Abstract.
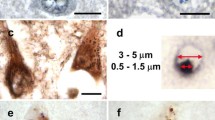
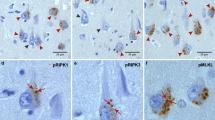
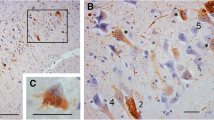
The cellular distribution of an advanced glycation end product [N ε-(carboxymethyl)lysine (CML)] in aged and Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains was assessed immunohistochemically. CML was localized in the cytoplasm of neurons, astrocytes, and microglia in both aged and AD brains. Glial deposition was far more marked in AD brains than in aged brains, and neuronal deposition was also increased. On electron microscopic immunohistochemistry, neuronal CML formed granular or linear deposits associated with lipofuscin, and glial deposits formed lines around the vacuoles. Neuronal and glial deposits were prominent throughout the cerebral cortex and hippocampus, but were sparse in the putamen, globus pallidus, substantia nigra, and cerebellum, with glial deposits being far more prominent in AD brains. The distribution of neuronal and glial deposits did not correspond with the distribution of AD pathology. The extent of CML deposits was inversely correlated with neurofibrillary tangle formation, particularly in the hippocampus. Most hippocampal pyramidal neurons with neurofibrillary tangles did not have CML, and most of the neurons with heavy CML deposits did not have neurofibrillary tangles. In the hippocampus, neuronal CML was prominent in the region where neuronal loss was mild. These observations suggest that CML deposition does not directly cause neurofibrillary tangle formation or neuronal loss in AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takeda, A., Wakai, M., Niwa, H. et al. Neuronal and glial advanced glycation end product [N ε-(carboxymethyl)lysine] in Alzheimer's disease brains. Acta Neuropathol 101, 27–35 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010000256
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010000256