounds. Int J Legal Med 105:329–332
Betz P, Nerlich A, Wilske J, Tübel J, Penning R, Eisenmenger W (1993) Immunohistochemical localization collagen types I and VI in human skin wounds. Int J Legal Med 106:31–34
Betz P (1995) Immunohistochemical parameters for the age estimation of human skin wounds. A review. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 16:203–209
Betz P, Nerlich A, Tübel J, Wiest I, Hausmann R (1997) Detection of cell death in human skin wounds of various ages by an in situ end labeling of nuclear DNA fragments. Int J Legal Med 110:240–243
Dreßler J, Bachmann L, Kasper M, Hauck JG, Müller E (1997) Time dependence of the expression ICAM (CD-54) in human skin wound. Int J Legal Med 110:299–304
Dreßler J, Bachmann L, Koch R, Müller E (1998) Enhanced expression of selectins in human skin wounds. Int J Legal Med 112:39–44
Dreßler J, Bachmann L, Koch R, Müller E (1999) Estimation of wound age and VCAM-1 in human skin. Int J Legal Med 112:159–162
Kondo T, Ohshima T (1996) The dynamics of inflammatory cytokines in the healing process of mouse skin wound: a preliminary study for possible wound age determination. Int J Legal Med 108:231–236
Kondo T, Ohshima T, Eisenmenger W (1999) Immunohistochemical and morphometrical study on the temporal expression of interleukin-1a (IL-1a) in human skin wounds for forensic wound age determination. Int J Legal Med 112:249–252
Kondo T, Ohshima T, Mori R, Guan DW, Ohshima K, Eisenmenger W (2002) Immunohistochemical detection of chemokines in human skin wounds and its application to wound age determination. Int J Legal Med 116:87–91
Ohshima T, Sato Y (1998) Time-dependent expression of interleukin-10 (IL-10) mRNA during the early phase of skin wound healing as possible indicator of wound vitality. Int J Legal Med 1998:251–255
Guan D, Ohshima T, Kondo T (2000) Immunohistochemical study on Fas and Fas ligand in skin wound healing. Histochem J 32:85–91
Sato Y, Ohshima T (2000) The expression of mRNA by proinflammatory cytokines during skin wound healing in mice: a preliminary study for forensic wound age estimation (II). Int J Legal Med 113:140–145
Rebolledo Godoy M, Rebolledo Godoy AP, Oehmichen M (2000) AgNORs during the process of wound healing. Time dependency as evaluated in vital and postmortem biopsy. Int J Legal Med 113:244–246
Kondo T, Tanaka J, Ishida Y, Mori R, Takayasu T, Ohshima T (2002) Ubiquitin expression in skin wounds and its application to forensic wound age determination. Int J Legal Med 116:267–272
Hausmann R, Betz P (2001) Course of glial immunoreactivity for vimentin, tenascin and alpha1-antichymotrypsin after traumatic injury to human brain. Int J Legal Med 114:338–342
Hausmann R, Betz P (2000) The time course of the vascular response to human brain injury—an immunohistochemical study. Int J Legal Med 113:288–292
Hausmann R, Riess R, Fieguth A, Betz P (2000) Immunohistochemical investigations on the course of astroglial GFAP expression following human brain injury. Int J Legal Med 113:70–75
Hausmann R, Kaiser A, Lang C, Bohnert M, Betz P (1999) A quantitative immunohistochemical study on the time-dependent course of acute inflammatory cellular response to human brain injury. Int J Legal Med 112:227–232
Hayashi T, Ishida Y, Kimura A, Takayasu T, Eisenmenger W, Kondo T (2004) Forensic application of VEGF expression to skin wound age determination. Int J Legal Med 118:320–325
Takamiya M, Saigusa K, Nakayashiki N, Aoki Y (2003) Studies on mRNA expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in wound healing for wound age determination. Int J Legal Med 117:46–50
Dreßler J, Hanisch U, Kuhlisch E, Geiger KD (2007) Neuronal and glial apoptosis in human traumatic brain injury. Int J Legal Med 121:365–375
Hausmann R, Seidl S, Betz P (2006) Hypoxic changes in Purkinje cells of the human cerebellum. Int J Legal Med 12:175–183
Hausmann R, Vogel C, Seidl S, Betz P (2006) Value of morphological parameters for grading of brain swelling. Int J Legal Med 120:219–225
Hausmann R, Biermann T, Wiest I, Tübel J, Betz P (2004) Neuronal apoptosis following human brain injury. Int J Legal Med 118:32–36
Kuwabara K, Matsumoto M, Ikeda J, Hori O, Ogawa S, Maeda Y, Kitagawa K, Imuta N, Kinoshita T, Stern DM, Yanagi H, Kamada T (1996) Purification and characterization of a novel stress protein, the 150-kDa oxygen-regulated protein (ORP150), from cultured rat astrocytes and its expression in ischemic mouse brain. J Biol Chem 271:5025–5032
Ikeda J, Kaneda S, Kuwabara K, Ogawa S, Kobayashi T, Matsumoto M, Yura T, Yanagi H (1997) Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding the human 150 kDa oxygen-regulated protein, ORP150. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 230:94–99
Tamatani M, Matsuyama T, Yamaguchi A, Mitsuda N, Tsukamoto Y, Taniguchi M, Che YH, Ozawa K, Hori O, Nishimura H, Yamashita A, Okabe M, Yanagi H, Stern DM, Ogawa S, Tohyama M (2001) ORP150 protects against hypoxia/ischemia-induced neuronal death. Nat Med 7:317–323
Tsukamoto Y, Kuwabara K, Hirota S, Ikeda J, Stern D, Yanagi H, Matsumoto M, Ogawa S, Kitamura Y (1996) 150-kD oxygen-regulated protein is expressed in human atherosclerotic plaques and allows mononuclear phagocytes to withstand cellular stress on exposure to hypoxia and modified low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest 98:1930–1941
Ozawa K, Miyazaki M, Matsuhisa M, Takano K, Nakatani Y, Hatazaki M, Tamatani T, Yamagata K, Miyagawa J, Kitao Y, Hori O, Yamasaki Y, Ogawa S (2005) The endoplasmic reticulum chaperone improves insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 54:657–663
Ozawa K, Tsukamoto Y, Hori O, Kitao Y, Yanagi H, Stern DM, Ogawa S (2001) Regulation of tumor angiogenesis by oxygen-regulated protein 150, an inducible endoplasmic reticulum chaperone. Cancer Res 61:4206–4213
Kitao Y, Ozawa K, Miyazaki M, Tamatani M, Kobayashi T, Yanagi H, Okabe M, Ikawa M, Yamashima T, Stern DM, Hori O, Ogawa S (2001) Expression of the endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone (ORP150) rescues hippocampal neurons from glutamate toxicity. J Clin Invest 108:1439–1450
Ozawa K, Kondo T, Hori O, Kitao Y, Stern DM, Eisenmenger W, Ogawa S, Ohshima T (2001) Expression of the oxygen-regulated protein ORP150 accelerates wound healing by modulating intracellular VEGF transport. J Clin Invest 108:41–50
Kitao Y, Hashimoto K, Matsuyama T, Iso H, Tamatani T, Hori O, Stern DM, Kano M, Ozawa K, Ogawa S (2004) ORP150/HSP12A regulates Purkinje cell survival: a role for endoplasmic reticulum stress in cerebellar development. J Neurosci 24:1486–1496
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel DV, Ferrara N (1989) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science 246:1306–1309
Ferrara N, Henzel WJ (1989) Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 161:851–858
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S, Poltorak Z (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. FASEB J 13:9–22
Betz P, Nerlich A, Wilske J, Tübel J, Penning R, Eisenmenger W (1992) Time-dependent appearance of myofibroblasts in granulation tissue of human skin wounds. Int J Legal Med 105:99–103
Ikematsu K, Tsuda R, Kondo T, Kondo H, Ozawa K, Ogawa S, Nakasono I (2004) The expression of ‘150-kDa oxygen regulated protein (ORP-150)’ in human brain and its relationship with duration time until death. Legal Med 6:97–101
Ikematsu K, Tsuda R, Kondo T, Kondo H, Ozawa K, Ogawa S, Nakasono I (2003) The expression of a novel stress protein ‘150-kDa oxygen regulated protein’ in sudden infant death. Legal Med 5:15–19
Acknowledgment
This study was financially supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan. We sincerely thank Ms. Mariko Kawaguchi for her excellent assistant in preparing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishida, Y., Kimura, A., Takayasu, T. et al. Expression of oxygen-regulated protein 150 (ORP150) in skin wound healing and its application for wound age determination. Int J Legal Med 122, 409–414 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-008-0255-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-008-0255-1