Abstract
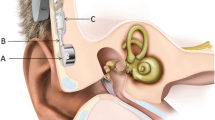
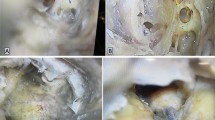
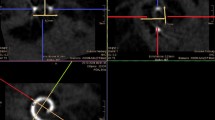
The objective of the present paper was to acquire information about the mastoidectomy size necessary to obtain an optimal placement of the direct acoustic cochlear implant actuator and fixation system. Ten human cadaveric temporal bones were dissected and implanted with direct acoustic cochlear implant. Mastoidectomy size was determined after implantation in each temporal bone. A bone bed for the receiver/stimulator, mastoidectomy and a large posterior tympanotomy were drilled out. The mastoidectomy was progressively enlarged posteriorly in small steps until the actuator template was judged adequately oriented to enable passage of the rod through the posterior tympanotomy without any contact with the bony walls. The distance between different landmarks in the mastoidectomy was measured. All measured values showed a high degree of consistency, with limited median absolute deviation values. One of the most critical measure, i.e. the distance between the posterior margin of the mastoidectomy to the superior rim of the bony external ear canal wall, ranged from 13 to 16 mm with a median value of 15 mm. Prior knowledge of the ideal size of the mastoidectomy for direct acoustic cochlear implant facilitates the positioning of the fixation system and may save time during implant surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernhard H, Stieger C, Perriard Y (2011) Design of a semi-implantable hearing device for direct acoustic cochlear stimulation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58:420–428
Häusler R, Stieger C, Bernhard H, Kompis M (2008) A novel implantable hearing system with direct acoustic cochlear stimulation. Audiol Neurootol 13:247–256
Lenarz T, Zwartenkot JW, Stieger C et al (2013) Multi-center study with a direct acoustic cochlear implant. Otol Neurotol 34:1215–1225
Kasic JF, Fredrickson JM (2001) The otologics MET ossicular stimulator. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 34:501–513
Luers JC, Hüttenbrink K-B, Zahnert T, Bornitz M, Beutner D (2013) Vibroplasty for mixed and conductive hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 34:1005–1012
Lenarz T, Verhaert N, Desloovere C, et al (2014) A comparative study on speech in noise understanding with a direct acoustic cochlear implant in subjects with severe to profound mixed hearing loss. Audiol Neurotol 19:164–174
Kludt E, Büchner A, Schwab B, Lenarz T, Maier H (2016) Indication of direct acoustical cochlea stimulation in comparison to cochlear implants. Hear Res 340:185–190
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful to Christiane D’hondt for her assistance in the English revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author has no financial relationship for the manuscript and work.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiorino, F., Amadori, M. Mastoidectomy dimensions for direct acoustic cochlear implantation: a human cadaveric temporal bone study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 2155–2160 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4504-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4504-0