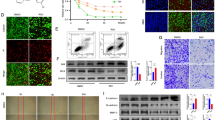
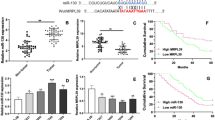
Abstract
Resveratrol (Res) is a natural compound with anti-cancer effects. The goal of this study is to evaluate the suppression of Res in melanoma and investigate its relationship with miRNAs during this process. The in vitro and in vivo anti-cancer abilities of Res were evaluated using cellular assays and animal model. Two melanoma cell lines (A375 and MV3) were used for both in vitro assay and in vivo experiments. qRT-PCR and Western blot were used to detect the changes in gene expressions and protein levels. Dual-luciferase reporter assay and bioinformatic tools were used to further confirm the protein binding and activation of targeted genes. In vitro experiments showed Res significantly decreased the expression of miR-221, an oncogenic microRNA, which was confirmed by the overexpression of miR-221 with or without Res treatment. Mechanistically, we showed that the inhibition of miR-221 by Res was achieved by regulating NF-κB (RELA) activity. In the meantime, we also identified that TFG, a tumor suppressor gene, was a target of miR-221. Finally, using in vivo melanoma model, we confirmed the tumor suppressive effects of Res and our in vitro regulatory network. Res displayed a significant anti-tumor effect on melanoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. The cellular mechanism under this effect involves miRNA regulation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babapoor S, Wu R, Kozubek J, Auidi D, Grant-Kels JM, Dadras SS (2017) Identification of microRNAs associated with invasive and aggressive phenotype in cutaneous melanoma by next-generation sequencing. Lab Investig. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2017.5
Basseres DS, Ebbs A, Levantini E, Baldwin AS (2010) Requirement of the NF-kappaB subunit p65/RelA for K-Ras-induced lung tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 70:3537–3546. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4290
Carter LG, D’Orazio JA, Pearson KJ (2014) Resveratrol and cancer: focus on in vivo evidence. Endocr Relat Cancer 21:R209–R225. doi:10.1530/ERC-13-0171
Dutton-Regester K, Aoude LG, Nancarrow DJ, Stark MS, O’Connor L, Lanagan C, Pupo GM, Tembe V, Carter CD, O’Rourke M, Scolyer RA, Mann GJ, Schmidt CW, Herington A, Hayward NK (2012) Identification of TFG (TRK-fused gene) as a putative metastatic melanoma tumor suppressor gene. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 51:452–461. doi:10.1002/gcc.21932
Felicetti F, Errico MC, Bottero L, Segnalini P, Stoppacciaro A, Biffoni M, Felli N, Mattia G, Petrini M, Colombo MP, Peschle C, Care A (2008) The promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger-microRNA-221/-222 pathway controls melanoma progression through multiple oncogenic mechanisms. Cancer Res 68:2745–2754. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2538
Gallagher SJ, Mijatov B, Gunatilake D, Gowrishankar K, Tiffen J, James W, Jin L, Pupo G, Cullinane C, McArthur GA, Tummino PJ, Rizos H, Hersey P (2014) Control of NF-kB activity in human melanoma by bromodomain and extra-terminal protein inhibitor I-BET151. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 27:1126–1137. doi:10.1111/pcmr.12282
Garofalo M, Quintavalle C, Romano G, Croce CM, Condorelli G (2012) miR221/222 in cancer: their role in tumor progression and response to therapy. Curr Mol Med 12:27–33
Giles KM, Brown RA, Ganda C, Podgorny MJ, Candy PA, Wintle LC, Richardson KL, Kalinowski FC, Stuart LM, Epis MR, Haass NK, Herlyn M, Leedman PJ (2016) microRNA-7-5p inhibits melanoma cell proliferation and metastasis by suppressing RelA/NF-kappaB. Oncotarget 7:31663–31680. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.9421
Ha M, Kim VN (2014) Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:509–524. doi:10.1038/nrm3838
Haass NK, Sproesser K, Nguyen TK, Contractor R, Medina CA, Nathanson KL, Herlyn M, Smalley KS (2008) The mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) induces growth arrest in melanoma cells and tumor regression when combined with docetaxel. Clin Cancer Res 14:230–239. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1440
Hua F, Shang S, Hu ZW (2017) Seeking new anti-cancer agents from autophagy-regulating natural products. J Asian Nat Prod Res 19:305–313. doi:10.1080/10286020.2017.1304385
Irvine M, Philipsz S, Frausto M, Mijatov B, Gallagher SJ, Fung C, Becker TM, Kefford RF, Rizos H (2010) Amino terminal hydrophobic import signals target the p14(ARF) tumor suppressor to the mitochondria. Cell Cycle 9:829–839. doi:10.4161/cc.9.4.10785
Jiang H, Shang X, Wu H, Gautam SC, Al-Holou S, Li C, Kuo J, Zhang L, Chopp M (2009) Resveratrol downregulates PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in human U251 glioma cells. J Exp Ther Oncol 8:25–33
Junco JJ, Mancha-Ramirez A, Malik G, Wei SJ, Kim DJ, Liang H, Slaga TJ (2015) Ursolic acid and resveratrol synergize with chloroquine to reduce melanoma cell viability. Melanoma Res 25:103–112. doi:10.1097/CMR.0000000000000137
Lehman TA, Modali R, Boukamp P, Stanek J, Bennett WP, Welsh JA, Metcalf RA, Stampfer MR, Fusenig N, Rogan EM et al (1993) p53 mutations in human immortalized epithelial cell lines. Carcinogenesis 14:833–839
Leibowitz-Amit R, Sidi Y, Avni D (2012) Aberrations in the micro-RNA biogenesis machinery and the emerging roles of micro-RNAs in the pathogenesis of cutaneous malignant melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 25:740–757. doi:10.1111/pcmr.12018
Lelli D, Pedone C, Majeed M, Sahebkar A (2017) Curcumin and lung cancer: the role of microRNAs. Curr Pharm Des 23:1–5
Lujambio A, Lowe SW (2012) The microcosmos of cancer. Nature 482:347–355. doi:10.1038/nature10888
Luke JJ, Flaherty KT, Ribas A, Long GV (2017) Targeted agents and immunotherapies: optimizing outcomes in melanoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:463–482. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.43
Luo C, Shen J (2017) Research progress in advanced melanoma. Cancer Lett. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.037
Mattia G, Errico MC, Felicetti F, Petrini M, Bottero L, Tomasello L, Romania P, Boe A, Segnalini P, Di Virgilio A, Colombo MP, Care A (2011) Constitutive activation of the ETS-1-miR-222 circuitry in metastatic melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 24:953–965. doi:10.1111/j.1755-148X.2011.00881.x
McCourt C, Dolan O, Gormley G (2014) Malignant melanoma: a pictorial review. Ulster Med J 83:103–110
Miranda C, Roccato E, Raho G, Pagliardini S, Pierotti MA, Greco A (2006) The TFG protein, involved in oncogenic rearrangements, interacts with TANK and NEMO, two proteins involved in the NF-kappaB pathway. J Cell Physiol 208:154–160. doi:10.1002/jcp.20644
Mobley AK, Braeuer RR, Kamiya T, Shoshan E, Bar-Eli M (2012) Driving transcriptional regulators in melanoma metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31:621–632. doi:10.1007/s10555-012-9358-8
Nivelle L, Hubert J, Courot E, Jeandet P, Aziz A, Nuzillard JM, Renault JH, Clement C, Martiny L, Delmas D, Tarpin M (2017) Anti-cancer activity of resveratrol and derivatives produced by grapevine cell suspensions in a 14 L stirred bioreactor. Molecules. doi:10.3390/molecules22030474
Panday A, Inda ME, Bagam P, Sahoo MK, Osorio D, Batra S (2016) Transcription factor NF-kappaB: an update on intervention strategies. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 64:463–483. doi:10.1007/s00005-016-0405-y
Quintavalle C, Garofalo M, Zanca C, Romano G, Iaboni M, del Basso De Caro M, Martinez-Montero JC, Incoronato M, Nuovo G, Croce CM, Condorelli G (2012) miR-221/222 overexpression in human glioblastoma increases invasiveness by targeting the protein phosphate PTPmu. Oncogene 31:858–868. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.280
Ren Z, Wang L, Cui J, Huoc Z, Xue J, Cui H, Mao Q, Yang R (2013) Resveratrol inhibits NF-kB signaling through suppression of p65 and IkappaB kinase activities. Pharmazie 68:689–694
Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, Stein K, Mariotto A, Smith T, Cooper D, Gansler T, Lerro C, Fedewa S, Lin C, Leach C, Cannady RS, Cho H, Scoppa S, Hachey M, Kirch R, Jemal A, Ward E (2012) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62:220–241. doi:10.3322/caac.21149
Singh SK, Banerjee S, Acosta EP, Lillard JW, Singh R (2017) Resveratrol induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis with docetaxel in prostate cancer cells via a p53/p21WAF1/CIP1 and p27KIP1 pathway. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.15303
Smalley KS, Brafford P, Haass NK, Brandner JM, Brown E, Herlyn M (2005) Up-regulated expression of zonula occludens protein-1 in human melanoma associates with N-cadherin and contributes to invasion and adhesion. Am J Pathol 166:1541–1554. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62370-X
Smalley KS, Contractor R, Haass NK, Lee JT, Nathanson KL, Medina CA, Flaherty KT, Herlyn M (2007) Ki67 expression levels are a better marker of reduced melanoma growth following MEK inhibitor treatment than phospho-ERK levels. Br J Cancer 96:445–449. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603596
Thiel G, Rossler OG (2017) Resveratrol regulates gene transcription via activation of stimulus-responsive transcription factors. Pharmacol Res 117:166–176. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2016.12.029
Weber CE, Luo C, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Gardyan A, Kordass T, Holland-Letz T, Osen W, Eichmuller SB (2016) miR-339-3p is a tumor suppressor in melanoma. Cancer Res 76:3562–3571. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2932
Zehavi L, Schayek H, Jacob-Hirsch J, Sidi Y, Leibowitz-Amit R, Avni D (2015) MiR-377 targets E2F3 and alters the NF-kB signaling pathway through MAP3K7 in malignant melanoma. Mol Cancer 14:68. doi:10.1186/s12943-015-0338-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Funding
None.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, F., Cui, L. Resveratrol suppresses melanoma by inhibiting NF-κB/miR-221 and inducing TFG expression. Arch Dermatol Res 309, 823–831 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-017-1784-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-017-1784-6