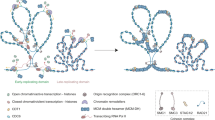
Abstract
The past two decades of research into transcriptional control of protein-encoding genes in eukaryotes have focused on regulatory mechanisms that act by controlling the recruitment of Pol II to a gene’s promoter. Recent genome-wide analyses of the distribution of Pol II indicates that Pol II is concentrated in the promoter regions of thousands of genes in human and Drosophila cells. In many cases, Pol II may have initiated transcription but paused in the promoter proximal region. Hence, release of Pol II from the promoter region into the body of a gene is now recognized as a common rate-limiting step in the control of gene expression. Notably, most genes with paused Pol II are expressed indicating that the pause can be transient. What causes Pol II to concentrate in the promoter region and how it is released to transcribe a gene are the focus of this review.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelman K, Marr MT, Werner J, Saunders A, Ni Z, Andrulis ED, Lis JT (2005) Efficient release from promoter-proximal stall sites requires transcript cleavage factor TFIIS. Mol Cell 17:103–112
Aida M, Chen Y, Nakajima K, Yamaguchi Y, Wada T, Handa H (2006) Transcriptional pausing caused by NELF plays a dual role in regulating immediate-early expression of the junB gene. Mol Cell Biol 26:6094–6104
Ainbinder E, Amir-Zilberstein L, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H, Dikstein R (2004) Elongation inhibition by DRB sensitivity-inducing factor is regulated by the A20 promoter via a novel negative element and NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Biol 24:2444–2454
Aiyar SE, Blair AL, Hopkinson DA, Bekiranov S, Li R (2006) Regulation of clustered gene expression by cofactor of BRCA1 (COBRA1) in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 26(18):2543–2553
Aiyar SE, Sun JL, Blair AL, Moskaluk CA, Lu YZ, Ye QN, Yamaguchi Y, Mukherjee A, Ren DM, Handa H, Li R (2004) Attenuation of estrogen receptor alpha-mediated transcription through estrogen-stimulated recruitment of a negative elongation factor. Genes Dev 18:2134–2146
Andrecka J, Lewis R, Bruckner F, Lehmann E, Cramer P, Michaelis J (2008) Single-molecule tracking of mRNA exiting from RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:135–140
Armstrong JA, Papoulas O, Daubresse G, Sperling AS, Lis JT, Scott MP, Tamkun JW (2002) The Drosophila BRM complex facilitates global transcription by RNA polymerase II. Embo J 21:5245–5254
Benjamin LR, Gilmour DS (1998) Nucleosomes are not necessary for promoter-proximal pausing in vitro on the Drosophila hsp70 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res 26:1051–1055
Biggin MD, Tjian R (1988) Transcription factors that activate the Ultrabithorax promoter in developmentally staged extracts. Cell 53:699–711
Blau J, Xiao H, McCracken S, O’Hare P, Greenblatt J, Bentley D (1996) Three functional classes of transcriptional activation domain. Mol Cell Biol 16:2044–2055
Boehm AK, Saunders A, Werner J, Lis JT (2003) Transcription factor and polymerase recruitment, modification, and movement on dhsp70 in vivo in the minutes following heat shock. Mol Cell Biol 23:7628–7637
Bondarenko VA, Steele LM, Ujvari A, Gaykalova DA, Kulaeva OI, Polikanov YS, Luse DS, Studitsky VM (2006) Nucleosomes can form a polar barrier to transcript elongation by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell 24:469–479
Brown SA, Imbalzano AN, Kingston RE (1996) Activator-dependent regulation of transcriptional pausing on nucleosomal templates. Genes Dev 10:1479–1490
Brown SA, Kingston RE (1997) Disruption of downstream chromatin directed by a transcriptional activator. Genes Dev 11:3116–3121
Brown SA, Weirich CS, Newton EM, Kingston RE (1998) Transcriptional activation domains stimulate initiation and elongation at different times and via different residues. Embo J 17:3146–3154
Buratowski S (2003) The CTD code. Nat Struct Biol 10:679–680
Cai W, Bao X, Deng H, Jin Y, Girton J, Johansen J, Johansen KM (2008) RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription at active loci does not require histone H3S10 phosphorylation in Drosophila. Development 135:2917–2925
Chao SH, Price DH (2001) Flavopiridol inactivates P-TEFb and blocks most RNA polymerase II transcription in vivo. J Biol Chem 276:31793–31799
Cheng B, Price DH (2007) Properties of RNA Polymerase II Elongation Complexes Before and After the P-TEFb-mediated Transition into Productive Elongation. J Biol Chem 282:21901–21912
Chopra VS, Srinivasan A, Kumar RP, Mishra K, Basquin D, Docquier M, Seum C, Pauli D, Mishra RK (2008) Transcriptional activation by GAGA factor is through its direct interaction with dmTAF3. Dev Biol 317:660–670
Cojocaru M, Jeronimo C, Forget D, Bouchard A, Bergeron D, Cote P, Poirier GG, Greenblatt J, Coulombe B (2008) Genomic location of the human RNA polymerase II general machinery: evidence for a role of TFIIF and Rpb7 at both early and late stages of transcription. Biochem J 409:139–147
Core LJ, Lis JT (2008) Transcription regulation through promoter-proximal pausing of RNA polymerase II. Science 319:1791–1792
Corey LL, Weirich CS, Benjamin IJ, Kingston RE (2003) Localized recruitment of a chromatin-remodeling activity by an activator in vivo drives transcriptional elongation. Genes Dev 17:1392–1401
de La Serna IL, Carlson KA, Hill DA, Guidi CJ, Stephenson RO, Sif S, Kingston RE, Imbalzano AN (2000) Mammalian SWI-SNF complexes contribute to activation of the hsp70 gene. Mol Cell Biol 20:2839–2851
Dellino GI, Schwartz YB, Farkas G, McCabe D, Elgin SC, Pirrotta V (2004) Polycomb silencing blocks transcription initiation. Mol Cell 13:887–893
Emanuel PA, Gilmour DS (1993) TFIID recognizes DNA sequences downstream of the TATA element in the hsp 70 heat shock gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:8449–8453
Fish RN, Kane CM (2002) Promoting elongation with transcript cleavage stimulatory factors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1577:287–307
Giardina C, Perez-Riba M, Lis JT (1992) Promoter Melting and TFIID Complexes on Drosophila Genes In Vivo. Genes Dev 6:2190–2200
Gilchrist DA, Nechaev S, Lee C, Ghosh SKB, Collins JB, Li L, Gilmour DS, Adelman K (2008) NELF-mediated stalling of Pol II can enhance gene expression by blocking promoter-proximal nucleosome assembly. Genes Dev 22(14):1921–1933
Gilmour DS, Lis JT (1986) RNA Polymerase II Interacts With the Promoter Region of the Noninduced hsp70 Gene in Drosophila melanogaster Cells. Mol Cell Biol 6:3984–3989
Greive SJ, von Hippel PH (2005) Thinking quantitatively about transcriptional regulation. Nat Rev 6:221–232
Gu W, Wind M, Reines D (1996) Increased accommodation of nascent RNA in a product site on RNA polymerase II during arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:6935–6940
Guenther MG, Levine SS, Boyer LA, Jaenisch R, Young RA (2007) A chromatin landmark and transcription initiation at most promoters in human cells. Cell 130:77–88
Hendrix DA, Hong JW, Zeitlinger J, Rokhsar DS, Levine MS (2008) Promoter elements associated with RNA Pol II stalling in the Drosophila embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:7762–7767
Ivaldi MS, Karam CS, Corces VG (2007) Phosphorylation of histone H3 at Ser10 facilitates RNA polymerase II release from promoter-proximal pausing in Drosophila. Genes Dev 21:2818–2831
Izban MG, Luse DS (1991) Transcription on nucleosomal templates by RNA polymerase II in vitro: inhibition of elongation with enhancement of sequence-specific pausing. Genes Dev 5:683–696
Kettenberger H, Armache KJ, Cramer P (2003) Architecture of the RNA polymerase II-TFIIS complex and implications for mRNA cleavage. Cell 114:347–357
Krumm A, Hickey LB, Groudine M (1995) Promoter-proximal pausing of RNA polymerase II defines a general rate limiting step after transcription initiation. Genes Dev 9:559–572
Lee H, Kraus KW, Wolfner MF, Lis JT (1992) DNA sequence requirements for generating paused polymerase at the start of hsp70. Genes Dev 6:284–295
Lee C, Li X, Hechmer A, Eisen M, Biggin MD, Venters BJ, Jiang C, Li J, Pugh BF, Gilmour DS (2008) NELF and GAGA factor are linked to promoter proximal pausing at many genes in Drosophila. Mol Cell Biol 28:3290–3300
Li P, Yao H, Zhang Z, Li M, Luo Y, Thompson PR, Gilmour DS, Wang Y (2008) Regulation of p53 target gene expression by peptidylarginine deiminase 4. Mol Cell Biol 28(15):4745–4758
Lis J (1998) Promoter-associated pausing in promoter architecture and postinitiation transcriptional regulation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 63:347–356
Lis J, Wu C (1993) Protein traffic on the heat shock promoter: parking, stalling and trucking along. Cell 74:1–4
Lis JT, Wu C (1994) Transcriptional regulation of heat shock genes. In: Conaway RC, Conaway JW (eds) Transcription: Mechanisms and regulation. Raven Press, Ltd, New York, pp 459–475
Mandal SS, Chu C, Wada T, Handa H, Shatkin AJ, Reinberg D (2004) Functional interactions of RNA-capping enzyme with factors that positively and negatively regulate promoter escape by RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:7572–7577
Margaritis T, Holstege FC (2008) Poised RNA polymerase II gives pause for thought. Cell 133:581–584
Marshall NF, Price DH (1992) Control of formation of two distinct classes of RNA polymerase II elongation complexes. Mol Cell Biol 12:2078–2090
Marshall NF, Price DH (1995) Purification of P-TEFb, a transcription factor required for the transition into productive elongation. J Biol Chem 270:12335–12338
Mason PB Jr., Lis JT (1997) Cooperative and competitive protein interactions at the hsp70 promoter. J Biol Chem 272:33227–33233
Mavrich TN, Jiang C, Ioshikhes IP, Li X, Venters BJ, Zanton SJ, Tomsho LP, Qi J, Glaser RL, Schuster SC, Gilmour DS, Albert I, Pugh BF (2008) Nucleosome organization in the Drosophila genome. Nature 453:358–362
Muse GW, Gilchrist DA, Nechaev S, Shah R, Parker JS, Grissom SF, Zeitlinger J, Adelman K (2007) RNA polymerase is poised for activation across the genome. Nat Genet 39:1507–1511
Nakayama T, Nishioka K, Dong YX, Shimojima T, Hirose S (2007) Drosophila GAGA factor directs histone H3.3 replacement that prevents the heterochromatin spreading. Genes Dev 21:552–561
Narita T, Yamaguchi Y, Yano K, Sugimoto S, Chanarat S, Wada T, Kim DK, Hasegawa J, Omori M, Inukai N, Endoh M, Yamada T, Handa H (2003) Human transcription elongation factor NELF: identification of novel subunits and reconstitution of the functionally active complex. Mol Cell Biol 23:1863–1873
Narita T, Yung TM, Yamamoto J, Tsuboi Y, Tanabe H, Tanaka K, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H (2007) NELF interacts with CBC and participates in 3′ end processing of replication-dependent histone mRNAs. Mol Cell 26:349–365
Ni Z, Saunders A, Fuda NJ, Yao J, Suarez JR, Webb WW, Lis JT (2008) P-TEFb is critical for the maturation of RNA polymerase II into productive elongation in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 28:1161–1170
O’Brien T, Lis JT (1991) RNA polymerase II pauses at the 5′ end of the transcriptionally induced Drosophila hsp70 gene. Mol Cell Biol 11:5285–5290
Orphanides G, Lagrange T, Reinberg D (1996) The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev 10:2657–2683
Palangat M, Renner DB, Price DH, Landick R (2005) A negative elongation factor for human RNA polymerase II inhibits the anti-arrest transcript-cleavage factor TFIIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:15036–15041
Park JM, Werner J, Kim JM, Lis JT, Kim YJ (2001) Mediator, not holoenzyme, is directly recruited to the heat shock promoter by HSF upon heat shock. Mol Cell 8:9–19
Peterlin BM, Price DH (2006) Controlling the elongation phase of transcription with P-TEFb. Mol Cell 23:297–305
Petesch SJ, Lis JT (2008) Rapid, transcription-independent loss of nucleosomes over a large chromatin domain at Hsp70 loci. Cell 134:74–84
Price DH (2008) Poised polymerases: on your mark…get set…go!. Mol Cell 30:7–10
Price DH, Sluder AE, Greenleaf AL (1989) Dynamic interaction between a Drosophila transcription factor and RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol 9:1465–1475
Purnell BA, Emanuel PA, Gilmour DS (1994) TFIID sequence recognition of the initiator and sequences farther downstream in Drosophila class II genes. Genes Dev 8:830–842
Radonjic M, Andrau JC, Lijnzaad P, Kemmeren P, Kockelkorn TT, van Leenen D, van Berkum NL, Holstege FC (2005) Genome-wide analyses reveal RNA polymerase II located upstream of genes poised for rapid response upon S. cerevisiae stationary phase exit. Mol Cell 18:171–183
Rao JN, Schweimer K, Wenzel S, Wohrl BM, Rosch P (2008) NELF-E RRM Undergoes Major Structural Changes in Flexible Protein Regions on Target RNA Binding. Biochemistry 47:3756–3761
Rasmussen EB, Lis JT (1993) In vivo transcriptional pausing and cap formation on three Drosophila heat shock genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:7923–7927
Rasmussen EB, Lis JT (1995) Short transcripts of the ternary complex provide insight into RNA polymerase II elongational pausing. J Mol Biol 252:522–535
Renner DB, Yamaguchi Y, Wada T, Handa H, Price DH (2001) A highly purified RNA polymerase II elongation control system. J Biol Chem 276:42601–42609
Rougvie AE, Lis JT (1988) The RNA polymerase II molecule at the 5′ end of the uninduced hsp70 gene of D. melanogaster is transcriptionally engaged. Cell 54:795–804
Samkurashvili I, Luse DS (1998) Structural changes in the RNA polymerase II transcription complex during transition from initiation to elongation. Mol Cell Biol 18:5343–5354
Shopland LS, Hirayoshi K, Fernandes M, Lis JT (1995) HSF access to heat shock elements in vivo depends critically on promoter architecture defined by GAGA factor, TFIID, and RNA polymerase II binding sites. Genes Dev 9:2756–2769
Sims RJ 3rd, Belotserkovskaya R, Reinberg D (2004) Elongation by RNA polymerase II: the short and long of it. Genes Dev 18:2437–2468
Smale ST, Kadonaga JT (2003) The RNA polymerase II core promoter. Annu Rev Biochem 72:449–479
Sullivan EK, Weirich CS, Guyon JR, Sif S, Kingston RE (2001) Transcriptional activation domains of human heat shock factor 1 recruit human SWI/SNF. Mol Cell Biol 21:5826–5837
Tanese N, Saluja D, Vassallo MF, Chen JL, Admon A (1996) Molecular cloning and analysis of two subunits of the human TFIID complex: hTAFII130 and hTAFII100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:13611–13616
Ujvari A, Luse DS (2006) RNA emerging from the active site of RNA polymerase II interacts with the Rpb7 subunit. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13:49–54
Ujvari A, Pal M, Luse DS (2002) RNA polymerase II transcription complexes may become arrested if the nascent RNA is shortened to less than 50 nucleotides. J Biol Chem 277:32527–32537
Wada T, Takagi T, Yamaguchi Y, Ferdous A, Imai T, Hirose S, Sugimoto S, Yano K, Hartzog GA, Winston F, Buratowski S, Handa H (1998) DSIF, a novel transcription elongation factor that regulates RNA polymerase II processivity, is composed of human Spt4 and Spt5 homologs. Genes Dev 12:343–356
Wang G, Balamotis MA, Stevens JL, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H, Berk AJ (2005a) Mediator requirement for both recruitment and postrecruitment steps in transcription initiation. Mol Cell 17:683–694
Wang YV, Tang H, Gilmour DS (2005b) Identification in vivo of different rate-limiting steps associated with transcriptional activators in the presence and absence of a GAGA element. Mol Cell Biol 25:3543–3552
Wang X, Lee C, Gilmour DS, Gergen JP (2007) Transcription elongation controls cell fate specification in the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev 21:1031–1036
Weber JA, Taxman DJ, Lu Q, Gilmour DS (1997) Molecular architecture of the hsp70 promoter after deleting the TATA box or the upstream regulatory region. Mol Cell Biol 17:3799–3808
Wu CH, Yamaguchi Y, Benjamin LR, Horvat-Gordon M, Washinsky J, Enerly E, Larsson J, Lambertsson A, Handa H, Gilmour D (2003) NELF and DSIF cause promoter proximal pausing on the hsp70 promoter in Drosophila. Genes Dev 17:1402–1414
Wu CH, Lee C, Fan R, Smith MJ, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H, Gilmour DS (2005) Molecular characterization of Drosophila NELF. Nucleic Acids Res 33:1269–1279
Xiao H, Sandaltzopoulos R, Wang HM, Hamiche A, Ranallo R, Lee KM, Fu D, Wu C (2001) Dual functions of largest NURF subunit NURF301 in nucleosome sliding and transcription factor interactions. Mol Cell 8:531–543
Yamada T, Yamaguchi Y, Inukai N, Okamoto S, Mura T, Handa H (2006) P-TEFb-mediated phosphorylation of hSpt5 C-terminal repeats is critical for processive transcription elongation. Mol Cell 21:227–237
Yamaguchi Y, Takagi T, Wada T, Yano K, Furuya A, Sugimoto S, Hasegawa J, Handa H (1999) NELF, a multisubunit complex containing RD, cooperates with DSIF to repress RNA polymerase II elongation. Cell 97:41–51
Yamaguchi Y, Filipovska J, Yano K, Furuya A, Inukai N, Narita T, Wada T, Sugimoto S, Konarska MM, Handa H (2001) Stimulation of RNA polymerase II elongation by hepatitis delta antigen. Science 293:124–127
Yamaguchi Y, Inukai N, Narita T, Wada T, Handa H (2002) Evidence that Negative Elongation Factor Represses Transcription Elongation through Binding to a DRB Sensitivity-Inducing Factor/RNA Polymerase II Complex and RNA. Mol Cell Biol 22:2918–2927
Yamaguchi Y, Mura T, Chanarat S, Okamoto S, Handa H (2007) Hepatitis delta antigen binds to the clamp of RNA polymerase II and affects transcriptional fidelity. Genes Cells 12:863–875
Yankulov KY, Pandes M, McCracken S, Bouchard D, Bentley DL (1996) TFIIH functions in regulating transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Cell Biol 16:3291–3299
Zeitlinger J, Stark A, Kellis M, Hong JW, Nechaev S, Adelman K, Levine M, Young RA (2007) RNA polymerase stalling at developmental control genes in the Drosophila melanogaster embryo. Nat Genet 39:1512–1516
Zhang Z, Wu CH, Gilmour DS (2004) Analysis of Pol II elongation complexes by native gel electrophoresis: evidence for a novel CTD-mediated termination mechanism. J Biol Chem 279:23223–23228
Zhang Z, Klatt A, Gilmour DS, Henderson AJ (2007a) Negative elongation factor NELF represses human immunodeficiency virus transcription by pausing the RNA polymerase II complex. J Biol Chem 282:16981–16988
Zhang Z, Klatt A, Henderson AJ, Gilmour DS (2007b) Transcription termination factor Pcf11 limits the processivity of Pol II on an HIV provirus to repress gene expression. Genes Dev 21:1609–1614
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by E. Nigg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilmour, D.S. Promoter proximal pausing on genes in metazoans. Chromosoma 118, 1–10 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-008-0182-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-008-0182-4