Abstract
Introduction
Patients with limited disease small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) receive radiochemotherapy followed by prophylactic cranial irradiation. The prognosis of these patients remains poor with a median survival of 16–24 months. Systemic inflammation was suggested as an important prognostic factor for outcomes. This study investigated the impact of systemic inflammation measured with neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) at first diagnosis in patients with limited disease SCLC for outcomes.
Methods
Data of 65 patients receiving radiochemotherapy for limited disease SCLC were analyzed. NLR and PLR were obtained from blood sample at first diagnosis of SCLC and 12 characteristics including gender, age, ECOG, T-category, N-category, pack years, smoking during radiotherapy, respiratory insufficiency, hemoglobin levels during radiotherapy, radiation dose (<56 vs. ≥56 Gy), concurrent radiochemotherapy, and prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) were evaluated for local control, metastasis-free survival, and overall survival.
Results
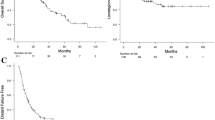
Survival rates at 1, 2, and 3 years were 71, 45, and 28%, respectively. Median survival time was 20 months. Independent factors for improved survival were NLR < 4 (p = 0.03), ECOG 0–1 (p = 0.002), and PCI (p = 0.015). Lower T-category was an independent positive factor of local control (p = 0.035). Improved metastasis-free survival was associated with NLR < 4 (p = 0.011), ECOG 0–1 (p = 0.002), N-category 0–1 (p = 0.048), non-smoking during radiotherapy (p = 0.009), and PCI (p = 0.006).
Conclusion
NLR was found to be an independent prognostic factor for overall survival. The evaluation of NLR can help identify patients with poor prognosis and appears a useful prognostic marker in clinical practice. A prospective analysis is warranted to confirm these findings.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2015) Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 65:5–29
Pietanza MC, Byers LA, Minna JD et al (2015) Small cell lung cancer: will recent progress lead to improved outcomes? Clin Cancer Res 21:2244–2255
Jeremic B, Dobric Z, Casas F (2011) Limited-disease small-cell lung cancer. Advances in radiation oncology in lung cancer. Springer, Heidelberg
Alifano M, Mansuet-Lupo A, Lococo F, et al. (2014) Systemic inflammation, nutritional status and tumor immune microenvironment determine outcome of resected non-small cell lung cancer. PloS ONE 9:e106914
Zhou T, Zhan J, Hong S et al (2015) Ratio of C-reactive protein/albumin is an inflammatory prognostic score for predicting overall survival of patients with small-cell lung cancer. Sci Rep 18(5):10481
He X, Zhou T, Yang Y et al (2015) Advanced lung cancer inflammation index, a new prognostic score, predicts outcome in patients with small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 16:e165–e171
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Cannon NA, Meyer J, Iyengar P et al (2015) Neutrophil–lymphocyte and platelet–lymphocyte ratios as prognostic factors after stereotactic radiation therapy for early-stage non–small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 10:280–285
Walsh S, Cook E, Goulder F et al (2005) Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol 91:181–184
Asaoka T, Miyamoto A, Maeda S et al (2016) Prognostic impact of preoperative NLR and CA19-9 in pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology 16:434–440
Berardi R, Rinaldi S, Santoni M, Newsom-Davis T, Tiberi M, Morgese F, Caramanti M, Savini A, Ferrini C, Torniai M, Fiordoliva I, et al. (2016) Prognostic models to predict survival in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with first-line chemo-or targeted therapy. Oncotarget 7(18):26916–26924
Tang H, Ma H, Peng F et al (2016) Prognostic performance of inflammation-based prognostic indices in locally advanced non-small-lung cancer treated with endostar and concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Mol Clin Oncol 4:801–806
Pinato D, Shiner R, Seckl M et al (2014) Prognostic performance of inflammation-based prognostic indices in primary operable non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 110:1930–1935
Gu X, Sun S, Gao X-S et al (2016) Prognostic value of platelet to lymphocyte ratio in non-small cell lung cancer: evidence from 3,430 patients. Sci Rep 30(6):23893
Mizunuma M, Yokoyama Y, Futagami M et al (2015) The pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts therapeutic response to radiation therapy and concurrent chemoradiation therapy in uterine cervical cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 20:989–996
Kang MH, Go SI, Song H et al (2014) The prognostic impact of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 111:452–460
Kaplan E, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observation. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Ma X, Yan F, Deng Q, et al. (2015) Modulation of tumorigenesis by the pro-inflammatory microRNA miR-301a in mouse models of lung cancer and colorectal cancer. Cell Discov 19(1):15005
Nakamura H, Kato Y, Kato H (2004) Outcome of surgery for small cell lung cancer–response to induction chemotherapy predicts survival. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 52:206–210
Vallieres E, Shepherd FA, Crowley J et al (2009) The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals regarding the relevance of TNM in the pathologic staging of small cell lung cancer in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 4:1049–1059
Rades D, Setter C, Schild SE et al (2008) Effect of smoking during radiotherapy, respiratory insufficiency, and hemoglobin levels on outcome in patients irradiated for non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71:1134–1142
Videtic GM, Truong PT, Ash RB et al (2005) Does sex influence the impact that smoking, treatment interruption and impaired pulmonary function have on outcomes in limited stage small cell lung cancer treatment? Can Respir J 12:245–250
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any conflict of interest to declare in relation to this work.
Ethical Standards
All procedures performed were in accordance with ethical standards and the Helsinki declaration from 1964 and its later amendments.
Informed Consent
Due to its retrospective design, informed consent specifically for this study was not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Käsmann, L., Bolm, L., Schild, S.E. et al. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Outcome in Limited Disease Small-cell Lung Cancer. Lung 195, 217–224 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-017-9976-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-017-9976-6