Abstract
Background
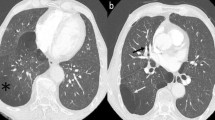
IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD) is a recently recognized disease entity. Differentiating IgG4RD from plasma cell type Castleman’s disease (PCD) is important but also difficult using only pathological findings. In addition, little is known about the association between these two diseases with diffuse parenchymal lung involvement.
Methods
We analyzed the serum IgG4 levels and the ratio of IgG4/IgG-positive plasmacytes in the lung and lymph node specimens of eight patients previously pathologically diagnosed of PCD with diffuse parenchymal lung involvement (DL-PCD). We also compared the clinical and laboratory findings observed in these patients.
Results
Six of the eight patients exhibited abundant IgG4-positive plasmacytes in the lung and lymph node tissues and elevated serum IgG4 levels, thereby fulfilling the diagnostic criteria of IgG4RD with DL (DL-IgG4RD) in addition to having obstructive phlebitis and massive lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with fibrosis. However, three of these six patients exhibited higher levels of serum interleukin-6 and were still diagnosed with DL-PCD. Accordingly, three of these eight patients were considered as IgG4RD with DL (DL-IgG4RD), and the other five patients were ultimately given a diagnosis of DL-PCD. These two diseases have different characteristics in terms of age, symptoms, serum levels of C-reactive protein, and IgA, complicating allergic disorders, response to corticosteroids, and prognosis.
Conclusions
This is the first report to show a high prevalence of DL-IgG4RD in DL-PCD patients, although additional large investigations are necessary. Clinical and laboratory findings are important for distinguishing between these two diseases in other organs, as previously described.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y et al (2012) IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol 22:1–14
Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V (2012) IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med 366:539–551
Cheuk W, Yuen HK, Chu SY et al (2008) Lymphadenopathy of IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Am J Surg Pathol 32:671–681
Masaki Y, Dong L, Kurose N et al (2009) Proposal for a new clinical entity, IgG4-positive multiorgan lymphoproliferative syndrome: analysis of 64 cases of IgG4-related disorders. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1310–1315
Smyrk TC (2011) Pathological features of IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol 23:74–79
Zen Y, Nakanuma Y (2010) IgG4-related disease: a cross-sectional study of 114 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 34:1812–1819
Fujinaga Y, Kadoya M, Kawa S et al (2010) Characteristic findings in images of extra-pancreatic lesions associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Eur J Radiol 76:228–238
Matsui S, Taki H, Shinoda K et al (2012) Respiratory involvement in IgG4-related Mikulicz’s disease. Mod Rheumatol 22:31–39
Matsui S, Hebisawa A, Sakai F et al (2013) Immunoglobulin G4-related lung disease: clinicoradiological and pathological features. Respirology 18:480–487
Ryu JH, Sekiguchi H, Yi ES (2012) Pulmonary manifestations of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease. Eur Respir J 39:180–186
Castleman B, Iverson L, Menendez VP (1956) Localized mediastinal lymph node hyperplasia resembling thymoma. Cancer 9:822–830
Frizzera G (1988) Castleman’s disease and related disorders. Semin Diagn Pathol 5:346–364
Weisenburger DD, Nathwani BN, Winberg CD, Rappaport H (1985) Multicentric angiofollicular lymph node hyperplasia: a clinicopathologic study of 16 cases. Hum Pathol 16:162–172
Yoshizaki K, Matsuda T, Nishimoto N et al (1989) Pathogenic significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6/BSF-2) in Castleman’s disease. Blood 74:1360–1367
Nishimoto N (2005) Clinical studies in patients with Castleman’s disease, Crohn’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis in Japan. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 28:221–230
Ishida F, Kitano K, Kobayashi H, Saito H, Kiyosawa K (1997) Elevated IgG4 levels in a case with multicentric Castleman’s disease. Br J Haematol 99:981–982
Kojima M, Nakamura N, Motoori T et al (2010) Castleman’s disease of the retroperitoneum: with special reference to IgG4-related disorder. J Clin Exp Hematop 50:39–44
Sato Y, Kojima M, Takata K et al (2010) Multicentric Castleman’s disease with abundant IgG4-positive cells: a clinical and pathological analysis of six cases. J Clin Pathol 63:1084–1089
Shrestha B, Sekiguchi H, Colby TV et al (2009) Distinctive pulmonary histopathology with increased IgG4-positive plasma cells in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis: report of 6 and 12 cases with similar histopathology. Am J Surg Pathol 33:1450–1462
Strehl JD, Hartmann A, Agaimy (2011) A Numerous IgG4-positive plasma cells are ubiquitous in diverse localised non-specific chronic inflammatory conditions and need to be distinguished from IgG4-related systemic disorders. J Clin Pathol 64:237–243
Ogoshi T, Yatera K, Nagata S et al (2011) A case of multicentric Castleman disease with massive infiltration of plasmacytes presenting IgG4. JJRS 49:437–442
Sato Y, Kojima M, Takata K et al (2009) Systemic IgG4-related lymphadenopathy: a clinical and pathologic comparison to multicentric Castleman’s disease. Mod Pathol 22:589–599
Webb WR, Muller NL, Naidich DP (2001) Illustrated glossary of high-resolution computed tomography term. High-resolution CT of the lung, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Flendrig JA, Schillings PHM (1969) Benign giant lymphoma: the clinical signs and symptoms. Folia Med Neerl 12:119
Keller AR, Hochholzer L, Castleman B (1972) Hyaline-vascular and plasma-cell types of giant lymph node hyperplasia of the mediastinum and other locations. Cancer 29:670–683
Jo JH, Park YS, Jeon YK, Nam SJ, Huh J (2011) Comparison of plasma cell type of Castleman’s disease and IgG4-related sclerosing disease: a histopathological and immunohistochemical study. Pathobiology 78:227–232
Zen Y, Fujii T, Harada K et al (2007) Th2 and regulatory immune reactions are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis and cholangitis. Hepatology 45:1538–1546
Inoue D, Zen Y, Abo H et al (2009) Immunoglobulin G4-related lung disease: CT findings with pathologic correlations. Radiology 251:260–270
Johkoh T, Muller NL, Ichikado K et al (1998) Intrathoracic multicentric Castleman disease: CT findings in 12 patients. Radiology 209:477–481
Frizzera G, Peterson BA, Bayrd ED et al (1985) A systemic lymphoproliferative disorder with morphologic features of Castleman’s disease: clinical findings and clinicopathologic correlations in 15 patients. J Clin Oncol 3:1202–1216
Herrada J, Cabanillas F, Rice L, Manning J, Pugh W (1998) The clinical behavior of localized and multicentric Castleman disease. Ann Intern Med 128:657–662
Bowne WB, Lewis JJ, Filippa DA et al (1999) The management of unicentric and multicentric Castleman’s disease: a report of 16 cases and a review of the literature. Cancer 85:706–717
Beck JT, Hsu SM, Wijdenes J et al (1994) Brief report: alleviation of systemic manifestations of Castleman’s disease by monoclonal anti-interleukin-6 antibody. N Engl J Med 330:602–605
van Rhee F, Fayad L, Voorhees P et al (2010) Siltuximab, a novel anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody, for Castleman’s disease. J Clin Oncol 28:3701–3708
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogoshi, T., Kido, T., Yatera, K. et al. Assessment of Pathologically Diagnosed Patients with Castleman’s Disease associated with Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Involvement Using the Diagnostic Criteria for IgG4-Related Disease. Lung 191, 575–583 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-013-9497-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-013-9497-x