Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study is to evaluate the sperm DNA fragmentation index (DFI) in oocyte donation cycles and correlate it with the sperm parameters, the male characteristics, the embryo quality and the outcome of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Methods
A total of 150 couples participating in an oocyte donation program were included in the study. Sperm samples were assessed by conventional sperm analysis. DFI was evaluated using the Halosperm kit, a sperm chromatin dispersion test (SCD).
Results
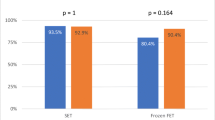
The relations between DNA damage and epidemiological male factors (age, height, weight), standard semen parameters (concentration, total and forward motility, and morphology), and embryological and clinical parameters (fertilization rate, total blastocyst number, number of good quality blastocyst, clinical pregnancy) were analyzed. DFI was positively correlated with advanced male age (r = 0.23, p < 0.05) and negatively correlated with total sperm and forward motility (r = − 0.29, r = − 0.27, respectively; p < 0.05). DFI was not significantly correlated with pregnancy outcome in oocyte donation cycles (r = − 0.05, p > 0.05). When good quality blastocysts were chosen, a trend toward the development of good quality embryos was detected in the presence of a low DFI (r = − 0.20, p = 0.08).
Conclusions
DFI does not significantly affect the outcome of ICSI in oocyte donation cycles. Even in cases of advanced paternal age that a high DFI resulted sperm DNA fragmentation seems not to adversely affect the final outcome.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schulte RT, Ohl DA, Sigman M, Smith GD (2010) Sperm DNA damage in male infertility: etiologies, assays, and outcomes. J Assist Reprod Genet 27:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-009-9359-x
Sakkas D, Alvarez JG (2010) Sperm DNA fragmentation: mechanisms of origin, impact on reproductive outcome, and analysis. Fertil Steril 93:1027–1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.10.046
Avendaño C, Franchi A, Duran H, Oehninger S (2010) DNA fragmentation of normal spermatozoa negatively impacts embryo quality and intracytoplasmic sperm injection outcome. Fertil Steril 94:549–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.02.050
Li Z, Wang L, Cai J, Huang H (2006) Correlation of sperm DNA damage with IVF and ICSI outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Assist Reprod Genet 23:367–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-006-9066-9
Aitken RJ, Gordon E, Harkiss D, Twigg JP, Milne P, Jennings Z, Irvine DS (1998) Relative impact of oxidative stress on the functional competence and genomic integrity of human spermatozoa. Biol Reprod 59:1037–1046
Taherzadeh S, Khalili MA, Agha-Rahimi A, Anbari F, Ghazali S, Macchiarelli G (2017) Vitrification increased vacuolization of human spermatozoa: application of MSOME technology. J Reprod Infertil 18:225–230
Nottola SA, Albani E, Coticchio G, Palmerini MG, Lorenzo C, Scaravelli G, Borini A, Levi-Setti PE, Macchiarelli G (2016) Freeze/thaw stress induces organelle remodeling and membrane recycling in cryopreserved human mature oocytes. J Assist Reprod Genet 33:1559–1570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-016-0798-x
Palmerini MG, Antinori M, Maione M, Cerusico F, Versaci C, Nottola SA, Macchiarelli G, Khalili MA, Antinori S (2014) Ultrastructure of immature and mature human oocytes after cryotop vitrification. J Reprod Dev 60:411–420. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.2014-027
Agha-Rahimi A, Khalili MA, Nottola SA, Miglietta S, Moradi A (2016) Cryoprotectant-free vitrification of human spermatozoa in new artificial seminal fluid. Andrology 4:1037–1044. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.12212
Chohan KR, Griffin JT, Lafromboise M, Jonge CJ, Carrell DT (2006) Comparison of chromatin assays for DNA fragmentation evaluation in human sperm. J Androl 27:53–59. https://doi.org/10.2164/jandrol.05068
Fernández JL, Muriel L, Goyanes V, Segrelles E, Gosálvez J, Enciso M, LaFromboise M, De Jonge C (2005) Simple determination of human sperm DNA fragmentation with an improved sperm chromatin dispersion test. Fertil Steril 84:833–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2004.11.089
Ribas-Maynou J, García-Peiró A, Fernández-Encinas A, Abad C, Amengual MJ, Prada E, Navarro J, Benet J (2013) Comprehensive analysis of sperm DNA fragmentation by five different assays: TUNEL assay, SCSA, SCD test and alkaline and neutral Comet assay. Andrology 1:715–722. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2047-2927.2013.00111.x
Fernández JL, Muriel L, Rivero MT, Goyanes V, Vazquez R, Alvarez JG (2003) The sperm chromatin dispersion test: a simple method for the determination of sperm DNA fragmentation. J Androl 24:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1939-4640.2003.tb02641.x
Cissen M, Wely MV, Scholten I, Mansell S, Bruin JP, Mol BW, Braat D, Repping S, Hamer G (2016) Measuring sperm DNA fragmentation and clinical outcomes of medically assisted reproduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 11:e0165125. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0165125
Kirkman-Brown JC, De Jonge C (2017) Sperm DNA fragmentation in miscarriage—a promising diagnostic, or a test too far? Reprod Biomed Online 34:3–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2016.12.002
Osman A, Alsomait H, Seshadri S, El-Toukhy T, Khalaf Y (2015) The effect of sperm DNA fragmentation on live birth rate after IVF or ICSI: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Reprod Biomed Online 30:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2014.10.018
Ioannou D, Tempest HG (2018) Does genome organization matter in spermatozoa? A refined hypothesis to awaken the silent vessel. Syst Biol Reprod Med 64:518–534. https://doi.org/10.1080/19396368.2017.1421278
Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (2013) The clinical utility of sperm DNA integrity testing: a guideline. Fertil Steril 99:673–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.12.049
Ménézo Y, Dale B, Cohen M (2010) DNA damage and repair in human oocytes and embryos: a review. Zygote 18:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0967199410000286
Vazharova R, Kremensky I (2016) Individual capacity for DNA repair and maintenance of genomic integrity: a fertile ground for studies in the field of assisted reproduction. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 30:419–433
Marchetti F, Essers J, Kanaar R, Wyrobek AJ (2007) Disruption of maternal DNA repair increases sperm-derived chromosomal aberrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:17725–17729. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0705257104
Gat I, Li N, Yasovich N, Antes R, Kuznyetsov V, Zohni K, Weizman NF, Librach C (2018) Sperm DNA fragmentation index does not correlate with blastocyst euploidy rate in egg donor cycles. Gynecol Endocrinol 34:212–216. https://doi.org/10.1080/09513590.2017.1379500
Esbert M, Pacheco A, Vidal F, Florensa M, Riqueros M, Ballesteros A, Garrido N, Calderón G (2011) Impact of sperm DNA fragmentation on the outcome of IVF with own or donated oocytes. Reprod Biomed Online 23:704–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2011.07.010
Prapas N, Prapas Y, Panagiotidis Y, Prapa S, Vanderzwalmen P, Schoysman R, Makedos G (2005) GnRH agonist versus GnRH antagonist in oocyte donation cycles: a prospective randomized study. Hum Reprod 20:1516–1520. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deh832
Prapas N, Tavaniotou A, Panagiotidis Y, Prapa S, Kasapi E, Goudakou M, Papatheodorou A, Prapas Y (2009) GnRH antagonists and endometrial receptivity in oocyte recipients: a prospective randomized trial. Reprod Biomed Online 18:276-281. https://www.rbmonline.com/Article/3602
López G, Lafuente R, Checa MA, Carreras R, Brassesco M (2013) Diagnostic value of sperm DNA fragmentation and sperm high-magnification for predicting outcome of assisted reproduction treatment. Asian J Androl 15:790–794. https://doi.org/10.1038/aja.2013.81
Petousis S, Prapas Y, Papatheodorou A, Margioula-Siarkou C, Papatzikas G, Panagiotidis Y, Karkanaki A, Ravanos K, Prapas N (2018) Fluorescence in situ hybridisation sperm examination is significantly impaired in all categories of male infertility. Andrologia 50:e12847. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12847
Gorczyca W, Traganos F, Jesionowska H, Darzynkiewicz Z (1993) Presence of DNA strand breaks and increased sensitivity of DNA in situ to denaturation in abnormal human sperm cells: analogy to apoptosis of somatic cells. Exp Cell Res 207:202–205
Rybar R, Kopecka V, Prinosilova P, Markova P, Rubes J (2011) Male obesity and age in relationship to semen parameters and sperm chromatin integrity. Andrologia 43:286–291. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0272.2010.01057.x
Tunc O, Bakos HW, Tremellen K (2011) Impact of body mass index on seminal oxidative stress. Andrologia 43:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0272.2009.01032.x
Chavarro JE, Toth TL, Wright DL, Meeker JD, Hauser R (2010) Body mass index in relation to semen quality, sperm DNA integrity, and serum reproductive hormone levels among men attending an infertility clinic. Fertil Steril 93:2222–2231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.01.100
Fariello RM, Pariz JR, Spaine DM, Cedenho AP, Bertolla RP, Fraietta R (2012) Association between obesity and alteration of sperm DNA integrity and mitochondrial activity. B J U Int 110:863–867. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10813.x
Tandara M, Bajic A, Tandara L, Sunj M, Jurisic Z, Jukic M (2013) Correlation between proportions of sperm with DNA fragmentation assessed by Halosperm test and values of standard quality parameters of semen and possible impact on embryo quality. Zdrav Vestn 82:298–307
Vagnini L, Baruffi RLR, Mauri AL, Petersen CG, Massaro FC, Pontes A, Oliveira JB, Franco JG Jr (2007) The effects of male age on sperm DNA damage in an infertile population. Reprod Biomed Online 15:514–519
Schmid TE, Eskenazi B, Baumgartner A, Marchetti F, Young S, Weldon R, Anderson D, Wyrobek AJ (2006) The effects of male age on sperm DNA damage in healthy non-smokers. Hum Reprod 22:180–187. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/del338
Frattarelli JL, Miller KA, Miller BT, Elkind-Hirsch K, Scott RT (2008) Male age negatively impacts embryo development and reproductive outcome in donor oocyte assisted reproductive technology cycles. Fertil Steril 90:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.06.009
Kaarouch I, Bouamoud N, Madkour A, Louanjli N, Saadani B, Assou S, Aboulmaouahib S, Amzazi S, Copin H, Benkhalifa M, Sefrioui O (2018) Paternal age: negative impact on sperm genome decays and IVF outcomes after 40 years. Mol Reprod Dev. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrd.22963
Irvine DS, Twigg JP, Gordon EL, Fulton N, Milne PA, Aitken R (2000) DNA integrity in human spermatozoa: relationships with semen quality. J Androl 21:33–44
Sheikh N, Amiri I, Farimani M, Najafi R, Hadeie J (2008) Correlation between sperm parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation in fertile and infertile men. Int J Reprod Biomed (Yazd) 6:13–18
Avendaño C, Oehninger S (2011) DNA fragmentation in morphologically normal spermatozoa: how much should we be concerned in the ICSI era? J Androl 32:356–363. https://doi.org/10.2164/jandrol.110.012005
Belloc S, Benkhalifa M, Cohen-Bacrie M, Dalleac A, Chahine H, Amar E, Zini A (2014) Which isolated sperm abnormality is most related to sperm DNA damage in men presenting for infertility evaluation. J Assist Reprod Genet 31:527–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-014-0194-3
Rafighdoost H, Farsi MM, Javadi M, Khafri S (2013) Relationship between sperm parameters and DNA fragmentation using a halosperm kit. Anat Sci J 10:79–86
Enciso M, Iglesias M, Galán I, Sarasa J, Gosálvez A, Gosálvez J (2011) The ability of sperm selection techniques to remove single-or double-strand DNA damage. Asian J Androl 13:764–768. https://doi.org/10.1038/aja.2011.46
Zini A, Sigman M (2009) Are tests of sperm DNA damage clinically useful? Pros and cons. J Androl 30:219–229. https://doi.org/10.2164/jandrol.108.006908
Yılmaz S, Zergeroğlu AD, Yılmaz E, Sofuoglu K, Delikara N, Kutlu P (2010) Effects of sperm DNA fragmentation on semen parameters and ICSI outcome determined by an improved SCD test, Halosperm. Int J Fertil Steril 4:73–78
Larson-Cook KL, Brannian JD, Hansen KA, Kasperson KM, Aamold ET, Evenson DP (2003) Relationship between the outcomes of assisted reproductive techniques and sperm DNA fragmentation as measured by the sperm chromatin structure assay. Fertil Steril 80:895–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0015-0282(03)01116-6
Morris ID, Ilott S, Dixon L, Brison DR (2002) The spectrum of DNA damage in human sperm assessed by single cell gel electrophoresis (Comet assay) and its relationship to fertilization and embryo development. Hum Reprod 17:990–998
Høst E, Lindenberg S, Smidt-Jensen S (2000) The role of DNA strand breaks in human spermatozoa used for IVF and ICSI. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 79:559–563. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0412.2000.079007559.x
Muriel L, Garrido N, Fernández JL, Remohí J, Pellicer A, de los Santos MJ, Meseguer M (2006) Value of the sperm deoxyribonucleic acid fragmentation level, as measured by the sperm chromatin dispersion test, in the outcome of in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil Steril 85:371–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2005.07.1327
Zhylkova I, Feskov O, Feskova I, Fedota O, Feskov V (2014) Sperm DNA fragmentation as a factor of male low reproductive function in IVF practice. Int J Biol 6:75–81
Twigg JP, Irvine DS, Aitken RJ (1998) Oxidative damage to DNA in human spermatozoa does not preclude pronucleus formation at intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod 13:1864–1871
Simon L, Murphy K, Shamsi MB, Liu L, Emery B, Aston KI, Hotaling J, Carrell DT (2014) Paternal influence of sperm DNA integrity on early embryonic development. Hum Reprod 29:2402–2412. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deu228
Virro MR, Larson-Cook KL, Evenson DP (2004) Sperm chromatin structure assay (SCSA®) parameters are related to fertilization, blastocyst development, and ongoing pregnancy in in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection cycles. Fertil Steril 81:1289–1295
Fatehi AN, Bevers MM, Schoevers E, Roelen BAJ, Colenbrander B, Gadella BM (2006) DNA damage in bovine sperm does not block fertilization and early embryonic development but induces apoptosis after the first cleavages. J Androl 27:176–188. https://doi.org/10.2164/jandrol.04152
Sakkas D, Urner F, Bianchi PG, Bizzaro D, Wagner I, Jaquenoud N, Manicardi G, Campana A (1996) Sperm chromatin anomalies can influence decondensation after intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod 11:837–843
Bungum M, Humaidan P, Spano M, Jepson K, Bungum L, Giwercman A (2004) The predictive value of sperm chromatin structure assay (SCSA) parameters for the outcome of intrauterine insemination, IVF and ICSI. Hum Reprod 19:1401–1408. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deh280
Henkel R, Hajimohammad M, Stalf T, Hoogendijk C, Mehnert C, Menkveld R, Gips H, Schill WB, Kruger TF (2004) Influence of deoxyribonucleic acid damage on fertilization and pregnancy. Fertil Steril 81:965–972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2003.09.044
Gandini L, Lombardo F, Paoli D, Caruso F, Eleuteri P, Leter G, Ciriminna R, Culasso F, Dondero F, Lenzi A, Spanò M (2004) Full-term pregnancies achieved with ICSI despite high levels of sperm chromatin damage. Hum Reprod 19:1409–1417. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deh233
Borini A, Tarozzi N, Nadalini M (2017) Sperm DNA fragmentation testing in male infertility work-up: are we ready? Transl Androl Urol 6:S580–S582 https://doi.org/10.21037/tau.2017.03.81
Simon L, Lutton D, McManus J, Lewis SE (2011) Sperm DNA damage measured by the alkaline Comet assay as an independent predictor of male infertility and in vitro fertilization success. Fertil Steril 95:652–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2010.08.019
Muratori M, Tarozzi N, Cambi M, Boni L, Iorio AL, Passaro C, Luppino B, Nadalini M, Marchiani S, Tamburrino L, Forti G, Maggi M, Baldi E, Borini A (2016) Variation of DNA fragmentation levels during density gradient sperm selection for assisted reproduction techniques: a possible new male predictive parameter of pregnancy? Medicine (Baltimore) 95:e3624. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000003624
Jayaraman V, Upadhya D, Narayan PK, Adiga SK (2012) Sperm processing by swim-up and density gradient is effective in elimination of sperm with DNA damage. J Assist Reprod Genet 29:557–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-012-9742-x
Malvezzi H, Sharma R, Agarwal A, Abuzenadah AM, Abu-Elmagd M (2014) Sperm quality after density gradient centrifugation with three commercially available media: a controlled trial. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 12:121. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-12-121
Shafik A, Shafik AA, Shafik I, El Sibai O (2006) Molecular andrology as related to sperm DNA fragmentation/sperm chromatin biotechnology. Arch Androl 52:299–310. https://doi.org/10.1080/01485010600668363
Lin MH, Kuo-Kuang Lee R, Li SH, Lu CH, Sun FJ, Hwu YM (2008) Sperm chromatin structure assay parameters are not related to fertilization rates, embryo quality, and pregnancy rates in in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection, but might be related to spontaneous abortion rates. Fertil Steril 90:352–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.06.018
Acknowledgements
Preliminary data regarding this study were presented as poster at the 10th European Congress of Andrology, October 2018 in Budapest, Hungary.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SA: Data collection or management, data analysis, manuscript writing. AP: Protocol/project development, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing. YPa: Protocol/project development, data analysis. SP: Data management, data analysis. NP: Data management, data analysis, manuscript editing. SAN: Data analysis, manuscript editing. MGP: Data collection or management. GM: Data analysis, manuscript editing. YPr: Protocol/project development, data management, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee, and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The Institutional Review Board of Iakentro Advanced Medical Center/ethics committee of Thessaloniki, Greece approved the study at 2/9/2013, Ref. Number 9/2013.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonouli, S., Papatheodorou, A., Panagiotidis, Y. et al. The impact of sperm DNA fragmentation on ICSI outcome in cases of donated oocytes. Arch Gynecol Obstet 300, 207–215 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-019-05133-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-019-05133-9