Abstract
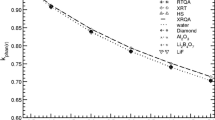
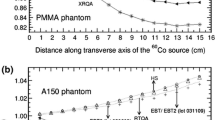
Precise positioning of source and dosimeters is essential in the experimental determination of dosimetric characteristics of brachytherapy sources. Various near-water equivalent solid phantoms have been used to achieve the necessary precision in the positioning. However, the uncertainties in their chemical compositions may lead to non-negligible uncertainties in the determined doses. It is proposed here that ice may be used as an alternative to the conventional solid phantoms, since its chemical composition is identical to water while the positioning advantage associated with solid phantoms is retained. In this work, the feasibility of using ice as a solid phantom for brachytherapy dosimetry is investigated. Ice-to-water conversion factors are calculated at distances of 0.2–10 cm from the source, for six high- and low-energy photon-emitting brachytherapy sources and mono-energetic photons between 10 keV to 2.0 MeV. Practical issues and challenges associated with measuring dose in an ice phantom are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meigooni A, Awan S, Thompson N, Dini S (2006) Updated Solid Water™ to water conversion factors for 125I and 103Pd brachytherapy sources. Med Phys 33(11):3988–3992
Demarco JJ, Wallace RE, Boedeker K (2002) An analysis of MCNP cross-sections and tally methods for low-energy photon emitter. Phys Med Biol 47:1321–1332
X-5 Monte Carlo Team (2000) MCNP-A general Monte Carlo N-Particle transport code. Version 5, Los Alamos National Laboratory Report BNL-NCS-17541, 8th edn. National Nuclear Data Center
Cross Section Evaluation Working Group (2000) ENDF/B-VI summary documentation (ENDF-201). Brookhaven National Laboratory Report BNL-NCS-17541, 8th edn. National Nuclear Data Center
Rivard MJ, Coursey BM, DeWard LA, Hanson WF, Huq MS, Ibbott GS, Mitch MG, Nath R, Williamson JF (2004) Update of AAPM Task Group No. 43 Report: a revised AAPM protocol for brachytherapy dose calculations. Med Phys 31(3):633–674
Chen Z, Nath R (2001) Dose rate constant and energy spectrum of interstitial brachytherapy sources. Med Phys 28(1):86–96
Glasgow GP, Dillman LT (1979) Specific gamma-ray constant and exposure rate constant of 192Ir. Med Phys 6(1):49–52
NuDat Program for Nuclear Data (2006) Brookhaven National Laboratory, National Nuclear Data Center. http://www.nndc.bnl.gov/nndc/nudat/
Murphy MK, Piper RK, Greenwood LR, Mitch MG, Lamperti PJ, Seltzer SM, Bales MJ, Phillips MH (2004) Evaluation of the new 131Cs seed for use in low energy X-ray brachytherapy. Med Phys 31(6):1529–1538
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, H., Chen, Z., Yue, N. et al. Ice as a water-equivalent solid medium for brachytherapy dosimetric measurements. Radiat Environ Biophys 48, 145–151 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-008-0205-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-008-0205-9