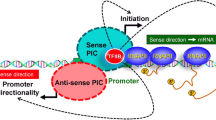
Abstract
Accurate transcription of a gene by RNA polymerase II requires the assembly of a group of general transcription factors at the promoter. The general transcription factor TFIIB plays a central role in preinitiation complex assembly, providing a bridge between promoter-bound TFIID and RNA polymerase II. TFIIB makes extensive contact with the core promoter via two independent DNA-recognition modules. In addition to interacting with other general transcription factors, TFIIB directly modulates the catalytic center of RNA polymerase II in the transcription complex. Moreover, TFIIB has been proposed as a target of transcriptional activator proteins that act to stimulate preinitiation complex assembly. In this review, we will discuss our current understanding of these activities of TFIIB.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostini I, Navarro JM, Bouhamdan M, Willettes K, Rey F, Spire B, Vigne R, Pomerantz R, Sire J (1999) The HIV-1 Vpr co-activator induces a conformational change in TFIIB. FEBS Lett 450:235–239
Andel F, Ladurner AG, Inouye C, Tjian R, Nogales E (1999) Three-dimensional structure of the human TFIID–IIA–IIB complex. Science 286:2153–2156
Apone LM, Virbasius CM, Reese JC, Green MR (1996) Yeast TAF(II)90 is required for cell-cycle progression through G2/M but not for general transcription activation. Genes Dev 10:2368–2380
Bagby S, Kim S, Maldonado E, Tong KI, Reinberg D, Ikura M (1995) Solution structure of the C-terminal core domain of human TFIIB: similarity to cyclin A and interaction with TATA-binding protein. Cell 82:857–867
Baldwin DA, Gurley WB (1996) Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding transcription factor IIB from Arabidopsis and soybean. Plant J 10:569–578
Bangur CS, Pardee TS, Ponticelli AS (1997) Mutational analysis of the D1/E1 core helices and the conserved N-terminal region of yeast transcription factor IIB (TFIIB): identification of an N-terminal mutant that stabilizes TATA-binding protein–TFIIB DNA complexes. Mol Cell Biol 17:6784–6793
Bangur CS, Faitar SL, Folster JP, Ponticelli AS (1999) An interaction between the N terminal region and the core domain of yeast TFIIB promotes the formation of TATA-binding protein–TFIIB–DNA complexes. J Biol Chem 274:23203–23209
Baniahmad A, Ha I, Reinberg D, Tsai S, Tsai MJ, O’Malley BW (1993) Interaction of human thyroid hormone receptor beta with transcription factor TFIIB may mediate target gene derepression and activation by thyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:8832–8836
Barberis A, Muller CW, Harrison, SC, Ptashne M (1993) Delineation of an N-terminal region of transcription factors TFIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:5628–5632
Bartlett MS (2005) Determinants of transcription initiation by archaeal RNA polymerase. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:677–684
Bell SD, Jackson SP (2000) The role of transcription factor B in transcription initiation and promoter clearance in the archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Biol Chem 275:12934–12940
Bell SD, Kosa PL, Sigler PB, Jackson SP (1999) Orientation of the transcription preinitiation complex in archaea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:13662–13667
Benson JD, Lawande R, Howley PM (1997) Conserved interaction of the papillomavirus E2 transcriptional activator proteins with human and yeast TFIIB proteins. J Virol 71:8041–8047
Blair WS, Bogerd HP, Madore SJ, Cullen BR (1994) Mutational analysis of the transcription activation domain of RelA: identification of a highly synergistic minimal acidic activation module. Mol Cell Biol 14:7226–7234
Buratowski S, Zhou H (1993) Functional domains of transcription factor TFIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:5633–5637
Buratowski S, Hahn S, Guarente, L, Sharp PA (1989) Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell 56:549–561
Buratowski RM, Downs J, Buratowski S (2002) Interdependent interactions between TFIIB, TATA binding protein, and DNA. Mol Cell Biol 22:8735–8743
Bushnell DA, Westover KD, Davis RE, Kornberg RD (2004) Structure basis of transcription: an RNA polymerase II–TFIIB cocrystal at 4.5 angstroms. Science 303:983–988
Butler JEF, Kadonaga JT (2002) The RNA polymerase II core promoter: a key component in the regulation of gene expression. Gene Dev 16:2583–2592
Caswell R, Hagemeier C, Chiou CJ, Hayward G, Kouzarides T, Sinclair J (1993) The human cytomegalovirus 86K immediate early (IE) 2 protein requires the basic region of the TATA-box binding protein (TBP) for binding, and interacts with TBP and transcription factor TFIIB via regions of IE2 required for transcriptional regulation. J Gen Virol 74:2691–2698
Chen HT, Hahn S (2003) Binding of TFIIB to RNA polymerase II: mapping the binding site for the TFIIB zinc ribbon domain within the preinitiation complex. Mol Cell 12:437–447
Chen HT, Hahn S (2004) Mapping the location of TFIIB within the RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex: a model for the structure of the PIC. Cell 119:169–180
Chen BS, Hampsey M (2004) Functional interaction between TFIIB and the RBP2 subunit of RNA polymerae II: Implications for the mechanism of transcription initiation. Mol Cell Biol 24:3983–3991
Chen Z, Manley JL (2003) Core promoter elements and TAFs contribute to the diversity of transcriptional activation in vertebrates. Mol Cell Biol 23:7350–7362
Chen HT, Legault P, Glushka J, Omichinski JG, Scott RA (2000) Structure of a (Cys3His) zinc ribbon, a ubiquitous motif in archaeal and eucaryal transcription. Protein Sci 9:1743–1752
Chiang YC, Komarnitsky P, Chase D, Denis CL (1996) ADR1 activation domains contact the histone acetyltransferase GCN5 and the core transcriptional factor TFIIB. J Biol Chem 271:32359–33265
Cho EJ, Buratoski (1999) Evidence that transcription IIB is required for post assembly step in transcription initiation. J Biol Chem 274:25807–25813
Chou S, Struhl K (1997) Transcriptional activation by TFIIB mutants that are severely impaired in interaction with promoter DNA and acidic activation domains. Mol Cell Biol 17:6794–6802
Choy B, Green MR (1993) Eukaryotic activators function during multiple steps of preinitiation complex assembly. Nature 366:531–536
Colgan J, Wampler S, Manley JL (1993) Interaction between a transcriptional activator and transcription factor IIB in vivo. Nature 362:549–553
Colgan J, Ashali H, Manley JL (1995) A direct interaction between a glutamine-rich activator and the N terminus of TFIIB can mediate transcriptional activation in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 15:2311–2320
Coulombe B, Li J, Greenblatt J (1994) Topological localization of the human transcription factors IIA, IIB, TATA box-binding protein and RNA polymeraseII-associated protein 30 on a class II promoter. J Biol Chem 269:19962–19967
Creti R, Londei P, Cammarano P (1993) Complete nucleotide sequence of an archaeal (Pyrococcus woesei) gene encoding a homolog of eukaryotic transcription factor IIB. Nucleic Acids Res 21:2942–2949
Deng W, Roberts SGE (2005) A core promoter element downstream of the TATA box that is recognized by TFIIB. Genes Dev 19:2418–2423
Deng W, Roberts SGE (2006) Core promoter elements recognized by transcription factor IIB. Biochem Soc Trans 34:1051–1053
Elsby LM, Roberts SGE (2004) The role of TFIIB conformation in transcriptional regulation. Biochem Soc Trans 32:1098–1099
Elsby LM, O’Donnell AJM, Green LM, Sharrocks AD, Roberts SGE (2006) Assembly of TFIIB at a promoter in vivo requires contact with RNA polymerase II. EMBO Rep 7:898–903
Evans R, Failey JA, Roberts SGE (2001) Activator-mediated disruption of sequence-specific DNA contacts by the general transcription factor TFIIB. Genes Dev 15:2945–2949
Fairley JA, Evans R, Hawkes NA, Roberts SG (2002) Core promoter-dependent TFIIB conformation and a role for TFIIB conformation in transcription start site selection. Mol Cell Biol 22:6697–6705
Faitar SL, Brodie SA, Ponticelli AS (2001) Promoter-specific shifts in transcription initiation conferred by yeast TFIIB mutations are determined by the sequence in the immediate vicinity of the start sites. Mol Cell Biol 21:4427–4440
Fang SM, Burton ZF (1996) RNA polymerase II-associated protein (RAP) 74 binds transcription factor (TF) IIB and blocks TFIIB-RAP30 binding. J Biol Chem 27:11703–11709
Franklin CC, McCulloch AV, Kraft AS (1995) In vitro association between the Jun protein family and the general transcription factors, TBP and TFIIB. Biochem J 305:967–974
Freire-Picos MA, Krishnamurthy S, Sun Z-W, Hampsey M (2005) Evidence that the Tfg1/Tfg2 dimer interface of TFIIF lies near the active center of the RNA polymerase II initiation complex. Nucleic Acid Res 33:5045–5052
Ge H, Roeder RG (1994) Purification, cloning, and characterization of a human coactivator, PC4, that mediates transcriptional activation of class II genes. Cell 78:513–523
Gershenzon NI, Ioshikhes IP (2005a) Synergy of human Pol II core promoter elements revealed by statistical sequence analysis. Bioinformatics 21:1295–1300
Gershenzon NI, Ioshikhes IP (2005b) Promoter classifier: software package for promoter database analysis. Appl Bioinformatics 4:205–209
Ghosh M, Elsby LM, Mal TK, Gooding JM, Roberts SGE, Ikura M (2004) Probing zinc-binding effects on the zinc ribbon domain of human general transcription factor TFIIB. Biochem J 378:317–324
Gibson TJ, Thompson JD, Blocker A, Kouzarides T (1994) Evidence for a protein domain superfamily shared by the cyclins, TFIIB and RB/p107. Nucleic Acids Res 22:946–952
Glossop JA, Dafforn TR, Roberts SGE (2004) A conformational change in TFIIB is required for activator-mediated assembly of the preinitiation complex. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1829–1835
Gonzalez-Couto E, Klages N, Strubin M (1997) Synergistic and promoter-selective activation of transcription by recruitment of transcription factors TFIID and TFIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:8036–8041
Goodrich JA, Hoey T, Thut CJ, Admon A, Tjian R (1993) Drosophila TAFII40 interacts with both a VP16 activation domain and the basal transcription factor TFIIB. Cell 75:519–530
Grossmann JG, Sharff AJ, O’Hare P, Luisi B (2001) Molecular shapes of transcription factors TFIIB and VP16 in solution: implications for recognition. Biochemistry 40:6267–6274
Gu B, Kuddus R, DeLuca NA (1995) Repression of activator-mediated transcription by herpes simplex virus ICP4 via a mechanism involving interactions with the basal transcription factors TATA-binding protein and TFIIB. Mol Cell Biol 15:3618–3626
Ha I, Lane WS, Reinberg D (1991) Cloning of a human gene encoding the general transcription initiation factor IIB. Nature 352:689–695
Ha I, Roberts, S, Maldonado E, Sun X, Kim LV, Green M, Reinberg D (1993) Multiple function domain of human transcription factor IIB: distinct interactions with two general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev 7:1021–1032
Hall DB, Struhl K (2002) The VP16 activation domain interacts with multiple transcriptional components as determined by protein–protein cross-linking in vivo. J Biol Chem 277:46043–46050
Hawkes NA, Roberts SG (1999) The role of human TFIIB in transcription start site selection in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 274:14337–14343
Hawkes NA, Evans R, Roberts SGE (2000) The conformation of the transcription factor TFIIB modulates the response to transcriptional activators in vivo. Curr Biol 10:273–276
Hayashi F, Ishima R, Liu D, Tong KI, Kim S, Reinberg D, Bagby S, Ikura M (1998) Human general transcription factor TFIIB: conformational variability and interaction with VP16 activation domain. Biochemistry 37:7941–7951
He X, Khan AU, Cheng H, Pappas DL Jr, Hampsey M, Moore CL (2003) Functional interactions between the transcription and mRNA 3′ end processing machineries mediated by Ssu72 and Sub1. Genes Dev 17:1030–1042
Hellqyist M, Mahlapuu M, Blixt A, Enerback S, Carlsson P (1998) The human forkhead protein FREAC-2 contains two functionally redundant activation domains and interacts with TBP and TFIIB. J Biol Chem 273(36):23335–23343
Hisatake K, Malik S, Roeder RG, Horikoshi M (1991) Conserved structural motifs between Xenopus and human TFIIB. Nucleic Acids Res 19:6639–6646
Hori R, Pyo S, Carey M (1995) Protease footprinting reveals a surface on transcription factor TFIIB that serves as an interface for activators and coactivators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:6047–6051
Juven-Gershon T, Hsu J-Y, Kadonaga JT (2006) Perspectives on the RNA polymerase II core promoter. Biochem Soc Trans 34:1047–1049
Kim TK, Roeder RG (1994) Proline-rich activator CTF1 targets the TFIIB assembly step during transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:4170–4174
Kimura H, Tao Y, Roeder RG, Cook PR (1999) Quantitation of RNA polymerase II and its transcription factors in an HeLa cell: little soluble holoenzyme but significant amounts of polymerases attached to the nuclear substructure. Mol Cell Biol 19:5383–5392
Knaus R, Pollock R, Guarente L (1996) Yeast SUB1 is a suppressor of TFIIB mutations and has homology to the human co-activator PC4. EMBO J 15:1933–1940
Kobor MS, Simon LD, Omichinski J, Zhong G, Archambault J, Greenblatt J (2000) A motif shared by TFIIF and TFIIB mediates their interaction with the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain phosphatase Fcp1p in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 20:7438–7449
Koleske AJ, Young RA (1994) An RNA polymerase II holoenzyme responsive to activators. Nature 368:466–469
Kretzschmar M, Kaiser K, Lottspeich F, Meisterernst M (1994) A novel mediator of class II gene transcription with homology to viral immediate–early transcriptional regulators. Cell 78:525–534
Krishnamurthy S, He X, Reyes-Reyes M, Moore C, Hampsey M (2004) Ssu72 is an RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase. Mol Cell 14:387–394
Kuehner JN, Brow DA (2006) Quantitative analysis of in vivo initiator selection by yeast RNA polymerase II supports a scanning model. J Biol Chem 281:14119–14128
Kwok RP, Lundblad JR, Chrivia JC, Richards JP, Bachinger HP, Brennan RG, Roberts SG, Green MR, Goodman RH (1994) Nuclear protein CBP is a coactivator for the transcription factor CREB. Nature 370:223–226
Lagrange T, Kim TK, Orphanides G, Ebright YW, Ebright RH, Reinberg D (1996) High-resolution mapping of nucleoprotein complexes by site-specific protein–DNA photocrosslinking: Organization of the human TBP–TFIIA–DNA quanternary complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:10620–10625
Lagrange T, Kapanidis AN, Tang H, Reinberg D, Ebright RH (1998) New core promoter element in RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription: sequence-specific DNA binding by transcription factor IIB. Genes Dev 12:34–44
Lee S, Hahn S (1995) Model for binding of transcription factor TFIIB to the TBP–DNA complex. Nature 376:609–612
Leurent C, Sanders S, Ruhlmann C, Mallouh V, Weil PA, Kirschner DB, Tora L, Schultz P (2002) Mapping histone fold TAFs within yeast TFIID. EMBO J 21:3424–3433
Li Y, Flanagan PM, Tschochner H, Kornberg RD (1994) RNA polymerase II initiation factor interactions and transcription start site selection. Science 263:805–807
Li LA, Chiang EF, Chen JC, Hsu NC, Chen YJ, Chung BC (1999) Function of steroidogenic factor 1 domains in nuclear localization, transactivation, and interaction with transcription factor TFIIB and c-Jun. Mol Endocrinol 13:1588–1598
Lin YS, Green MR (1991) Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell 64:971–981
Lin YS, Ha I, Maldonado E, Reinberg D, Green MR (1991) Binding of general transcription factor TFIIB to an acidic activating region. Nature 353:569–571
Littllefield O, Korkhin Y, Sigler PB (1999) The structural basis for the oriented assembly of a TBP/TFB/promoter complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:13668–13673
Liu X, Berk AJ (1995) Reversal of in vitro p53 squelching by both TFIIB and TFIID. Mol Cell Biol 15:6474–6478
Malik S, Hisatake K, Sumimoto H, Horikoshi M, Roeder RG (1991) Sequence of general transcription factor TFIIB and relationships to other initiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:9553–9557
Malik S, Lee DK, Roeder RG (1993) Potential RNA polymerase II-induced interactions of transcription factor TFIIB. Mol Cell Biol 13:6253–6259
Martianov I, Ramadass A, Serra Barros A, Chow N, Akoulitchev A (2007) Repression of the human dihydrofolate reductase gene by a non-coding interfering transcript. Nature 445:666–670
Masuyama H, Jefcoat SC Jr, MacDonald PN (1997) The N-terminal domain of transcription factor IIB is required for direct interaction with the vitamin D receptor and participates in vitamin D-mediated transcription. Mol Endocrinol 11:218–228
McKay LM, Carpenter B, Roberts SGE (1999) Regulation of the Wilms’ tumour suppressor protein transcriptional activation domain. Oncogene 18:6546–6554
Nevado J, Gaudreau L, Adam M, Ptashne M (1999) Transcriptional activation by artificial recruitment in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:2674–2677
Nguyen BD, Chen HT, Kobor MS, Greenblatt J, Legault P, Omichinski JG (2003) Solution structure of the carboxyl-terminal domain of RAP74 and NMR characterization of the FCP1-binding sites of RAP74 and human TFIIB. Biochemistry 42:1460–1469
Nikolov DB, Chen H, Halay ED, Usheva AA, Hisatake K, Lee DK, Roeder RG, Burley SK (1995) Crystal structure of a TFIIB–TBP–TATA–element ternary complex. Nature 377:119–128
Ossipow V, Tassan JP, Nigg EA, Schibler U (1995) A mammalian RNA polymerase II holoenzyme containing all components required for promoter-specific transcription initiation. Cell 83:137–146
Pal M, Ponticelli AS, Luse DS (2005) The role of the transcription bubble and TFIIB in promoter clearance by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell 19:101–110
Palenchar JB, Liu W, Palenchar PM, Bellofatto V (2006) A divergent transcription factor TFIIB in trypanosomes is required for RNA polymerase II-dependent spliced leader RNA transcription and cell viability. Eukaryot Cell 5:293–300
Pan S, Sehnke PC, Ferl RJ, Gurley WB (1999) Specific interactions with TBP and TFIIB in vitro suggest that 14–3–3 proteins may participate in the regulation of transcription when part of a DNA binding complex. Plant Cell 11:1591–1602
Pappas DL, Hampsey M (2000) Functional interaction between Ssu72 and the Rpb2 subunit of RNA polymerase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 20:8343–8351
Pardee TS, Bangur CS, Ponticelli AS (1998) The N-terminal region of yeast TFIIB contains two adjacent functional domains involved in stable RNA polymerase II binding and transcription start site selection. J Biol Chem 273:17859–17864
Parvin JD, Sharp PA (1993) DNA topology and a minimal set of basal factors for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Cell 73:533–540
Pinto I, Ware DE, Hampsey M (1992) The yeast SUA7 gene encodes a homolog of human transcription factor TFIIB and is required for normal start site selection in vivo. Cell 68:977–988
Pinto I, Wu WH, Na JG, Hampsey M (1994) Characterisation of sua7 mutations defines a domain of TFIIB involved in transcription start site selection in yeast. J Biol Chem 269:30569–30573
Qureshi SA, Jackson SP (1998) Sequence-specific DNA binding by the S. Shibatae TFIIB homolog, TFB , and its effect on promoter strength. Mol Cell 1:389–400
Qureshi SA, Khoo B, Baumann P, Jackson SP (1995) Molecular cloning of the transcription factor TFIIB homolog fromSulfolobus shibatae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:6077–6081
Ranish JA, Yudkovsky N, Hahn S (1999) Intermediates in formation and activity of the RNA polymerase preinitiation complex: Holoenzyme recruitment and a postrecruitment role for the TATA box and TFIIB. Genes Dev 13:49–63
Reinberg D, Roeder RG (1987) Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem 262:3310–3321
Renfrow MB, Naryshkin N, Lewis LM, Chen HT, Ebright RH, Scott RA (2004) Transcription factor B contacts promoter DNA near the transcription start site of the archaeal transcription initiation complex. J Biol Chem 279:2825–2831
Roberts SGE, Green MR (1994) Activator-induced conformational change in general transcription factor TFIIB. Nature 371:717–720
Roberts SGE, Ha I, Maldonado E, Reinberg D, Green MR (1993) Interaction between an acidic activator and transcription factor TFIIB is required for transcriptional activation. Nature 363:741–744
Roberts SGE, Choy B, Walker SS, Lin YS, Green MR (1995) A role for activator-mediated TFIIB recruitment in diverse aspects of transcriptional regulation. Curr Biol 5:508–516
Sauer F, Fondell JD, Ohkuma Y, Roeder RG, Jackle H. (1995) Control of transcription by Kruppel through interactions with TFIIB and TFIIE beta. Nature 375:162–164
Sawadogo M, Roeder RG (1985) Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell 43:165–175
Smale ST, Kadonaga JT (2003) The RNA polymerase II core promoter. Annu Rev Biochem 72:449–479
Sun ZW, Hampsey M (1995) Identification of the gene (SSU7/TFG1) encoding the largest subunit of transcription factor TFIIF as a suppressor of a TFIIB mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:3127–3131
Sun ZW, Hampsey M (1996) Synthetic enhancement of a TFIIB defect by a mutation in SSU72, an essential yeast gene encoding a novel protein that affects transcription start site selection in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 16:1557–1566
Sun ZW, Tessmer A, Hampsey M (1996) Functional interaction between TFIIB and the Rpb9 (Ssu73) subunit of RNA polymerase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res 24:2560–2566
Thomas MC, Chiang CM (2006) The general transcription machinery and general cofactors. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 41:105–178
Thompson NE, Strasheim LA, Nolan KM, Burgess RR (1995) Accessibility of epitopes on human transcription factor IIB in the native protein and in a complex with DNA. J Biol Chem 270:4735–4740
Tsai FT, Sigler PB (2000) Structural basis of preinitiation complex assembly on human Pol II promoters. EMBO J 19:25–36
Tubon TC, Tansey WP, Herr W (2004) A nonconserved surface of the TFIIB zinc ribbon domain plays a direct role in RNA polymerase II recruitment. Mol Cell Biol 24:2863–2874
Tyree CM, George CP, Lira-DeVito LM, Wampler SL, Dahmus ME, Zawel L, Kadonaga JT (1993) Identification of a minimal set of proteins that is sufficient for accurate initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev 7:1254–1265
Usheva A, Shenk T (1994) TATA-binding protein-independent initiation: YY1, TFIIB, and RNA polymerase II direct basal transcription on supercoiled template DNA. Cell 76:1115–1121
Wampler SL, Kadonaga JT (1992) Functional analysis of Drosophila transcription factor IIB. Genes Dev 6:1542–1552
Werner F, Weinzierl ROJ (2005) Direct modulation of RNA polymerase core function by basal transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol 25:8344–8355
Wu WH, Hampsey M (1999) An activation-specific role for transcription factor TFIIB in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:2764–2769
Wu Y, Reece RJ, Ptashne M (1996) Quantitation of putative activator-target affinities predicts transcriptional activating potentials. EMBO J 15:3951–3963
Yamashita S, Wada K, Horikoshi M, Gong DW, Kokubo T, Hisatake K, Yokotani N, Malik S, Roeder RG, Nakatani Y (1992) Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding Drosophila transcription factor TFIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:2839–2843
Zawel L, Kumar KP, Reinberg D (1995) Recycling of the general transcription factors during RNA polymerase II transcription. Genes Dev 9:1479–1490
Zhang DY, Dorsey MJ, Voth WP, Carson DJ, Zeng X, Stillman DJ, Ma J (2000) Intramolecular interaction of yeast TFIIB in transcription control. Nucleic Acids Res 28:1913–1920
Zhang DY, Carson DJ, Ma J (2002) The role of TFIIB–RNA polymerase II interaction in start site selection in yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res 30:3078–3085
Zheng L, Hoeflich KP, Elsby LM, Ghosh M, Roberts SG, Ikura M (2004) FRET evidence for a conformational change in TFIIB upon TBP–DNA binding. Eur J Biochem 271:792–800
Zhu W, Zeng Q, Colangelo, CM, Lewis M, Summers MF, Scott RA (1996) The N-terminal domain of TFIIB from Pyrococcus furiosus forms a zinc ribbon. Nat Struct Biol 3:122–124
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Sarah Goodfellow and Yuming Wang for comments on the manuscript. We are grateful to the Wellcome Trust for supporting our work on TFIIB. SGER is a Wellcome Trust Senior Research Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by E. A. Nigg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, W., Roberts, S.G.E. TFIIB and the regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Chromosoma 116, 417–429 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-007-0113-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-007-0113-9