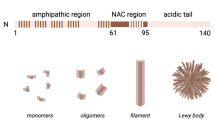
Abstract
Synucleinopathies are a group of neurodegenerative disorders caused by the misfolding and self-templating of the protein α-synuclein, or the formation of α-synuclein prions. Each disorder differs by age of onset, presenting clinical symptoms, α-synuclein inclusion morphology, and neuropathological distribution. Explaining this disease-specific variability, the strain hypothesis postulates that each prion disease is encoded by a distinct conformation of the misfolded protein, and therefore, each synucleinopathy is caused by a unique α-synuclein structure. This review discusses the current data supporting the role of α-synuclein strains in disease heterogeneity. Several in vitro and in vivo models exist for evaluating strain behavior, however, as the focus of this article is to compare strains across synucleinopathy patients, our discussion predominantly focuses on the two models most commonly used for this purpose: the α-syn140*A53T–YFP cell line and the TgM83+/− mouse model. Here we define each strain based on biochemical stability, ability to propagate in α-syn140–YFP cell lines, and incubation period, inclusion morphology and distribution, and neurological signs in TgM83+/− mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed Z, Asi YT, Sailer A, Lees AJ, Houlden H, Revesz T et al (2012) Review: the neuropathology, pathophysiology and genetics of multiple system atrophy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 38:4–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2990.2011.01234.x
Asante EA, Grimshaw A, Smidak M, Jakubcova T, Tomlinson A, Jeelani A et al (2015) Transmission properties of human PrP 102L prions challenge the relevance of mouse models of GSS. PLoS Pathog 11:e1004953. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004953
Atsmon-Raz Y, Miller Y (2015) A proposed atomic structure of the self-assembly of the non-amyloid-β component of human α-synuclein as derived by computational tools. J Phys Chem B 119:10005–10015. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b03760
Ayers JI, Brooks MM, Rutherford NJ, Howard JK, Sorrentino ZA, Riffe CJ et al (2017) Robust central nervous system pathology in transgenic mice following peripheral injection of alpha-synuclein fibrils. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02095-16
Ayers JI, Riffe CJ, Sorrentino ZA, Diamond J, Fagerli E, Brooks M et al (2018) Localized induction of wild-type and mutant alpha-synuclein aggregation reveals propagation along neuroanatomical tracts. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00586-18
Ayers JI, Schutt CR, Shikiya RA, Aguzzi A, Kincaid AE, Bartz JC (2011) The strain-encoded relationship between PrP replication, stability and processing in neurons is predictive of the incubation period of disease. PLoS Pathog 7:e1001317. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1001317
Bartz JC (2017) Prion strain diversity. In: Prusiner SB (ed) Prion diseases. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Med. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, pp 31–44. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a024349
Bernis ME, Babila JT, Breid S, Wüsten KA, Wüllner U, Tamgüney G (2015) Prion-like propagation of human brain-derived alpha-synuclein in transgenic mice expressing human wild-type alpha-synuclein. Acta Neuropathol Commun 3:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-015-0254-7
Bousset L, Pieri L, Ruiz-Arlandis G, Gath J, Jensen PH, Habenstein B, Madiona K, Olieric V, Böckmann A, Meier BH, Melki R (2013) Structural and functional characterization of two alpha-synuclein strains. Nat Commun 4:2575. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3575
Boyer DR, Li B, Sun C, Fan W, Sawaya MR, Jiang L, Eisenberg DS (2019) Structures of fibrils formed by alpha-synuclein hereditary disease mutant H50Q reveal new polymorphs. Nat Struct Mol Biol 26:1044–1052. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-019-0322-y
Boyer DR, Li B, Sun C, Fan W, Zhou K, Hughes MP, Sawaya MR, Jiang L, Eisenberg DS (2020) The α-synuclein hereditary mutation E46K unlocks a more stable, pathogenic fibril structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:3592–3602. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1917914117
Breid S, Bernis ME, Babila JT, Garza MC, Wille H, Tamgüney G (2016) Neuroinvasion of α-synuclein prionoids after intraperitoneal and intraglossal inoculation. J Virol 90:9182–9193. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01399-16
Brosamle C, Schwab ME (2000) Ipsilateral, ventral corticospinal tract of the adult rat: ultrastructure, myelination and synaptic connections. J Neurocytol 29:499–507. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1007297712821
Burke CM, Walsh DJ, Steele AD, Agrimi U, Di Bari MA, Watts JC, Supattapone S (2019) Full restoration of specific infectivity and strain properties from pure mammalian prion protein. PLoS Pathog 15:e1007662. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1007662
Burré J, Sharma M, Tsetsenis T, Buchman V, Etherton MR, Südhof TC (2010) Alpha-synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 329:1663–1667. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1195227
Bussell R Jr, Ramlall TF, Eliezer D (2005) Helix periodicity, topology, and dynamics of membrane-associated alpha-synuclein. Protein Sci 14:862–872. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.041255905
Cescatti M, Saverioni D, Capellari S, Tagliavini F, Kitamoto T, Ironside J et al (2016) Analysis of conformational stability of abnormal prion protein aggregates across the spectrum of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prions. J Virol 90:6244–6254. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00144-16
Chandra S, Chen X, Rizo J, Jahn R, Südhof TC (2003) A broken α-helix in folded α-synuclein. J Biol Chem 278:15313–15318. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M213128200
Chandra S, Gallardo G, Fernández-Chacón R, Schlüter OM, Südhof TC (2005) α-Synuclein cooperates with CSPα in preventing neurodegeneration. Cell 123:383–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.028
Chien P, Weissman JS (2001) Conformational diversity in a yeast prion dictates its seeding specificity. Nature 410:223–227. https://doi.org/10.1038/35065632
Chu Y, Kordower JH (2007) Age-associated increases of alpha-synuclein in monkeys and humans are associated with nigrostriatal dopamine depletion: is this the target for Parkinson's disease? Neurobiol Dis 25:134–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2006.08.021
Chu Y, Muller S, Tavares A, Barret O, Alagille D, Seibyl J et al (2019) Intrastriatal alpha-synuclein fibrils in monkeys: spreading, imaging and neuropathological changes. Brain 142:3565–3579. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz296
Dejerine JJ, Thomas A (1900) L’atrophie olivo-ponto-cérébelleuse. Nouvelle iconographie de la Salpêtrière 13:330–370
Deleault NR, Kascsak R, Geoghegan JC, Supattapone S (2010) Species-dependent differences in cofactor utilization for formation of the protease-resistant prion protein in vitro. Biochemistry 49:3928–3934. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi100370b
Deleault NR, Walsh DJ, Piro JR, Wang F, Wang X, Ma J et al (2012) Cofactor molecules maintain infectious conformation and restrict strain properties in purified prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:E1938–1946. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1206999109
Desplats P, Lee HJ, Bae EJ, Patrick C, Rockenstein E, Crews L et al (2009) Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13010–13015. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0903691106
Dhillon J-S, Trejo-Lopez JA, Riffe C, Levites Y, Sacino AN, Borchelt DR et al (2019) Comparative analyses of the in vivo induction and transmission of α-synuclein pathology in transgenic mice by MSA brain lysate and recombinant α-synuclein fibrils. Acta Neuropathol Commun 7:80. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-019-0733-3
Dickinson AG (1976) Scrapie in sheep and goats. In: Kimberlin RH (ed) Slow virus diseases of animals and man. North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam, pp 209–241
Djelloul M, Holmqvist S, Boza-Serrano A, Azevedo C, Yeung MS, Goldwurm S et al (2015) Alpha-synuclein expression in the oligodendrocyte lineage: an in vitro and in vivo study using rodent and human models. Stem Cell Rep 5:174–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2015.07.002
El-Agnaf OM, Jakes R, Curran MD, Middleton D, Ingenito R, Bianchi E et al (1998) Aggregates from mutant and wild-type alpha-synuclein proteins and NAC peptide induce apoptotic cell death in human neuroblastoma cells by formation of beta-sheet and amyloid-like filaments. FEBS Lett 440:71–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01418-5
Eliezer D, Kutluay E, Bussell R Jr, Browne G (2001) Conformational properties of alpha-synuclein in its free and lipid-associated states. J Mol Biol 307:1061–1073. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.4538
Firmin L, Field P, Maier MA, Kraskov A, Kirkwood PA, Nakajima K et al (2014) Axon diameters and conduction velocities in the macaque pyramidal tract. J Neurophysiol 112:1229–1240. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00720.2013
Forster E, Lewy FH (1912) Paralysis agitans. In: Lewandowsky M (ed) Pathologische Anatomie. Handbuch der Neurologie. Springer, Berlin, pp 920–933
Fraser H, Dickinson AG (1967) Distribution of experimentally induced scrapie lesions in the brain. Nature 216:1310–1311. https://doi.org/10.1038/2161310a0
Freundt EC, Maynard N, Clancy EK, Roy S, Bousset L, Sourigues Y et al (2012) Neuron-to-neuron transmission of alpha-synuclein fibrils through axonal transport. Ann Neurol 72:517–524. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23747
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Quinn SM, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2002) Neuronal α-synucleinopathy with severe movement disorder in mice expressing A53T human α-synuclein. Neuron 34:521–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00682-7
Giasson BI, Murray IV, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2001) A hydrophobic stretch of 12 amino acid residues in the middle of alpha-synuclein is essential for filament assembly. J Biol Chem 276:2380–2386. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M008919200
Gilman S, Wenning GK, Low PA, Brooks DJ, Mathias CJ, Trojanowski JQ et al (2008) Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 71:670–676. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000324625.00404.15
Goedert M (2015) Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: the prion concept in relation to assembled Aβ, tau, and α-synuclein. Science 349:1255555. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1255555
Gomez-Isla T, Irizarry MC, Mariash A, Cheung B, Soto O, Schrump S et al (2003) Motor dysfunction and gliosis with preserved dopaminergic markers in human α-synuclein A30P transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging 24:245–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-4580(02)00091-x
Graham JG, Oppenheimer DR (1969) Orthostatic hypotension and nicotine sensitivity in a case of multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 32:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.32.1.28
Guerrero-Ferreira R, Taylor NM, Arteni AA, Kumari P, Mona D, Ringler P et al (2019) Two new polymorphic structures of human full-length alpha-synuclein fibrils solved by cryo-electron microscopy. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.48907
Guerrero-Ferreira R, Taylor NM, Mona D, Ringler P, Lauer ME, Riek R et al (2018) Cryo-EM structure of alpha-synuclein fibrils. eLife 7:e36402. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36402
Guo JL, Covell DJ, Daniels JP, Iba M, Stieber A, Zhang B et al (2013) Distinct α-synuclein strains differentially promote tau inclusions in neurons. Cell 154:103–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.057
Hansen C, Angot E, Bergstrom AL, Steiner JA, Pieri L, Paul G et al (2011) alpha-Synuclein propagates from mouse brain to grafted dopaminergic neurons and seeds aggregation in cultured human cells. J Clin Investig 121:715–725. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI43366
Iwai A, Masliah E, Yoshimoto M, Ge N, Flanagan L, de Silva HA et al (1995) The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer's disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron 14:467–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-6273(95)90302-x
Jellinger KA, Seppi K, Wenning GK (2005) Grading of neuropathology in multiple system atrophy: proposal for a novel scale. Mov Disord 20:S29–S36. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20537
Jucker M, Walker LC (2018) Propagation and spread of pathogenic protein assemblies in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Neurosci 21:1341–1349. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0238-6
Kahle PJ, Neumann M, Ozmen L, Muller V, Jacobsen H, Schindzielorz A et al (2000) Subcellular localization of wild-type and Parkinson’s disease-associated mutant α-synuclein in human and transgenic mouse brain. J Neurosci 20:6365–6373
Kahle PJ, Neumann M, Ozmen L, Müller V, Jacobsen H, Spooren W et al (2002) Hyperphosphorylation and insolubility of alpha-synuclein in transgenic mouse oligodendrocytes. EMBO Rep 3:583–588. https://doi.org/10.1093/embo-reports/kvf109
Kanaan NM, Kordower JH, Collier TJ (2007) Age-related accumulation of Marinesco bodies and lipofuscin in rhesus monkey midbrain dopamine neurons: relevance to selective neuronal vulnerability. J Comp Neurol 502:683–700. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21333
Kordower JH, Chu Y, Hauser RA, Freeman TB, Olanow CW (2008) Lewy body-like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson's disease. Nat Med 14:504–506. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1747
Kordower JH, Dodiya HB, Kordower AM, Terpstra B, Paumier K, Madhavan L et al (2011) Transfer of host-derived alpha synuclein to grafted dopaminergic neurons in rat. Neurobiol Dis 43:552–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.05.001
Kordower JH, Freeman TB, Snow BJ, Vingerhoets FJ, Mufson EJ, Sanberg PR et al (1995) Neuropathological evidence of graft survival and striatal reinnervation after the transplantation of fetal mesencephalic tissue in a patient with Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 332:1118–1124. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199504273321702
Kuo YM, Li Z, Jiao Y, Gaborit N, Pani AK, Orrison BM et al (2010) Extensive enteric nervous system abnormalities in mice transgenic for artificial chromosomes containing Parkinson disease-associated alpha-synuclein gene mutations precede central nervous system changes. Hum Mol Genet 19:1633–1650. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq038
Kuzdas-Wood D, Stefanova N, Jellinger KA, Seppi K, Schlossmacher MG, Poewe W et al (2014) Towards translational therapies for multiple system atrophy. Prog Neurobiol 118:19–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.02.007
Lau A, So RWL, Lau HHC, Sang JC, Ruiz-Riquelme A, Fleck SC et al (2019) α-Synuclein strains target distinct brain regions and cell types. Nat Neurosci 23:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-019-0541-x
Lee MK, Stirling W, Xu Y, Xu X, Qui D, Mandir AS et al (2002) Human alpha-synuclein-harboring familial Parkinson's disease-linked Ala-53 –%3e Thr mutation causes neurodegenerative disease with alpha-synuclein aggregation in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8968–8973. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.132197599
Leenen LP, Meek J, Posthuma PR, Nieuwenhuys R (1985) A detailed morphometrical analysis of the pyramidal tract of the rat. Brain Res 359:65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(85)91413-1
Li B, Ge P, Murray KA, Sheth P, Zhang M, Nair G et al (2018) Cryo-EM of full-length α-synuclein reveals fibril polymorphs with a common structural kernel. Nat Commun 9:3609. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05971-2
Li JY, Englund E, Holton JL, Soulet D, Hagell P, Lees AJ et al (2008) Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in subjects with Parkinson's disease suggest host-to-graft disease propagation. Nat Med 14:501–503. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1746
Li W, Englund E, Widner H, Mattsson B, van Westen D, Latt J et al (2016) Extensive graft-derived dopaminergic innervation is maintained 24 years after transplantation in the degenerating parkinsonian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:6544–6549. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1605245113
Li Y, Zhao C, Luo F, Liu Z, Gui X, Luo Z et al (2018) Amyloid fibril structure of α-synuclein determined by cryo-electron microscopy. Cell Res 28:897–903. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0075-x
Lindvall O, Widner H, Rehncrona S, Brundin P, Odin P, Gustavii B et al (1992) Transplantation of fetal dopamine neurons in Parkinson's disease: one-year clinical and neurophysiological observations in two patients with putaminal implants. Ann Neurol 31:155–165. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410310206
Luk KC, Kehm VM, Zhang B, O'Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2012) Intracerebral inoculation of pathological α-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative α-synucleinopathy in mice. J Exp Med 209:975–986. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20112457
Luk KC, Song C, O'Brien P, Stieber A, Branch JR, Brunden KR et al (2009) Exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils seed the formation of Lewy body-like intracellular inclusions in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:20051–20056. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0908005106
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Takeda A et al (2000) Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in a-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science 287:1265–1269. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5456.1265
Miller MB, Wang DW, Wang F, Noble GP, Ma J, Woods VL Jr et al (2013) Cofactor molecules induce structural transformation during infectious prion formation. Structure 21:2061–2068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2013.08.025
Mougenot A-L, Nicot S, Bencsik A, Morignat E, Verchère J, Lakhdar L et al (2012) Prion-like acceleration of a synucleinopathy in a transgenic mouse model. Neurobiol Aging 33:2225–2228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.06.022
Papp MI, Kahn JE, Lantos PL (1989) Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in the CNS of patients with multiple system atrophy (striatonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar atrophy and Shy-Drager syndrome). J Neurol Sci 94:79–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-510x(89)90219-0
Papp MI, Lantos PL (1992) Accumulation of tubular structures in oligodendroglial and neuronal cells as the basic alteration in multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Sci 107:172–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-510x(92)90286-t
Parkinson J (1817) An essay on the shaking palsy. Sherwood, Neely, and Jones, London
Peelaerts W, Baekelandt V (2016) α-Synuclein strains and the variable pathologies of synucleinopathies. J Neurochem 139:256–274. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13595
Peelaerts W, Bousset L, Van der Perren A, Moskalyuk A, Pulizzi R, Giugliano M et al (2015) α-Synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration. Nature 522:340–344. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14547
Peng C, Gathagan RJ, Covell DJ, Medellin C, Stieber A, Robinson JL et al (2018) Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological α-synuclein strains in α-synucleinopathies. Nature 557:558–563. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0104-4
Peretz D, Scott M, Groth D, Williamson A, Burton D, Cohen FE et al (2001) Strain-specified relative conformational stability of the scrapie prion protein. Protein Sci 10:854–863. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.39201
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A et al (1997) Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science 276:2045–2047. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5321.2045
Prusiner SB (2017) An introduction to prion biology. In: Prusiner SB (ed) Prion biology. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, pp 1–15
Prusiner SB, Woerman AL, Mordes DA, Watts JC, Rampersaud R, Berry DB et al (2015) Evidence for α-synuclein prions causing multiple system atrophy in humans with parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:E5308–E5317. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1514475112
Ralston DD, Milroy AM, Ralston HJ 3rd (1987) Non-myelinated axons are rare in the medullary pyramids of the macaque monkey. Neurosci Lett 73:215–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(87)90247-3
Recasens A, Dehay B, Bové J, Carballo-Carbajal I, Dovero S, Pérez-Villalba A et al (2014) Lewy body extracts from Parkinson's disease brains trigger alpha-synuclein pathology and neurodegeneration in mice and monkeys. Ann Neurol 75:351–362. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24066
Reyes JF, Olsson TT, Lamberts JT, Devine MJ, Kunath T et al (2015) A cell culture model for monitoring α-synuclein cell-to-cell transfer. Neurobiol Dis 77:266–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.07.003
Reyes JF, Rey NL, Bousset L, Melki R, Brundin P, Angot E (2014) Alpha-synuclein transfers from neurons to oligodendrocytes. Glia 62:387–398. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22611
Rodriguez JA, Ivanova MI, Sawaya MR, Cascio D, Reyes FE, Shi D et al (2015) Structure of the toxic core of α-synuclein from invisible crystals. Nature 525:486–490. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15368
Rutherford NJ, Dhillon JS, Riffe CJ, Howard JK, Brooks M, Giasson BI (2017) Comparison of the in vivo induction and transmission of alpha-synuclein pathology by mutant alpha-synuclein fibril seeds in transgenic mice. Hum Mol Genet 26:4906–4915. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx371
Sacino AN, Brooks M, Thomas MA, McKinney AB, Lee S, Regenhardt RW et al (2014) Intramuscular injection of α-synuclein induces CNS α-synuclein pathology and a rapid-onset motor phenotype in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:10732–10737. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1321785111
Safar J, Wille H, Itri V, Groth D, Serban H, Torchia M et al (1998) Eight prion strains have PrPSc molecules with different conformations. Nat Med 4:1157–1165. https://doi.org/10.1038/2654
Sanders DW, Kaufman SK, DeVos SL, Sharma AM, Mirbaha H, Li A et al (2014) Distinct tau prion strains propagate in cells and mice and define different tauopathies. Neuron 82:1271–1288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.04.047
Schweighauser M, Shi Y, Tarutani A, Kametani F, Murzin AG, Ghetti B et al (2020) Structures of α-synuclein fiaments from multiple system atrophy. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.05.935619
Sharon R, Bar-Joseph I, Mirick GE, Serhan CN, Selkoe DJ (2003) Altered fatty acid composition of dopaminergic neurons expressing α-synuclein and human brains with α-synucleinopathies. J Biol Chem 278:49874–49881. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M309127200
Shimozawa A, Ono M, Takahara D, Tarutani A, Imura S, Masuda-Suzukake M et al (2017) Propagation of pathological α-synuclein in marmoset brain. Acta Neuropathol Commun 5:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-017-0413-0
Shults CW, Rockenstein E, Crews L, Adame A, Mante M, Larrea G et al (2005) Neurological and neurodegenerative alterations in a transgenic mouse model expressing human α-synuclein under oligodendrocyte promoter: Implications for multiple system atrophy. J Neurosci 25:10689–10699. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3527-05.2005
Shy GM, Drager GA (1960) A neurological syndrome associated with orthostatic hypotension: a clinical-pathologic study. Arch Neurol 2:511–527
Spencer DD, Robbins RJ, Naftolin F, Marek KL, Vollmer T, Leranth C et al (1992) Unilateral transplantation of human fetal mesencephalic tissue into the caudate nucleus of patients with Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 327:1541–1548. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199211263272201
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL, Goedert M (1998) Filamentous α-synuclein inclusions link multiple system atrophy with Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci Lett 251:205–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(98)00504-7
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840. https://doi.org/10.1038/42166
Strohaker T, Jung BC, Liou SH, Fernandez CO, Riedel D, Becker S et al (2019) Structural heterogeneity of alpha-synuclein fibrils amplified from patient brain extracts. Nat Commun 10:5535. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13564-w
Telling GC, Scott M, Hsiao KK, Foster D, Yang S-L, Torchia M et al (1994) Transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease from humans to transgenic mice expressing chimeric human-mouse prion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9936–9940. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.21.9936
Telling GC, Scott M, Mastrianni J, Gabizon R, Torchia M, Cohen FE et al (1995) Prion propagation in mice expressing human and chimeric PrP transgenes implicates the interaction of cellular PrP with another protein. Cell 83:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(95)90236-8
Tuttle MD, Comellas G, Nieuwkoop AJ, Covell DJ, Berthold DA, Kloepper KD et al (2016) Solid-state NMR structure of a pathogenic fibril of full-length human alpha-synuclein. Nat Struct Mol Biol 23:409–415. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3194
van der Eecken H, Adams RD, van Bogaert L (1960) Striopallidal-nigral degeneration. An hitherto undescribed lesion in paralysis agitans. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 19:159–161
Verges KJ, Smith MH, Toyama BH, Weissman JS (2011) Strain conformation, primary structure and the propagation of the yeast prion [PSI+]. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18:493–499. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2030
Wakabayashi K, Yoshimoto M, Tsuji S, Takahashi H (1998) α-Synuclein immunoreactivity in glial cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy. Neurosci Lett 249:180–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(98)00407-8
Watts JC, Giles K, Oehler A, Middleton L, Dexter DT, Gentleman SM et al (2013) Transmission of multiple system atrophy prions to transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:19555–19560. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1318268110
Wenning G, Trojanowski JQ, Kaufmann H, Wisniewski T, Rocca WA, Low PA (2018) Is multiple system atrophy an infectious disease? Ann Neurol 83:10–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25132
Woerman AL, Kazmi SA, Patel S, Aoyagi A, Oehler A, Widjaja K et al (2018) Familial Parkinson’s point mutation abolishes multiple system atrophy prion replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:409–414. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1719369115
Woerman AL, Kazmi SA, Patel S, Freyman Y, Oehler A, Aoyagi A et al (2018) MSA prions exhibit remarkable stability and resistance to inactivation. Acta Neuropathol 135:49–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1762-2
Woerman AL, Oehler A, Kazmi SA, Lee J, Halliday GM, Middleton LT et al (2019) Multiple system atrophy prions retain strain specificity after serial propagation in two different Tg(SNCA*A53T) mouse lines. Acta Neuropathol 137:437–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-019-01959-4
Woerman AL, Patel S, Kazmi SA, Oehler A, Lee J, Mordes DA et al (2020) Kinetics of α-synuclein prions preceding neuropathological inclusions in multiple system atrophy. PLoS Pathog 16:e1008222. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1008222
Woerman AL, Stöhr J, Aoyagi A, Rampersaud R, Krejciova Z, Watts JC et al (2015) Propagation of prions causing synucleinopathies in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:E4949–E4958. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1513426112
Yamasaki TR, Holmes BB, Furman JL, Dhavale DD, Su BW, Song E-S et al (2019) Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy have distinct α-synuclein seed characteristics. J Biol Chem 294:1045–1058. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.004471
Yazawa I, Giasson BI, Sasaki R, Zhang B, Joyce S, Uryu K et al (2005) Mouse model of multiple system atrophy α-synuclein expression in oligodendrocytes causes glial and neuronal degeneration. Neuron 45:847–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2005.01.032
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gómez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I et al (2004) The new mutation, E46K, of α-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol 55:164–173. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.10795
Acknowledgements
We thank Steven H. Olson for his assistance with modeling the E46K mutation and Sarah Pyle for her graphic design work. This work was supported by the University of Massachusetts, Amherst.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holec, S.A.M., Woerman, A.L. Evidence of distinct α-synuclein strains underlying disease heterogeneity. Acta Neuropathol 142, 73–86 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-020-02163-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-020-02163-5