Abstract
Introduction
Chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyposis (CRSsNP) and Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP) present distinct tissue remodeling processes. The proteins involved in the process of tissue remodeling have their production and activity related to the inflammatory environment they are. This study aimed to evaluate the protein expression of BMP-7, MMP-9, TGF-β in chronic sinusitis with and without nasal polyposis and their relations with IL-6 and IL-10.
Methods
Cross-sectional observational study with 86 participants was divided into three groups: patients with CRSwNP (n = 34), patients with CRSsNP (n = 26), and a control group (CG) without inflammatory disease of the nasal mucosa (n = 26). The primary outcomes were the concentrations of BMP-7, MMP-9, TGF-β, IL-6, and IL-10. Secondary outcomes were the correlations of these markers.
Results
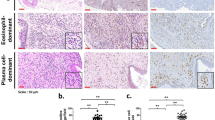
The TGF-β dosage was elevated in the CRSsNP group and reduced in the CSwNP group. The dosage of IL-6 was higher in the CSwNP group, and the IL-10 dosage lower in the groups with sinusitis, and IL-10 was positively correlated with BMP-7 in all groups. There was a negative correlation between IL-6 and IL-10 in all groups observed. The correlation between MMP-9 and interleukins was lost in the CRSsNP group. There was a positive correlation between TGF-β and IL-6 in the CG, and negative in the CRSsNP group.
Conclusion
An inflammation shown in rhinosinusitis with an increase in IL-6 and decrease in IL-10 when compared with the control group; only TGF-β was altered in the tissue remodeling process when compared with BMP-7 and MMP-9 in rhinosinusitis. There is a loss of correlation between tissue remodeling proteins and interleukins studied in CRSsNP.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, Hellings PW, Kern R, Reltsma S et al (2020) European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps. Rhinology 58(Suppl. 29):1–464. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhin20.600
Pezato R, Voegels RL, Pinto Bezerra TF, Perez-Novo C, Stamm AC, Gregorio LC (2014) Mechanical dysfunction in the mucosal oedema formation of patients with nasal polyps. Rhinology 52(2):162–166. https://doi.org/10.4193/rhin13.066
Van Bruaene N, Derycke L, Perez-Novo CA, Gevaert P, Holtappels G, De Ruyck N, Culiver C, Cauwenberge PV, Barchet C (2009) TGF-beta signaling and collagen deposition in chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124(2):253-259e1-2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2009.04.013
Meng J, Zhou P, Liu Y, Liu F, Yi X, Liu S, Holtappels G, Bachert C, Zhang N (2013) The development of nasal polyp disease involves early nasal mucosal inflammation and remodelling. PLoS One 8:e82373
Van Buraene N, Pérez-Novo CA, Basinski TM, Van Zele T, Holtappels G, RuyckN De, Schmidt-Weber C, Akids C, Cauwenberge PV, Bachert C, Geavaert P (2008) T-cell regulation in chronic paranasal sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 121:1435-1441.e1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2008.02.018
Gazzerro E, Canalis E (2006) Bone morphogenetic proteins and their antagonists. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 7:51–65
Bragdon B, Moseychuk O, Saldanha S, King D, Julian J, Nohe A (2011) Bone morphogenetic proteins: a critical review. Cell Signal 23(4):609–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.10.003
Yang T, Chen M, Sun T (2013) Simvastatin attenuates TGF-beta1-unduced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human alveolar epithelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 31:863–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1159/000350104
Izumi N, Mizuguchi S, Inagaki Y, Saika S, Kawada N, Nakajima Y, Inoue K, Suehiro C, Friedman SL, Ikeda K (2006) BMP-7 opposes TGF-beta1-mediated collagen induction in mouse pulmonar myofibroblasts through Id2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290(1):L120–L126. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00171.2005
Zeisberg M, Bottiglio C, Kumar N, Maeshima Y et al (2003) Bone morphogenic protein-7 inhibits progression of chronic renal fibrosis associated with two genetic mouse models. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285(6):F1060–F1067. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00191.2002
Parks WC, Wilson CL, Lopez-Boado YS (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 4:617–629
Watelet JB, Bachert C, Claseys C, Van Cauwernberge P (2004) Matrix metalloproteinase MMP-7, MMP-9 and their tissue inhibitor TIMP-1: expression in chronic sinusitis vs nasal polyposis. Allergy 59:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1398-9995.2003.00364.x
Li X, Meng J, Qiao X, Liu Y, Liu F, Zhang N, Zhang J, Holtappels G, Luo B, Zhou P, Zheng Y, Lin P, Liu S, Bachert C (2010) Expression of TGF, matrix metalloproteinases, and tissue inhibitors in Chinese chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immnuol 125:1061–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2010.02.023
Gaffar O, Lavigne F, Kamil A, Renzi P, Hamid Q (1998) Interleukin-6 expression in chronic sinusitis: colocalization of gene transcripts to eosinophils, macrophages, T lymphocytes, and mast cells. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118:504–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0194-5998(98)70209-8
Iyer SS, Cheng G (2012) Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit Rev Immunol 32(1):23–63. https://doi.org/10.1615/CritRevImmunol.v32.i1.30
Peter AT, Kato A, Zhang N, Conley D, Suh L, Tancowny B, Carter D, Carr T, Radtke M, Hulse KE, Seshadri S, Chandra R, Grammer LC, Harris KE, Kern R, Schleimer RP (2010) Evidence for altered activity of the IL-6 pathway in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125(2):397-403.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2009.10.072
Ozkara S, Keles E, Ilhan N, Gungor H, Kaygusuz I, Alpay HC (2012) The relationship between Th1/Th2 balance and 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) in patients with nasal polyposis. European archives of otorhinolaryngology: official journal of the European Federation of Oto-Rhino-Laryngological Societies. Severity (Objective) 12:2519–2524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-1967-x
Baba S, Kagoya R, Kondo K, Suzukawa M, Ohta K, Yamasoba T (2015) T-cell phenotypes in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Japanese patients. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol Severity (Objective) 33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-015-0100-2
Kim DW, Eun KM, Jin HR, Cho SH, Kim DK (2016) Prolonged allergen exposure is associated with increased thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression and Th2-skewing in mouse models of chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope Severity (Objective). https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.26004
Shen Y, Hu GH, Kang HY, Tang XY, Hong SL (2014) Allergen induced Treg response in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of patients with nasal polyposis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 4:300–307. https://doi.org/10.12932/AP0469.32.4.2014
Zhang Q, Wang CS, Han DM, Sy C, Huang Q, Sun Y, Fan EZ, Li Y, Zhou B (2013) Differential expression of Toll-like receptor pathway genes in chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps. Acta Otolaryngol 2:165–173. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2012.717713 (PMID: 23157229)
Wu D, Wang J, Zhang M (2016) Altered Th17/Treg ratio in nasal polyps with distinct cytokine profile: association with patterns of inflammation and mucosal remodeling medicine. Severity (objective) (10):e2998. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000002998
Pezato R, Świerczyńska-Krępa M, Niżankowska-Mogilnicka E, Holtappels G, De Ruyck N, Sanak M, Derycke L, Crombruggen KV, Bachert C, Pérez-Novo CA (2016) Systemic expression of inflammatory mediators in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps with and without aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease. Cytokine 77:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2015.10.011
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Zaravinos A, Soufla G, Bizakis J, Spandidos DA (2008) Expression analysis of VEGFA, FGF2, TGFbeta1, EGF and IGF1 in human nasal polyposis. Oncol Rep 19:385–391. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.19.2.385
Pezato R, Voegels RL, Stamm AC, Gregório LC (2016) Why we should avoid using inferior turbinate tissue as control to nasal polyposis studies. Acta Otolaryngol 136(9):973–975. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2016.1166262
Jones SA (2005) Directing transition from innate to acquired immunity: defining a role for IL-6. J Immunol 173:3463–3468. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.175.6.3463
Kaplanski G, Marin V, Montero-Julian F, Mantovani A, Farnarier C (2003) IL-6: a regulator of the transition from neutrophil to monocyte recruitment during inflammation. Trends Immunol 24(1):25–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1471-4906(02)00013-3
Romano M, Sironi M, Toniatti C, Polentarutti N, Fruscella P, Ghezzi P, Faggioni R, Luini W, Hinsbergh V, Sozzani S, Bussolino F, Poli V, Ciliberto G, Mantovani A (1997) Role of IL-6 and its soluble receptor in induction of chemokines and leukocyte recruitment. Immunity 6:315–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80334-9
Bernstein JM, Ballow M, Rich G, Allen C, Swanson M, Dmochowski J (2004) Lymphocyte subpopulations and cytokines in nasal polyps: is there a local immune system in the nasal polyp? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:526–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2003.12.022
Sanchez-Segura J, Brieva JA, Rodriguez C (1998) T lymphocytes that infiltrate nasal polyps have a specialized phenotype and produce a mixed TH1/TH2 pattern of cytokines. J Allergy Clin Immunol 102:953–960. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-6749(98)70333-1
Gevaert P, Holtappels G, Johansson SG, Cuvelier C, Cauwenberge P, Bachert C (2005) Organization of secondary lymphoid tissue and local IgE formation to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins in nasal polyp tissue. Allergy 60:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2004.00621.x
Ganeshan K, Bryce PJ (2012) Regulatory T cells enhance mast cell production of IL-6 via surface-bound TGF-β. J Immunol 188(2):594–603. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1102389
Pezato R, Balsalobre L, Lima M, Bezerra TF, Voegels RL, Gregório LC, Stamm AC, van Zele T (2013) Convergence of two major pathophysiologic mechanisms in nasal polyposis: immune response to Staphylococcus aureus and airway remodeling. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 42:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1916-0216-42-27
Iyer SS, Cheng G (2012) Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit Rev Immunol 32(1):23–63. Epub 21 March 2012
Xu J, Han R, Kim DW, Mo J-H, Jin Y, Rha K-S, Kim YM (2016) Role of interleukin-10 on nasal polypogenesis in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. PLoS One 11(9):e0161013. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0161013
Okano M, Fujiwara T, Kariya S, Higaki T, Haruna T, Matsushita O, Noda Y, Makihara S, Kanai K, Noyama Y, Taniguchi M, Nishizaki K (2014) Cellular responses to Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Allergol Int 63(4):563–573. https://doi.org/10.2332/allergolint.14-OA-0703S1323-8930(15)30069-1[pii]
Oliveira PWB, Pezato R, Agudelo JSH, Perez-Novo CA, Berghe WV, Câmara NO, de Almeida DC, Gregorio LC (2017) Nasal polyp-derived mesenchymal stromal cells exhibit lack of immune-associated molecules and high levels of stem/progenitor cells markers. Front Immunol 8:39. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00039
Zeisberg M, Shah AA, Kalluri R (2005) Bone morphogenic protein-7 induces mesenchymal to epithelial transition in adult renal fibroblasts and facilitates regeneration of injured kidney. J Biol Chem 280(9):8094–8100. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M413102200
Pezato R, de Almeida DC, Bezerra TF, Silva FA, Gregório LC, Voegels RL et al (2014) Immunoregulatory effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the nasal polyp microenvironment. Mediators Inflamm 2014:583409. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/583409
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lucas, B.R., Voegels, R.L., do Amaral, J.B. et al. BMP-7, MMP-9, and TGF-β tissue remodeling proteins and their correlations with interleukins 6 and 10 in chronic rhinosinusitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278, 4335–4343 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06722-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06722-8