Abstract
Purpose
This study aims to understand the factors contributing to the severity of oropharyngeal dysphagia and its persistence in the sub-acute phase of stroke.
Methods
We retrospectively collected the data of all the patients suffering from a stroke in the last year. The severity of stroke was reported according to the NIHSS score. All the patients were evaluated with the Dysphagia Risk Score and with a FEES. We classified the Dysphagia Risk Score and FEES results using the PAS score and ASHA-NOMS levels. The data were analysed statistically with ANOVA test, Student’s t test and Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
Results
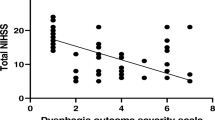
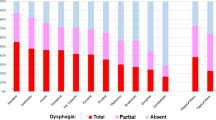
A series of 54 patients were evaluated. The ANOVA test did not find any difference in the mean score of Dysphagia Risk Score, PAS and ASHA-NOMS when compared with the brain area of stroke. An NIHSS at hospital admission (stroke unit) of more than 12 was predictive of ASHA-NOMS score 1–4 after 60 days (p < 0.05). A PAS score between 6 and 8 at first FEES evaluation was predictive of poor (1–4) ASHA-NOMS score after 60 days (p < 0.01). A moderate positive linear correlation was found between NIHSS score and both PAS (r 0.65) and Dysphagia Risk Score (r 0.50); a moderate negative linear correlation was recorded between NIHSS and ASHA-NOMS (r − 0.66) scores.
Conclusion
In the sub-acute phase of stroke, the predictive factors of persistent dysphagia are not linked to the damaged neuroanatomical region and others factors such as NIHSS value and high PAS score seem more useful.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Otto DM, Ribeiro MC, Barea LM, Mancopes R, Almeida ST (2016) Association between neurological injury and the severity of oropharyngeal dysphagia after stroke. Codas 28(6):724–729
Kuklina EV, Tong X, George MG, Bansil P (2012) Epidemiology and prevention of stroke: a worldwide perspective. Expert Rev Neurother 12(2):199–208
Smithard DG, O’Neill PA, England RE et al (1997) The natural history of dysphagia following a stroke. Dysphagia 12(4):188–193
Benvenuti CM, Pereira LM, Revay MA. Disfagia pos-acidente vascular cerebral isquemico unilaterale m adultos: estudo de caso (thesis). Florianopolis (SC). Centro de EspecializaḈao em Fonoaudiologia clinica; 2005: 29p.
González-Fernández M, Ottenstein L, Atanelov L, Christian AB (2013) Dysphagia after stroke: an overview. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep 1(3):187–196
Carnaby-Mann G, Lenius K (2008) The bedside examination in dysphagia. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 19:747–768
Heijnen BJ, Böhringer S, Speyer R (2020) Prediction of aspiration in dysphagia using logistic regression: oral intake and self-evaluation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277(1):197–205
Kelly AM, Leslie P, Beale T et al (2006) Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing and videofluoroscopy: does examination type influence perception of pharyngeal residue severity? Clin Otolaryngol 31:425–432
Hsueh HW, Chen YC, Chang CF, Wang TG, Chiu MJ (2020) Predictors and associating factors of nasogastric tube removal: clinical and brain imaging data analysis in post-stroke dysphagia. J Formos Med Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2020.02.015
Humbert IA, Fitzgerald ME, McLaren DG, Johnson S, Porcaro E, Kosmatka K et al (2009) Neurophysiology of swallowing: effects of age and bolus type. Neuroimage 44:982–991
Bass N (1997) The neurology of swallowing. In: Groher M (ed) Dysphagia diagnosis and management. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, pp 23–33
Dehaghani SE, Yadegari F, Asgari A, Chitsaz A, Karami M (2016) Brain regions involved in swallowing: evidence from stroke patients in a cross-sectional study. J Res Med Sci 14(21):45
Mosier K, Bereznaya I (2001) Parallel cortical networks for volitional control of swallowing in humans. Exp Brain Res 140(3):280–289
Martin RE, Goodyear BG, Gati JS, Menon RS (2001) Cerebral cortical representation of automatic and volitional swallowing in humans. J Neurophysiol 85:938–950
Hamdy S, Rothwell JC, Brooks DJ, Bailey D, Aziz Q, Thompson DG (1999) Identification of the cerebral loci processing human swallowing with H2(15) O PET activation. J Neurophysiol 81:1917–1926
Lowell SY, Reynolds RC, Chen G, Horwitz B, Ludlow CL (2012) Functional connectivity and laterality of the motor and sensory components in the volitional swallowing network. Exp Brain Res 219:85–96
Aho K, Harmsen P, Hatano S, Marquardsen J, Smirnov VE, Strasser T (1980) Cerebrovascular disease in the community: results of a WHO collaborative study. Bull World Health Organ 58:113–130
Tatu L, Moulin T, Vuillier F, Bogousslavsky J (2012) Arterial territories of the human brain. Front Neurol Neurosci 30:99–110
Brott T, Adams HP Jr, Olinger CP, Marler JR, Barsan WG, Biller J, Spilker J, Holleran R, Eberle R, Hertzberg V (1989) Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: a clinical examination scale. Stroke 20(7):864–870
Amitrano A (2018) Dysphagia risk score. Audiologia Foniatria 3:15–16
Steele CM, Grace-Martin K (2017) Reflections on clinical and statistical use of the penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 32:601–616
O’Neil KH, Purdy M, Falk J, Gallo L (1999) The dysphagia outcome and severity scale. Dysphagia 14:139–145
Vose A, Nonnenmacher J, Singer ML, Gonzalez FM (2014) Dysphagia management in acute and sub acute stroke. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep 2(4):197–206
Suntrup S, Kemmling A, Warnecke T, Hamacher C, Oelemberg S, Niederstadt T, Heindel W, Wiendl H, Dziewas R (2015) The impact of lesion on dysphagia incidence, pattern, and complications in acute stroke. Part 1: dysphagia incidence, severity and aspiration. Eur J Neur 22:832–838
Cohen DL, Roffe C, Beavan J, Blackett B, Fairfield CA, Hamdy S, Harvard D, McFarlane M, McLauglinn C, Randall M, Robson K, Scutt P, Smith C, Smithard D, Sprigg N, Warusevitane A, Watkins C, Woodhouse L, Bath PM (2016) Post stroke dysphagia: a review and design considerations for future trials. Int J Stroke 11:399–411
Hamdy S, Aziz Q, Rothwell JC, Crone R, Hughes D, Tallis RC, Thompson DG (1997) Explaining oropharyngeal dysphagia after unilateral hemispheric stroke. Lancet 350:686–692
Hamdy S, Rothwell JC, Aziz Q, Thompson DG (2000) Organization and reorganization of the human swallowing motor cortex: implication for recovery after stroke. Clin Sci 98:151–157
Kim YK, Cha JH, Lee KY (2019) Comparison of dysphagia between infratentorial and supratentorial stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med 43(2):149–155
Kumar S, Doughty C, Doros G, Selim M, Lahoti S, Gokhale S, Schlaug G (2014) Recovery of swallowing after dysphagic stroke: an analysis of prognostic factors. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 23(1):56–62
Toscano M, Cecconi E, Capiluppi E, Viganò A, Bertora P, Campiglio L, Mariani C, Petolicchio B, Sasso D’Elia T, Verzina A, Vicenzini E, Fiorelli M, Cislaghi G, Di Piero V (2015) Neuroanatomical, clinical and cognitive correlates of post-stroke dysphagia. Eur Neurol 74(3–4):171–177
English KL, Paddon-Jones D (2010) Protecting muscle mass and function in older adults during bed rest. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 13:34–39
Jardine M, Miles A, Allen J (2018) Dysphagia onset in older adults during unrelated hospital admission: quantitative videofluoroscopic measures. Geriatrics (Basel) 3(4):66
Kortebein P, Symons TB, Ferrando A, Paddon-Jones D, Ronsen O, Protas E, Conger S, Lombeida J, Wolfe R, Evans WJ (2008) Functional impact of 10 days of bed rest in healthy older adults. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci 63:1076–1081
Maeda K, Koga T, Akagi J (2016) Tentative nil per os leads to poor outcomes in older adults with aspiration pneumonia. Clin Nutr 35:1147–1152
Arreola V, Vilardell N, Ortega O, Rofes L, Muriana D, Palomeras E, Álvarez-Berdugo D, Clavé P (2019) Natural history of swallow function during the three-month period after stroke. Geriatrics (Basel) 4(3):42
Mann G, Hankey GJ, Cameron D (1999) Swallowing function after stroke: prognosis and prognostic factors at 6 months. Stroke 30:744–774
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Stefano, A., Dispenza, F., Kulamarva, G. et al. Predictive factors of severity and persistence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in sub-acute stroke. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278, 741–748 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06429-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06429-2