Abstract
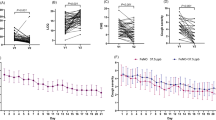
Eosinophilia occurs in up to 75–90% of nasal polyps in Caucasians. The chemokines eotaxin and RANTES increase eosinophil recruitment, activation, and survival, and these chemokines are significantly expressed in nasal polyps. We hypothesized that eotaxin and RANTES plasma levels might be correlated with disease severity. We compared the eotaxin and RANTES plasma levels in 20 Taiwanese patients with chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps and 20 Taiwanese healthy controls. Eotaxin and RANTES plasma levels were measured by ELISA and disease severity was scored by CT scans. Compared to controls, patients with nasal polyps had significantly elevated plasma levels of eotaxin and RANTES and increased peripheral blood eosinophils (p < 0.001). Eotaxin plasma levels were significantly correlated with disease severity in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis to a greater extent than were RANTES levels. RANTES and eotaxin levels were also positively correlated with the percentages of peripheral blood eosinophils. Eotaxin plasma levels are significantly correlated with disease severity in Taiwanese patients with nasal polyposis to a greater degree than are RANTES levels. Additional studies are needed to assess whether eotaxin plasma levels can be used to monitor disease progression and attenuation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wise MT, Hagaman DD (2007) An immunological approach to chronic and recurrent sinusitis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 15:10–17
Ramanathan M Jr, Lane AP (2007) Innate immunity of the sinonasal cavity and its role in chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136:348–356
Pawankar R (2003) Nasal polyposis an update: editorial review. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 3:1–6
Otto BA, Wenzel SE (2008) The role of cytokines in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 16:270–274
Hamilos DL, Leung DY, Huston DP, Kamil A, Wood R, Hamid Q (1998) GM-CSF, IL-5 and RANTES immunoreactivity and mRNA expression in chronic hyperplastic sinusitis with nasal polyposis (NP). Clin Exp Allergy 28:1145–1152
Yoshifuku K, Matsune S, Ohori J, Sagara Y, Fukuiwa T, Kurono Y (2007) IL-4 and TNF-alpha increased the secretion of eotaxin from cultured fibroblasts of nasal polyps with eosinophil infiltration. Rhinology 45:235–241
Nonaka M, Pawankar R, Fukumoto A, Ogihara N, Sakanushi A, Yagi T (2004) Induction of eotaxin production by interleukin-4, interleukin-13 and lipopolysaccharide by nasal fibroblasts. Clin Exp Allergy 34:804–811
Fan GK, Wang H, Takenaka H (2007) Eosinophil infiltration and activation in nasal polyposis. Acta Otolaryngol 127:521–526
Newman LJ, Platts-Mills TA, Phillips CD, Hazen KC, Gross CW (1994) Chronic sinusitis. Relationship of computed tomographic findings to allergy, asthma, and eosinophilia. JAMA 271:363–367
Stoop AE, van der Heijden HA, Biewenga J, van der Baan S (1993) Eosinophils in nasal polyps and nasal mucosa: an immunohistochemical study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 91:616–622
Kountakis SE, Arango P, Bradley D, Wade ZK, Borish L (2004) Molecular and cellular staging for the severity of chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 114:1895–1905
Bartels J, Maune S, Meyer JE, Kulke R, Schlüter C, Röwert J, Christophers E, Schröder JM (1997) Increased eotaxin-mRNA expression in non-atopic and atopic nasal polyps: comparison to RANTES and MCP-3 expression. Rhinology 35:171–174
Bernstein JM (2001) The molecular biology of nasal polyposis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 1:262–267
Shin SH, Park JY, Jeon CH, Choi JK, Lee SH (2000) Quantitative analysis of eotaxin and RANTES messenger RNA in nasal polyps: association of tissue and nasal eosinophils. Laryngoscope 110:1353–1357
Zhang N, Van Zele T, Perez-Novo C, Van Bruaene N, Holtappels G, DeRuyck N, Van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C (2008) Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122:961–968
Benninger MS, Ferguson BJ, Hadley JA et al (2003) Adult chronic rhinosinusitis: definitions, diagnostics, epidemiology, and pathophysiology. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129(3 suppl):S1–S32
Lund VJ, Kennedy DW (1997) Staging for rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 117:S35–S40
Stewart MG, Johnson RF (2004) Chronic sinusitis: symptoms versus CT scan findings. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 12:27–29
Pruna X (2003) Morpho-functional evaluation of osteomeatal complex in chronic sinusitis by coronal CT. Eur Radiol 13:1461–1468
Hopkins C, Browne JP, Slack R, Lund V, Brown P (2007) The Lund–Mackay staging system for chronic rhinosinusitis: how is it used and what does it predict? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137:555–561
Couto LG, Fernades AM, Brandao DF, Santi Neto D, Valera FC, Anselmo-Lima WT (2008) Histological aspects of rhinosinusal polyps. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 74:207–212
Van Cauwenberge P, Van Zele T, Bachert C (2008) Chronic rhinonsinusitis and nasal polyposis: the etiopathogenesis revealed? Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg 70:305–322
Bernstein JM, Ballow M, Schlievert PM, Rich G, Allen C, Dryja D (2003) A superantigen hypothesis for the pathogenesis of chronic hyperplastic sinusitis with massive nasal polyposis. Am J Rhinol 17:321–326
Chan Y, Kuhn FA (2009) An update on the classifications, diagnosis, and treatment of rhinosinusitis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 17:204–208
Di Lorenzo G, Drago A, Esposito Pellitteri M, Candore G, Colombo A, Gervasi F, Pacor ML, Purello D’Ambrosio F, Caruso C (2001) Measurement of inflammatory mediators of mast cells and eosinophils in native nasal lavage fluid in nasal polyposis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 125:164–175
Zadeh MH, Banthia V, Anand VK, Huang C (2002) Significance of eosinophilia in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol 16:313–317
Meyer JE, Bartels J, Görögh T, Sticherling M, Rudack C, Ross DA, Maune S (2005) The role of RANTES in nasal polyposis. Am J Rhinol 19:15–20
Allen JS, Eisma R, LaFreniere D, Leonard G, Kreutzer D (1998) Characterization of the eosinophil chemokine RANTES in nasal polyps. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 107:416–420
Danielsen A, Tynning T, Brokstad KA, Olofsson J, Davidsson A (2006) Interleukin 5, IL6, IL12, IFN-gamma, RANTES and Fractalkine in human nasal polyps, turbinate mucosa and serum. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263:282–289
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the academic cooperative research projects of Taipei Medical University Hospital and Taipei Medical University (96TMU-TMUH-20).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chao, PZ., Chou, CM. & Chen, CH. Plasma RANTES and eotaxin levels are correlated with the severity of chronic rhinosinusitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269, 2343–2348 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-1927-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-1927-5