Abstract
Purpose
Exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction (EILO) is suspected when dyspnea associated with upper airway symptoms is triggered by exercise. This condition affects mainly adolescent athletes. Visualization of the obstruction, while the patient is experiencing the symptoms during continuous laryngoscopy during exercise (CLE-test) is the gold standard for diagnosing EILO. Our study aims to evaluate the prevalence of EILO in a population presenting exercise-induced inspiratory symptoms (EIIS) or uncontrolled asthma with exertional symptoms. The second objective was to evaluate the diagnostic strength of laryngology consultation (LC) and pulmonary function tests (PFTs).
Methods
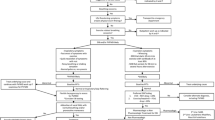
All patients referred to our center for EIIS or uncontrolled asthma with exertional symptoms were included. EILO diagnosis was made if Maat score was > 2 for patients with CLE-test or if there were inspiratory anomalies on PFTs and LC. The sensitivity and specificity of LC and PFTs as diagnostic tools were calculated considering CLE-test as the gold standard.
Results
Sixty two patients were referred to our center for EIIS or uncontrolled asthma with exertional symptoms. EILO was diagnosed in 28 patients (56%) with associated asthma in 9 patients (18%). The sensibility and specificity of LC for supraglottic anomalies were 75% and 60%, respectively. The sensibility and specificity of PFTs were 61% and 89%, respectively.
Conclusions
There was a high prevalence of EILO among patients with EIIS and uncontrolled asthma. Some clinical characteristics might guide the diagnosis. Nevertheless, CLE-test remained the gold standard for EILO diagnosis and identification of the dysfunctional upper airway site to provide specific management.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christensen PM, Thomsen SF, Rasmussen N, Backer V (2011) Exercise-induced laryngeal obstructions: prevalence and symptoms in the general public. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268:1313–1319
Johansson H, Norlander K, Berglund L, Janson C, Malinovschi A, Nordvall L, Nordang L, Emtner M (2015) Prevalence of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction and exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction in a general adolescent population. Thorax 70:57–63
Rundell KW, Spiering BA (2003) Inspiratory stridor in elite athletes. Chest 123:468–474
Carlsen K-H, Carlsen KCL (2002) Exercise-induced asthma. Paediatr Respir Rev 3:154–160
Rundell KW, Im J, Mayers LB, Wilber RL, Szmedra L, Schmitz HR (2001) Self-reported symptoms and exercise-induced asthma in the elite athlete. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:208–213
Maturo S, Hill C, Bunting G, Baliff C, Ramakrishna J, Scirica C, Fracchia S, Donovan A, Hartnick C (2011) Pediatric paradoxical vocal-fold motion: presentation and natural history. Pediatrics 128:e1443–e1449
Christopher KL, Wood RP 2nd, Eckert RC, Blager FB, Raney RA, Souhrada JF (1983) Vocal-cord dysfunction presenting as asthma. N Engl J Med 308:1566–1570
Christensen PM, Heimdal J-H, Christopher KL et al (2015) ERS/ELS/ACCP 2013 international consensus conference nomenclature on inducible laryngeal obstructions. Eur Respir Rev 24:445–450
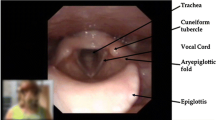
Heimdal J-H, Roksund OD, Halvorsen T, Skadberg BT, Olofsson J (2006) Continuous laryngoscopy exercise test: a method for visualizing laryngeal dysfunction during exercise. Laryngoscope 116:52–57
Maat RC, Røksund OD, Halvorsen T, Skadberg BT, Olofsson J, Ellingsen TA, Aarstad HJ, Heimdal J-H (2009) Audiovisual assessment of exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction: reliability and validity of observations. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266:1929–1936
Nielsen EW, Hull JH, Backer V (2013) High prevalence of exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction in athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 45:2030–2035
Buchvald F, Phillipsen LD, Hjuler T, Nielsen KG (2016) Exercise-induced inspiratory symptoms in school children. Pediatr Pulmonol 51:1200–1205
Heimdal J-H, Maat R, Nordang L (2018) Surgical intervention for exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 38:317–324
Maat RC, Hilland M, Røksund OD, Halvorsen T, Olofsson J, Aarstad HJ, Heimdal J-H (2011) Exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction: natural history and effect of surgical treatment. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268:1485–1492
Taverne J, Ramon P, Fournier C, Fry S, Wallaert B (2014) Diagnostic de la dysfonction des cordes vocales à l’exercice dans l’asthme sévère. La Presse Médicale 43:e393–e400
Kelly HW, Sternberg AL, Lescher R et al (2012) Effect of inhaled glucocorticoids in childhood on adult height. N Engl J Med 367:904–912
Gartner-Schmidt JL, Shembel AC, Zullo TG, Rosen CA (2014) Development and validation of the Dyspnea Index (DI): a severity index for upper airway-related dyspnea. J Voice 28:775–782
Giraud L, Wuyam B, Destors M, Atallah I (2021) Exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction: from clinical examination to continuous laryngoscopy during exercise. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anorl.2021.02.005
Shembel AC, Hartnick CJ, Bunting G, Ballif C, Vanswearingen J, Shaiman S, Johnson A, de Guzman V, Verdolini Abbott K (2018) The study of laryngoscopic and autonomic patterns in exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 127:754–762
Røksund OD, Maat RC, Heimdal JH, Olofsson J, Skadberg BT, Halvorsen T (2009) Exercise induced dyspnea in the young. Larynx as the bottleneck of the airways. Respir Med 103:1911–1918
Clemm HSH, Sandnes A, Vollsæter M, Hilland M, Heimdal J-H, Røksund OD, Halvorsen T (2018) The heterogeneity of exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 197:1068–1069
Liyanagedara S, McLeod R, Elhassan HA (2017) Exercise induced laryngeal obstruction: a review of diagnosis and management. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274:1781–1789
Garcia de la Rubia S, Pajarón-Fernandez MJ, Sanchez-Solís M, Martinez-Gonzalez Moro I, Perez-Flores D, Pajarón-Ahumada M (1998) Exercise-induced asthma in children: a comparative study of free and treadmill running. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 80:232–236
Thompson DM (2007) Abnormal sensorimotor integrative function of the larynx in congenital laryngomalacia: a new theory of etiology. Laryngoscope 117:1–33
Christopher KL (2006) Understanding vocal cord dysfunction: a step in the right direction with a long road ahead. Chest 129:842–843
Parsons JP, Kaeding C, Phillips G, Jarjoura D, Wadley G, Mastronarde JG (2007) Prevalence of exercise-induced bronchospasm in a cohort of varsity college athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:1487–1492
Halvorsen T, Walsted ES, Bucca C et al (2017) Inducible laryngeal obstruction: an official joint European Respiratory Society and European Laryngological Society statement. Eur Respir J. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.02221-2016
Røksund OD, Heimdal J-H, Clemm H, Vollsæter M, Halvorsen T (2017) Exercise inducible laryngeal obstruction: diagnostics and management. Paediatr Respir Rev 21:86–94
Christopher KL, Morris MJ (2010) Vocal cord dysfunction, paradoxic vocal fold motion, or laryngomalacia? Our understanding requires an interdisciplinary approach. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 43:43–66 (viii)
Andrianopoulos MV, Gallivan GJ, Gallivan KH (2000) PVCM, PVCD, EPL, and irritable larynx syndrome: what are we talking about and how do we treat it? J Voice 14:607–618
Tilles SA, Ayars AG, Picciano JF, Altman K (2013) Exercise-induced vocal cord dysfunction and exercise-induced laryngomalacia in children and adolescents: the same clinical syndrome? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 111:342-346.e1
Shembel AC, Hartnick CJ, Bunting G, Ballif C, Shaiman S, de Guzman V, Abbott KV (2019) Perceptual clinical features in exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction (EILO): toward improved diagnostic approaches. J Voice 33:880–893
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Giraud, L., Destors, M., Clin, R. et al. Diagnostic work-up of exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 1273–1281 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-022-07654-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-022-07654-7