Abstract
Introduction
Personalized treatment helps one achieve optimal outcomes in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Understanding patients’ survival prognoses in a palliative situation like intracerebral metastases is critical. A new survival score, the WBRT-30-NSCLC, was developed for patients with intracerebral metastases from NSCLC.
Methods
Eight factors were investigated in 157 patients receiving 10 × 3 Gy of whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) including age, gender, Karnofsky performance score (KPS), interval from diagnosis of NSCLC to WBRT, pre-WBRT systemic treatment, primary tumor control, number of intracerebral metastases, and metastasis outside the brain. Factors significant (p < 0.05) or showing a trend (p < 0.08) on multivariate analysis were used for the WBRT-30-NSCLC. Patient scores were derived by adding factor scores (6-month survival rates divided by 10). WBRT-30-NSCLC was compared to other scores for intracerebral metastases from NSCLC.
Results
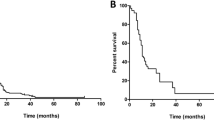
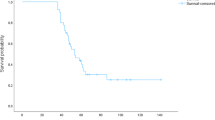
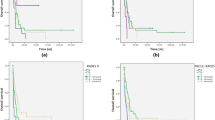
On multivariate analysis, age (p = 0.005), KPS (p < 0.001), systemic treatment (p = 0.018), and metastasis outside the brain (p < 0.001) were significant; number of intracerebral metastases (p = 0.075) showed a trend. Four groups were designed (912, 1317, 1820, and 22 points) with 6-month survival rates of 3, 26, 65, and 100%. Positive predictive value (PPV) to predict death ≤ 6 months after WBRT was 97% (updated DS-GPA classification 86%, Rades-NSCLC 88%), and PPV to predict survival ≥ 6 months was 100% (updated DS-GPA 78%, Rades-NSCLC 74%).
Conclusions
The WBRT-30-NSCLC appeared very precise in identifying patients with intracerebral metastases from NSCLC dying ≤ 6 months or surviving ≥ 6 months. It appeared more precise than previous scores and can support physicians developing personalized treatment regimens.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 69:7–34
Tsao MN, Rades D, Wirth A et al (2010) Radiotherapeutic and surgical management for newly diagnosed brain metastasis(es): an American Society for Radiation Oncology evidence-based guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol 2:210–225
Rades D (2011) Radiation therapy for metastatic disease. In: Jeremic B (ed) Advances in radiation oncology in lung cancer. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 561–573
Rades D, Huttenlocher S, Dziggel L et al (2015) A new tool predicting survival after radiosurgery alone for one or two cerebral metastases from lung cancer. Lung 193:299–302
Rades D, Kieckebusch S, Lohynska R et al (2007) Reduction of overall treatment time in patients irradiated for more than three brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 69:1509–1513
DeAngelis LM, Delattre JY, Posner JB (1989) Radiation-induced dementia in patients cured of brain metastases. Neurology 39:789–796
Rades D, Panzner A, Dziggel L et al (2012) Dose-escalation of whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastasis in patients with a favorable survival prognosis. Cancer 118:3852–3859
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D et al (2012) Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 30:419–425
Rades D, Dziggel L, Segedin B et al (2013) A new survival score for patients with brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 189:777–781
Rades D, Dziggel L, Nagy V et al (2013) A new survival score for patients with brain metastases who received whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) alone. Radiother Oncol 108:123–127
Kaplan E, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observation. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Mulvenna P, Nankivell M, Barton R et al (2016) Dexamethasone and supportive care with or without whole brain radiotherapy in treating patients with non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases unsuitable for resection or stereotactic radiotherapy (QUARTZ): results from a phase 3, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet 388:2004–2014
Wrona A, Dziadziuszko R, Jassem J (2018) Management of brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer in the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev 71:59–67
Karnath SD, Kumthekar PU (2018) Immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) metastatic disease. Front Oncol 8:414
Gondi V, Pugh SL, Tome WA et al (2014) Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (RTOG 0933): a phase II multi-institutional trial. J Clin Oncol 32:3810–3816
Brown PD, Pugh S, Laack N et al (2013) Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG): memantine for the prevention of cognitive dysfunction in patients receiving whole-brain radiotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neuro Oncol 15:1429–1437
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with ethical standards and the Helsinki declaration from 1964 and its later amendments. The study was approved by the ethic committee of the University of Lübeck (reference number: 19-003A). Due to its retrospective design, informed consent specifically for this study was not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rades, D., Hansen, H.C., Schild, S.E. et al. A New Diagnosis-Specific Survival Score for Patients to be Irradiated for Brain Metastases from Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung 197, 321–326 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-019-00223-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-019-00223-6