Abstract
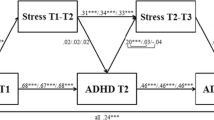
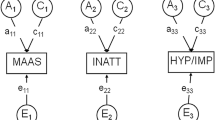
While an interactive effect of genes with adverse life events is increasingly appreciated in current concepts of depression etiology, no data are presently available on interactions between genetic and environmental (G × E) factors with respect to personality and related disorders. The present study therefore aimed to detect main effects as well as interactions of serotonergic candidate genes (coding for the serotonin transporter, 5-HTT; the serotonin autoreceptor, HTR1A; and the enzyme which synthesizes serotonin in the brain, TPH2) with the burden of life events (#LE) in two independent samples consisting of 183 patients suffering from personality disorders and 123 patients suffering from adult attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (aADHD). Simple analyses ignoring possible G × E interactions revealed no evidence for associations of either #LE or of the considered polymorphisms in 5-HTT and TPH2. Only the G allele of HTR1A rs6295 seemed to increase the risk of emotional-dramatic cluster B personality disorders (p = 0.019, in the personality disorder sample) and to decrease the risk of anxious-fearful cluster C personality disorders (p = 0.016, in the aADHD sample). We extended the initial simple model by taking a G × E interaction term into account, since this approach may better fit the data indicating that the effect of a gene is modified by stressful life events or, vice versa, that stressful life events only have an effect in the presence of a susceptibility genotype. By doing so, we observed nominal evidence for G × E effects as well as main effects of 5-HTT-LPR and the TPH2 SNP rs4570625 on the occurrence of personality disorders. Further replication studies, however, are necessary to validate the apparent complexity of G × E interactions in disorders of human personality.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baehne CG, Ehlis AC, Plichta MM, Conzelmann A, Pauli P, Jacob C, Gutknecht L, Lesch KP, Fallgatter AJ (2008) Tph2 gene variants modulate response control processes in adult ADHD patients and healthy individuals. Mol Psychiatry. doi:10.1038/mp.2008.39. 22 Apr 2008 [Epub ahead of print]
Baune BT, Hohoff C, Roehrs T, Deckert J, Arolt V, Domschke K (2008) Serotonin receptor 1A-1019C/G variant: impact on antidepressant pharmacoresponse in melancholic depression? Neurosci Lett 436:111–115
Brown SM, Peet E, Manuck SB, Williamson DE, Dahl RE, Ferrell RE, Hariri AR (2005) A regulatory variant of the human tryptophan hydroxylase-2 gene biases amygdala reactivity. Mol Psychiatry 10:884–888 (see also p 805)
Canli T, Congdon E, Gutknecht L, Constable RT, Lesch KP (2005) Amygdala responsiveness is modulated by tryptophan hydroxylase-2 gene variation. J Neural Transm 112:1479–1485
Canli T, Congdon E, Todd Constable R, Lesch KP (2008) Additive effects of serotonin transporter and tryptophan hydroxylase-2 gene variation on neural correlates of affective processing. Biol Psychol 79:118–125
Canli T, Lesch KP (2007) Long story short: the serotonin transporter in emotion regulation and social cognition. Nat Neurosci 10:1103–1109
Carola V, Frazzetto G, Gross C (2006) Identifying interactions between genes and early environment in the mouse. Genes Brain Behav 5:189–199
Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington H, McClay J, Mill J, Martin J, Braithwaite A, Poulton R (2003) Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science 301:386–389
Cloninger CR, Przybeck TR, Svrakic DM (1991) The tridimensional personality questionnaire: U.S. normative data. Psychol Rep 69:1047–1057
Costa PT, McCrae RR (1998) Revised NEO personality inventory (NEO PI-R) and NEO five- factor inventory (NEO-FFI) professional manual. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa
Covault J, Tennen H, Armeli S, Conner TS, Herman AI, Cillessen AH, Kranzler HR (2007) Interactive effects of the serotonin transporter 5-HTTLPR polymorphism and stressful life events on college student drinking and drug use. Biol Psychiatry 61:609–616
Dempfle A, Scherag A, Hein R, Beckmann L, Chang-Claude J, Schafer H (2008) Gene–environment interactions for complex traits: definitions, methodological requirements and challenges. Eur J Hum Genet 16:1164–1172
Domschke K, Braun M, Ohrmann P, Suslow T, Kugel H, Bauer J, Hohoff C, Kersting A, Engelien A, Arolt V, Heindel W, Deckert J (2006) Association of the functional -1019C/G 5-HT1A polymorphism with prefrontal cortex and amygdala activation measured with 3 T fMRI in panic disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 9:349–355
Fakra E, Hyde LW, Gorka A, Fisher PM, Munoz KE, Kimak M, Halder I, Ferrell RE, Manuck SB, Hariri AR (2009) Effects of HTR1A C(-1019)G on amygdala reactivity and trait anxiety. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:33–40
Faraone SV, Perlis RH, Doyle AE, Smoller JW, Goralnick JJ, Holmgren MA, Sklar P (2005) Molecular genetics of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 57:1313–1323
Gibb BE, McGeary JE, Beevers CG, Miller IW (2006) Serotonin transporter (5-HTTLPR) genotype, childhood abuse, and suicide attempts in adult psychiatric inpatients. Suicide Life Threat Behav 36:687–693
Gillespie NA, Whitfield JB, Williams B, Heath AC, Martin NG (2005) The relationship between stressful life events, the serotonin transporter (5-HTTLPR) genotype and major depression. Psychol Med 35:101–111
Gutknecht L, Jacob C, Strobel A, Kriegebaum C, Muller J, Zeng Y, Markert C, Escher A, Wendland J, Reif A, Mossner R, Gross C, Brocke B, Lesch KP (2007) Tryptophan hydroxylase-2 gene variation influences personality traits and disorders related to emotional dysregulation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10:309–320
Hariri AR, Mattay VS, Tessitore A, Kolachana B, Fera F, Goldman D, Egan MF, Weinberger DR (2002) Serotonin transporter genetic variation and the response of the human amygdala. Science 297:400–403
Jacob CP, Romanos J, Dempfle A, Heine M, Windemuth-Kieselbach C, Kruse A, Reif A, Walitza S, Romanos M, Strobel A, Brocke B, Schafer H, Schmidtke A, Boning J, Lesch KP (2007) Co-morbidity of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with focus on personality traits and related disorders in a tertiary referral center. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 257:309–317
Jacob CP, Strobel A, Hohenberger K, Ringel T, Gutknecht L, Reif A, Brocke B, Lesch KP (2004) Association between allelic variation of serotonin transporter function and neuroticism in anxious cluster C personality disorders. Am J Psychiatry 161:569–572
Jang KL, Livesley WJ (1999) Why do measures of normal and disordered personality correlate? A study of genetic comorbidity. J Personal Disord 13:10–17
Kendler KS, Gatz M, Gardner CO, Pedersen NL (2006) Personality and major depression: a Swedish longitudinal, population-based twin study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:1113–1120
Kim YK, Lee HJ, Yang JC, Hwang JA, Yoon HK (2009) A tryptophan hydroxylase 2 gene polymorphism is associated with panic disorder. Behav Genet 39:170–175
Koller G, Bondy B, Preuss UW, Zill P, Soyka M (2006) The C(-1019)G 5-HT1A promoter polymorphism and personality traits: no evidence for significant association in alcoholic patients. Behav Brain Funct 2:7
Lenze EJ, Munin MC, Ferrell RE, Pollock BG, Skidmore E, Lotrich F, Rogers JC, Quear T, Houck P, Reynolds CF 3rd (2005) Association of the serotonin transporter gene-linked polymorphic region (5-HTTLPR) genotype with depression in elderly persons after hip fracture. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 13:428–432
Lesch KP, Bengel D, Heils A, Sabol SZ, Greenberg BD, Petri S, Benjamin J, Muller CR, Hamer DH, Murphy DL (1996) Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Science 274:1527–1531
Lesch KP, Zeng Y, Reif A, Gutknecht L (2003) Anxiety-related traits in mice with modified genes of the serotonergic pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 480:185–204
Levinson DF (2006) The genetics of depression: a review. Biol Psychiatry 60:84–92
Mossner R, Walitza S, Geller F, Scherag A, Gutknecht L, Jacob C, Bogusch L, Remschmidt H, Simons M, Herpertz-Dahlmann B, Fleischhaker C, Schulz E, Warnke A, Hinney A, Wewetzer C, Lesch KP (2006) Transmission disequilibrium of polymorphic variants in the tryptophan hydroxylase-2 gene in children and adolescents with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 9:437–442
Reif A, Lesch KP (2003) Toward a molecular architecture of personality. Behav Brain Res 139:1–20
Reuter M, Kuepper Y, Hennig J (2007) Association between a polymorphism in the promoter region of the TPH2 gene and the personality trait of harm avoidance. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10:401–404
Rothe C, Gutknecht L, Freitag C, Tauber R, Mossner R, Franke P, Fritze J, Wagner G, Peikert G, Wenda B, Sand P, Jacob C, Rietschel M, Nothen MM, Garritsen H, Fimmers R, Deckert J, Lesch KP (2004) Association of a functional 1019C>G 5-HT1A receptor gene polymorphism with panic disorder with agoraphobia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 7:189–192
Saulsman LM, Page AC (2004) The five-factor model and personality disorder empirical literature: a meta-analytic review. Clin Psychol Rev 23:1055–1085
Strobel A, Dreisbach G, Muller J, Goschke T, Brocke B, Lesch KP (2007) Genetic variation of serotonin function and cognitive control. J Cogn Neurosci 19:1923–1931
Strobel A, Gutknecht L, Rothe C, Reif A, Mossner R, Zeng Y, Brocke B, Lesch KP (2003) Allelic variation in 5-HT1A receptor expression is associated with anxiety- and depression-related personality traits. J Neural Transm 110:1445–1453
Surtees PG, Wainwright NW, Willis-Owen SA, Luben R, Day NE, Flint J (2006) Social adversity, the serotonin transporter (5-HTTLPR) polymorphism and major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 59:224–229
Torgersen S, Lygren S, Oien PA, Skre I, Onstad S, Edvardsen J, Tambs K, Kringlen E (2000) A twin study of personality disorders. Compr Psychiatry 41:416–425
Uher R, McGuffin P (2008) The moderation by the serotonin transporter gene of environmental adversity in the aetiology of mental illness: review and methodological analysis. Mol Psychiatry 13:131–146
Walitza S, Renner TJ, Dempfle A, Konrad K, Wewetzer C, Halbach A, Herpertz-Dahlmann B, Remschmidt H, Smidt J, Linder M, Flierl L, Knolker U, Friedel S, Schafer H, Gross C, Hebebrand J, Warnke A, Lesch KP (2005) Transmission disequilibrium of polymorphic variants in the tryptophan hydroxylase-2 gene in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry 10:1126–1132
Zalsman G, Huang YY, Oquendo MA, Burke AK, Hu XZ, Brent DA, Ellis SP, Goldman D, Mann JJ (2006) Association of a triallelic serotonin transporter gene promoter region (5-HTTLPR) polymorphism with stressful life events and severity of depression. Am J Psychiatry 163:1588–1593
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to T. Töpner for excellent technical assistance. We also thank K. Zamzow and H. Zerlaut for their careful preparation of the data. This study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Grant RE1632/1-1 and 1-3 to A.R., KFO 125/1-1 to A.R., K.P.L., and C.P.J., and SFB581 to K.-P.L.), the IZKF Würzburg (01KS9603, to K.P.L; and N-4(1), to A.R.), and the European Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
C. P. Jacob, T. T. Nguyen and A. Dempfle contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacob, C.P., Nguyen, T.T., Dempfle, A. et al. A gene–environment investigation on personality traits in two independent clinical sets of adult patients with personality disorder and attention deficit/hyperactive disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 260, 317–326 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-009-0079-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-009-0079-0