Abstract
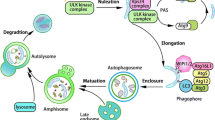
Autophagy delivers cytoplasmic components and organelles to lysosomes for degradation. This pathway serves to degrade nonfunctional or unnecessary organelles and aggregate-prone and oxidized proteins to produce substrates for energy production and biosynthesis. Macroautophagy delivers large aggregates and whole organelles to lysosomes by first enveloping them into autophagosomes that then fuse with lysosomes. Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) degrades proteins containing the KFERQ-like motif in their amino acid sequence, by transporting them from the cytosol across the lysosomal membrane into the lysosomal lumen. Autophagy is especially important for the survival and homeostasis of postmitotic cells like neurons, because these cells are not able to dilute accumulating detrimental substances and damaged organelles by cell division. Our current knowledge on the autophagic pathways and molecular mechanisms and regulation of autophagy will be summarized in this review. We will describe the physiological functions of macroautophagy and CMA in neuronal cells. Finally, we will summarize the current evidence showing that dysfunction of macroautophagy and/or CMA contributes to neuronal diseases. We will give an overview of our current knowledge on the role of autophagy in aging neurons, and focus on the role of autophagy in four types of neurodegenerative diseases, i.e., amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia, prion diseases, lysosomal storage diseases, and Parkinson’s disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AAA+-ATPase:
-
ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- AMBRA1:
-
Activating molecule in beclin 1-regulated autophagy
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- ATF6:
-
Activating transcription factor 6
- ATG:
-
Autophagy-related
- BECN1:
-
Beclin 1
- BNIP3:
-
BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa interacting protein 3
- CHMP2B:
-
Charged multivesicular protein 2B
- CMA:
-
Chaperone-mediated autophagy
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DAP1:
-
Death-associated protein 1
- DFCP1:
-
Double FYVE-containing protein 1
- DRG:
-
Dorsal root ganglion
- ESCRT-III:
-
Endosomal sorting complex required for transport-III
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- ERK2:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2
- FIP200:
-
200 kDa FAK family kinase-interacting protein
- FTD:
-
Frontotemporal dementia
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- GTPase:
-
Guanosine triphosphatase
- HIF:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor
- HSC70:
-
Heat shock cognate protein of 70 kDa
- IRE1:
-
Serine/threonine-protein kinase/endoribonuclease protein
- LAMP:
-
Lysosomal associated membrane protein
- LC3/MAP1-LC3:
-
Microtubule associated protein 1 light chain 3
- LRRK2:
-
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2
- LSD:
-
Lysosomal storage disorder
- MEF2D:
-
Myocyte enhancer factor 2D
- ML-II:
-
Mucolipidosis type II
- NCL:
-
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis
- NPC:
-
Niemann–Pick C
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- mTORC1:
-
mTOR complex 1
- MVB:
-
Multivesicular body
- OPTN:
-
Optineurin
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PERK:
-
Protein kinase-like ER kinase
- PI3P:
-
Phosphatidyl inositol 3-phosphate
- PI3KC3:
-
Phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase class 3
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- POMC:
-
Pro-opiomelanocortin
- RAPTOR:
-
Regulatory associated protein of mTOR)
- RB1CC1:
-
RB1-inducible coiled-coil 1
- REST:
-
Repressor element 1 silencing transcription factor
- Rheb:
-
Ras homolog enriched in brain
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SNARE:
-
Soluble N-ethyl-maleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- SQSTM1:
-
Sequestosome 1
- TDP-43:
-
Tar-DNA binding protein 43
- TFEB:
-
Transcription factor EB
- TSC:
-
Tuberous sclerosis complex
- UBA:
-
Ubiquitin-binding domain
- UBQLN2:
-
Ubiquilin 2
- ULK1:
-
Unc-51-like kinase 1
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein response
- V-ATPase:
-
Vacuolar ATPase
- VCP:
-
Valosin-containing protein
- WIPI:
-
WD repeat domain, phosphoinositide interacting
References
Aburto MR, Sanchez-Calderon H, Hurle JM, Varela-Nieto I, Magarinos M (2012) Early otic development depends on autophagy for apoptotic cell clearance and neural differentiation. Cell Death Dis 3:e394. doi:10.1038/cddis.2012.132
Aguib Y, Heiseke A, Gilch S, Riemer C, Baier M, Schatzl HM, Ertmer A (2009) Autophagy induction by trehalose counteracts cellular prion infection. Autophagy 5(3):361–369
Ahmed I, Liang YD, Schools S, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Savitt JM (2012) Development and characterization of a new Parkinson’s disease model resulting from impaired autophagy. J Neurosci 32(46):16503–16509. doi:10.1523/Jneurosci.0209-12.2012
Alers S, Loffler AS, Wesselborg S, Stork B (2012) Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy: cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol 32(1):2–11. doi:10.1128/Mcb.06159-11
Alirezaei M, Kemball CC, Flynn CT, Wood MR, Whitton JL, Kiosses WB (2010) Short-term fasting induces profound neuronal autophagy. Autophagy 6(6):702–710
Axe EL, Walker SA, Manifava M, Chandra P, Roderick HL, Habermann A et al (2008) Autophagosome formation from membrane compartments enriched in phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and dynamically connected to the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol 182(4):685–701
Baek SH, Noh AR, Kim KA, Akram M, Shin YJ, Kim ES et al (2014) Modulation of mitochondrial function and autophagy mediates carnosine neuroprotection against ischemic brain damage. Stroke 45(8):2438–2443. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.005183
Bains M, Zaegel V, Mize-Berge J, Heidenreich KA (2011) IGF-I stimulates Rab7-RILP interaction during neuronal autophagy. Neurosci Lett 488(2):112–117. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2010.09.018
Ballabio A, Gieselmann V (2009) Lysosomal disorders: from storage to cellular damage. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793(4):684–696. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.12.001
Ban BK, Jun MH, Ryu HH, Jang DJ, Ahmad ST, Lee JA (2013) Autophagy negatively regulates early axon growth in cortical neurons. Mol Cell Biol 33(19):3907–3919. doi:10.1128/MCB.00627-13
Bandyopadhyay U, Kaushik S, Varticovski L, Cuervo AM (2008) The chaperone-mediated autophagy receptor organizes in dynamic protein complexes at the lysosomal membrane. Mol Cell Biol 28(18):5747–5763. doi:10.1128/MCB.02070-07
Bandyopadhyay U, Sridhar S, Kaushik S, Kiffin R, Cuervo AM (2010) Identification of regulators of chaperone-mediated autophagy. Mol Cell 39(4):535–547. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.004
Bartlett BJ, Isakson P, Lewerenz J, Sanchez H, Kotzebue RW, Cumming RC et al (2011) p62, Ref(2)P and ubiquitinated proteins are conserved markers of neuronal aging, aggregate formation and progressive autophagic defects. Autophagy 7(6):572–583
Batlevi Y, La Spada AR (2011) Mitochondrial autophagy in neural function, neurodegenerative disease, neuron cell death, and aging. Neurobiol Dis 43(1):46–51. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2010.09.009
Bendikov-Bar I, Rapaport D, Larisch S, Horowitz M (2014) Parkin-mediated ubiquitination of mutant glucocerebrosidase leads to competition with its substrates PARIS and ARTS. Orphanet J Rare Dis 9(1):86. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-9-86
Bento CF, Puri C, Moreau K, Rubinsztein DC (2013) The role of membrane-trafficking small GTPases in the regulation of autophagy. J Cell Sci 126(Pt 5):1059–1069. doi:10.1242/jcs.123075
Bjorkoy G, Lamark T, Brech A, Outzen H, Perander M, Overvatn A et al (2005) p62/SQSTM1 forms protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol 171(4):603–614. doi:10.1083/jcb.200507002
Bjorkoy G, Lamark T, Johansen T (2006) p62/SQSTM1: a missing link between protein aggregates and the autophagy machinery. Autophagy 2(2):138–139
Boya P, Reggiori F, Codogno P (2013) Emerging regulation and functions of autophagy. Nat Cell Biol 15(7):713–720
Brady OA, Meng P, Zheng Y, Mao Y, Hu F (2011) Regulation of TDP-43 aggregation by phosphorylation and p62/SQSTM1. J Neurochem 116(2):248–259. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07098.x
Brunk UT, Terman A (2002) The mitochondrial-lysosomal axis theory of aging: accumulation of damaged mitochondria as a result of imperfect autophagocytosis. Eur J Biochem 269(8):1996–2002
Buchan JR, Kolaitis RM, Taylor JP, Parker R (2013) Eukaryotic stress granules are cleared by autophagy and Cdc48/VCP function. Cell 153(7):1461–1474. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.037
Bunge MB (1973) Fine structure of nerve fibers and growth cones of isolated sympathetic neurons in culture. J Cell Biol 56(3):713–735
Byun YJ, Kim SK, Kim YM, Chae GT, Jeong SW, Lee SB (2009) Hydrogen peroxide induces autophagic cell death in C6 glioma cells via BNIP3-mediated suppression of the mTOR pathway. Neurosci Lett 461(2):131–135. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.06.011
Caberlotto L, Nguyen TP (2014) A systems biology investigation of neurodegenerative dementia reveals a pivotal role of autophagy. BMC Syst Biol 8(1):65. doi:10.1186/1752-0509-8-65
Cao Y, Espinola JA, Fossale E, Massey AC, Cuervo AM, MacDonald ME, Cotman SL (2006) Autophagy is disrupted in a knock-in mouse model of juvenile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. J Biol Chem 281(29):20483–20493. doi:10.1074/jbc.M602180200
Carroll B, Hewitt G, Korolchuk VI (2013) Autophagy and ageing: implications for age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Essays Biochem 55:119–131. doi:10.1042/bse0550119
Castillo K, Nassif M, Valenzuela V, Rojas F, Matus S, Mercado G et al (2013) Trehalose delays the progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by enhancing autophagy in motoneurons. Autophagy 9(9):1308–1320
Celardo I, Martins LM, Gandhi S (2014) Unravelling mitochondrial pathways to Parkinson’s disease. Br J Pharmacol 171(8):1943–1957. doi:10.1111/bph.12433
Ching JK, Elizabeth SV, Ju JS, Lusk C, Pittman SK, Weihl CC (2013) mTOR dysfunction contributes to vacuolar pathology and weakness in valosin-containing protein associated inclusion body myopathy. Hum Mol Genet 22(6):1167–1179. doi:10.1093/hmg/dds524
Chua CE, Gan BQ, Tang BL (2011) Involvement of members of the Rab family and related small GTPases in autophagosome formation and maturation. Cell Mol Life Sci 68(20):3349–3358. doi:10.1007/s00018-011-0748-9
Cortes CJ, Qin K, Cook J, Solanki A, Mastrianni JA (2012) Rapamycin delays disease onset and prevents PrP plaque deposition in a mouse model of Gerstmann–Straussler–Scheinker disease. J Neurosci 32(36):12396–12405. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6189-11.2012
Coupe B, Ishii Y, Dietrich MO, Komatsu M, Horvath TL, Bouret SG (2012) Loss of autophagy in pro-opiomelanocortin neurons perturbs axon growth and causes metabolic dysregulation. Cell Metab 15(2):247–255. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.12.016
Cox LE, Ferraiuolo L, Goodall EF, Heath PR, Higginbottom A, Mortiboys H et al (2010) Mutations in CHMP2B in lower motor neuron predominant amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). PLoS One 5(3):e9872. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009872
Cuervo AM, Dice JF (2000) Age-related decline in chaperone-mediated autophagy. J Biol Chem 275(40):31505–31513
Cuervo AM, Dice JF, Knecht E (1997) A population of rat liver lysosomes responsible for the selective uptake and degradation of cytosolic proteins. J Biol Chem 272(9):5606–5615
Cuervo AM, Stefanis L, Fredenburg R, Lansbury PT, Sulzer D (2004) Impaired degradation of mutant alpha-synuclein by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Science 305(5688):1292–1295
Cuervo AM, Wong E (2014) Chaperone-mediated autophagy: roles in disease and aging. Cell Res 24(1):92–104. doi:10.1038/cr.2013.153
Cullen V, Sardi SP, Ng J, Xu YH, Sun Y, Tomlinson JJ et al (2011) Acid beta-glucosidase mutants linked to Gaucher disease, Parkinson disease, and Lewy body dementia alter alpha-synuclein processing. Ann Neurol 69(6):940–953. doi:10.1002/ana.22400
Curcio-Morelli C, Charles FA, Micsenyi MC, Cao Y, Venugopal B, Browning MF et al (2010) Macroautophagy is defective in mucolipin-1-deficient mouse neurons. Neurobiol Dis 40(2):370–377. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2010.06.010
d’Ydewalle C, Bogaert E, Van Den Bosch L (2012) HDAC6 at the intersection of neuroprotection and neurodegeneration. Traffic 13(6):771–779. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2012.01347.x
Dehay B, Ramirez A, Martinez-Vicente M, Perier C, Canron MH, Doudnikoff E et al (2012) Loss of P-type ATPase ATP13A2/PARK9 function induces general lysosomal deficiency and leads to Parkinson disease neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(24):9611–9616. doi:10.1073/pnas.1112368109
Deng HX, Chen W, Hong ST, Boycott KM, Gorrie GH, Siddique N et al (2011) Mutations in UBQLN2 cause dominant X-linked juvenile and adult-onset ALS and ALS/dementia. Nature 477(7363):211–215. doi:10.1038/nature10353
Dengjel J, Hoyer-Hansen M, Nielsen MO, Eisenberg T, Harder LM, Schandorff S et al (2012) Identification of autophagosome-associated proteins and regulators by quantitative proteomic analysis and genetic screens. Mol Cell Proteomics 11(3):M111 014035. doi:10.1074/mcp.M111.014035
Dere E, Dahm L, Lu D, Hammerschmidt K, Ju A, Tantra M et al (2014) Heterozygous ambra1 deficiency in mice: a genetic trait with autism-like behavior restricted to the female gender. Front Behav Neurosci 8:181. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00181
Di Nardo A, Wertz MH, Kwiatkowski E, Tsai PT, Leech JD, Greene-Colozzi E et al (2014) Neuronal Tsc1/2 complex controls autophagy through AMPK-dependent regulation of ULK1. Hum Mol Genet 23(14):3865–3874. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu101
Dice JF (2007) Chaperone-mediated autophagy. Autophagy 3(4):295–299
Dohi E, Tanaka S, Seki T, Miyagi T, Hide I, Takahashi T et al (2012) Hypoxic stress activates chaperone-mediated autophagy and modulates neuronal cell survival. Neurochem Int 60(4):431–442. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2012.01.020
Dong X, Levine B (2013) Autophagy and viruses: adversaries or allies? J Innate Immun 5(5):480–493. doi:10.1159/000346388
Dupuis L (2014) Mitochondrial quality control in neurodegenerative diseases. Biochimie 100:177–183. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2013.07.033
Ejlerskov P, Rasmussen I, Nielsen TT, Bergstrom AL, Tohyama Y, Jensen PH, Vilhardt F (2013) Tubulin polymerization-promoting protein (TPPP/p25alpha) promotes unconventional secretion of alpha-synuclein through exophagy by impairing autophagosome–lysosome fusion. J Biol Chem 288(24):17313–17335. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.401174
Eskelinen EL (2005) Maturation of autophagic vacuoles in mammalian cells. Autophagy 1:1–10
Eskelinen EL, Illert AL, Tanaka Y, Schwarzmann G, Blanz J, Von Figura K, Saftig P (2002) Role of LAMP-2 in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy. Mol Biol Cell 13(9):3355–3368. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-02-0114
Eskelinen EL, Reggiori F, Baba M, Kovacs AL, Seglen PO (2011) Seeing is believing: the impact of electron microscopy on autophagy research. Autophagy 7(9):935–956
Eskelinen EL, Saftig P (2009) Autophagy: a lysosomal degradation pathway with a central role in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1793(4):664–673. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.07.014
Fecto F, Siddique T (2012) UBQLN2/P62 cellular recycling pathways in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Muscle Nerve 45(2):157–162. doi:10.1002/mus.23278
Felbor U, Kessler B, Mothes W, Goebel HH, Ploegh HL, Bronson RT, Olsen BR (2002) Neuronal loss and brain atrophy in mice lacking cathepsins B and L. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(12):7883–7888. doi:10.1073/pnas.112632299
Feng Y, He D, Yao Z, Klionsky DJ (2014) The machinery of macroautophagy. Cell Res 24(1):24–41. doi:10.1038/cr.2013.168
Filimonenko M, Stuffers S, Raiborg C, Yamamoto A, Malerod L, Fisher EM et al (2007) Functional multivesicular bodies are required for autophagic clearance of protein aggregates associated with neurodegenerative disease. J Cell Biol 179(3):485–500. doi:10.1083/jcb.200702115
Fimia GM, Stoykova A, Romagnoli A, Giunta L, Di Bartolomeo S, Nardacci R et al (2007) Ambra 1 regulates autophagy and development of the nervous system. Nature 447:1121–1125
Fornai F, Longone P, Cafaro L, Kastsiuchenka O, Ferrucci M, Manca ML et al (2008) Lithium delays progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(6):2052–2057. doi:10.1073/pnas.0708022105
Fornai F, Longone P, Ferrucci M, Lenzi P, Isidoro C, Ruggieri S et al (2008) Autophagy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: the multiple roles of lithium. Autophagy 4(4):527–530
Fouillet A, Levet C, Virgone A, Robin M, Dourlen P, Rieusset J et al (2012) ER stress inhibits neuronal death by promoting autophagy. Autophagy 8(6):915–926. doi:10.4161/auto.19716
Fraldi A, Annunziata F, Lombardi A, Kaiser HJ, Medina DL, Spampanato C et al (2010) Lysosomal fusion and SNARE function are impaired by cholesterol accumulation in lysosomal storage disorders. EMBO J 29(21):3607–3620. doi:10.1038/emboj.2010.237
Friedman LG, Lachenmayer ML, Wang J, He LQ, Poulose SM, Komatsu M et al (2012) Disrupted autophagy leads to dopaminergic axon and dendrite degeneration and promotes presynaptic accumulation of alpha-synuclein and LRRK2 in the brain. J Neurosci 32(22):7585–7593. doi:10.1523/Jneurosci.5809-11.2012
Fu MM, Nirschl JJ, Holzbaur EL (2014) LC3 binding to the scaffolding protein JIP1 regulates processive dynein-driven transport of autophagosomes. Dev Cell 29(5):577–590. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2014.04.015
Fujita N, Itoh T, Omori H, Fukuda M, Noda T, Yoshimori T (2008) The Atg16L complex specifies the site of LC3 lipidation for membrane biogenesis in autophagy. Mol Biol Cell 19(5):2092–2100
Fukuda T, Ewan L, Bauer M, Mattaliano RJ, Zaal K, Ralston E et al (2006) Dysfunction of endocytic and autophagic pathways in a lysosomal storage disease. Ann Neurol 59(4):700–708. doi:10.1002/ana.20807
Fusco C, Micale L, Egorov M, Monti M, D’Addetta EV, Augello B et al (2012) The E3-ubiquitin ligase TRIM50 interacts with HDAC6 and p62, and promotes the sequestration and clearance of ubiquitinated proteins into the aggresome. PLoS One 7(7):e40440. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040440
Gal J, Strom AL, Kilty R, Zhang F, Zhu H (2007) p62 accumulates and enhances aggregate formation in model systems of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Biol Chem 282(15):11068–11077. doi:10.1074/jbc.M608787200
Gal J, Strom AL, Kwinter DM, Kilty R, Zhang J, Shi P et al (2009) Sequestosome 1/p62 links familial ALS mutant SOD1 to LC3 via an ubiquitin-independent mechanism. J Neurochem 111(4):1062–1073. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06388.x
Garami A, Zwartkruis FJ, Nobukuni T, Joaquin M, Roccio M, Stocker H et al (2003) Insulin activation of Rheb, a mediator of mTOR/S6K/4E-BP signaling, is inhibited by TSC1 and 2. Mol Cell 11(6):1457–1466
Ge L, Baskaran S, Schekman R, Hurley JH (2014) The protein-vesicle network of autophagy. Curr Opin Cell Biol 29C:18–24. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2014.02.005
Gelino S, Hansen M (2012) Autophagy—an emerging anti-aging mechanism. J Clin Exp Pathol Suppl 4:006
Gitcho MA, Strider J, Carter D, Taylor-Reinwald L, Forman MS, Goate AM, Cairns NJ (2009) VCP mutations causing frontotemporal lobar degeneration disrupt localization of TDP-43 and induce cell death. J Biol Chem 284(18):12384–12398. doi:10.1074/jbc.M900992200
Graef M, Friedman JR, Graham C, Babu M, Nunnari J (2013) ER exit sites are physical and functional core autophagosome biogenesis components. Mol Biol Cell 24(18):2918–2931. doi:10.1091/mbc.E13-07-0381
Guo YJ, Chang CM, Huang R, Liu B, Bao L, Liu W (2012) AP1 is essential for generation of autophagosomes from the trans-Golgi network. J Cell Sci 125(7):1706–1715. doi:10.1242/Jcs.093203
Gutierrez MG, Munafo DB, Beron W, Colombo MI (2004) Rab7 is required for the normal progression of the autophagic pathway in mammalian cells. J Cell Sci 117:2687–2697
Hadano S, Otomo A, Kunita R, Suzuki-Utsunomiya K, Akatsuka A, Koike M et al (2010) Loss of ALS2/Alsin exacerbates motor dysfunction in a SOD1-expressing mouse ALS model by disturbing endolysosomal trafficking. PLoS One 5(3):e9805. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009805
Hailey DW, Rambold AS, Satpute-Krishnan P, Mitra K, Sougrat R, Kim PK, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2010) Mitochondria supply membranes for autophagosome biogenesis during starvation. Cell 141(4):656–667. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.009
Hale AN, Ledbetter DJ, Gawriluk TR, Rucker EB (2013) Autophagy. Regulation and role in development. Autophagy 9:951–972
Hamasaki M, Furuta N, Matsuda A, Nezu A, Yamamoto A, Fujita N et al (2013) Autophagosomes form at ER-mitochondria contact sites. Nature 495(7441):389–393. doi:10.1038/nature11910
Hara T, Nakamura K, Matsui M, Yamamoto A, Nakahara Y, Suzuki-Migishima R et al (2006) Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature 441(7095):885–889
Hayashi-Nishino M, Fujita N, Noda T, Yamaguchi A, Yoshimori T, Yamamoto A (2009) A subdomain of the endoplasmic reticulum forms a cradle for autophagosome formation. Nat Cell Biol 11(12):1433–1437
He CC, Sumpter R, Levine B (2012) Exercise induces autophagy in peripheral tissues and in the brain. Autophagy 8(10):1548–1551. doi:10.4161/Auto.21327
He LQ, Lu JH, Yue ZY (2013) Autophagy in ageing and ageing-associated diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34(5):605–611. doi:10.1038/aps.2012.188
Heiseke A, Aguib Y, Riemer C, Baier M, Schatzl HM (2009) Lithium induces clearance of protease resistant prion protein in prion-infected cells by induction of autophagy. J Neurochem 109(1):25–34. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.05906.x
Heiseke A, Aguib Y, Schatzl HM (2010) Autophagy, prion infection and their mutual interactions. Curr Issues Mol Biol 12(2):87–97
Hernandez D, Torres CA, Setlik W, Cebrian C, Mosharov EV, Tang GM et al (2012) Regulation of presynaptic neurotransmission by macroautophagy. Neuron 74(2):277–284. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.02.020
Hollenbeck PJ (1993) Products of endocytosis and autophagy are retrieved from axons by regulated retrograde organelle transport. J Cell Biol 121(2):305–315
Huang CC, Bose JK, Majumder P, Lee KH, Huang JT, Huang JK, Shen CKJ (2014) Metabolism and mis-metabolism of the neuropathological signature protein TDP-43. J Cell Sci 127(Pt 14):3024–3038. doi:10.1242/jcs.136150
Hung YH, Chen LM, Yang JY, Yang WY (2013) Spatiotemporally controlled induction of autophagy-mediated lysosome turnover. Nat Commun 4:2111. doi:10.1038/ncomms3111
Inoki K, Li Y, Xu T, Guan KL (2003) Rheb GTPase is a direct target of TSC2 GAP activity and regulates mTOR signaling. Genes Dev 17(15):1829–1834. doi:10.1101/gad.1110003
Itakura E, Mizushima N (2010) Characterization of autophagosome formation site by a hierarchical analysis of mammalian Atg proteins. Autophagy 6(6):764–776
Iwata A, Riley BE, Johnston JA, Kopito RR (2005) HDAC6 and microtubules are required for autophagic degradation of aggregated huntingtin. J Biol Chem 280(48):40282–40292
Jackson WT, Giddings TH, Taylor MP, Mulinyawe S, Rabinovitch M, Kopito RR, Kirkegaard K (2005) Subversion of cellular autophagosomal machinery by RNA viruses. PLoS Biol 3(5):861–871. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030156
Jäger S, Bucci C, Tanida I, Ueno T, Kominami E, Saftig P, Eskelinen EL (2004) Role for Rab7 in maturation of late autophagic vacuoles. J Cell Sci 117(20):4837–4848. doi:10.1242/Jcs.01370
Jeong JK, Moon MH, Lee YJ, Seol JW, Park SY (2013) Autophagy induced by the class III histone deacetylase Sirt1 prevents prion peptide neurotoxicity. Neurobiol Aging 34(1):146–156. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.04.002
Jiang M, Wang J, Fu J, Du L, Jeong H, West T et al (2012) Neuroprotective role of Sirt1 in mammalian models of Huntington’s disease through activation of multiple Sirt1 targets. Nat Med 18(1):153–158. doi:10.1038/nm.2558
Jin M, He D, Backues SK, Freeberg MA, Liu X, Kim JK, Klionsky D (2014) Transcriptional regulation by pho23 modulates the frequency of autophagosome formation. Curr Biol 24(12):1314–1322. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.04.048
Johnson JO, Mandrioli J, Benatar M, Abramzon Y, Van Deerlin VM, Trojanowski JQ et al (2010) Exome sequencing reveals VCP mutations as a cause of familial ALS. Neuron 68(5):857–864. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.036
Ju JS, Fuentealba RA, Miller SE, Jackson E, Piwnica-Worms D, Baloh RH, Weihl CC (2009) Valosin-containing protein (VCP) is required for autophagy and is disrupted in VCP disease. J Cell Biol 187(6):875–888. doi:10.1083/jcb.200908115
Jung CH, Jun CB, Ro SH, Kim YM, Otto NM, Cao J et al (2009) ULK-Atg13-FIP200 complexes mediate mTOR signaling to the autophagy machinery. Mol Biol Cell 20(7):1992–2003. doi:10.1091/mbc.E08-12-1249
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A, Kirisako T, Noda T et al (2000) LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J 19:5720–5728
Kabuta T, Furuta A, Aoki S, Furuta K, Wada K (2008) Aberrant interaction between Parkinson disease-associated mutant UCH-L1 and the lysosomal receptor for chaperone-mediated autophagy. J Biol Chem 283(35):23731–23738. doi:10.1074/jbc.M801918200
Kabuta T, Suzuki Y, Wada K (2006) Degradation of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked mutant Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase proteins by macroautophagy and the proteasome. J Biol Chem 281(41):30524–30533. doi:10.1074/jbc.M603337200
Katsumata K, Nishiyama J, Inoue T, Mizushima N, Takeda J, Yuzaki M (2010) Dynein- and activity-dependent retrograde transport of autophagosomes in neuronal axons. Autophagy 6(3):378–385
Kaushik S, Cuervo AM (2012) Chaperone-mediated autophagy: a unique way to enter the lysosome world. Trends Cell Biol 22(8):407–417. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2012.05.006
Kaushik S, Massey AC, Mizushima N, Cuervo AM (2008) Constitutive activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy in cells with impaired macroautophagy. Mol Biol Cell 19(5):2179–2192. doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-11-1155
Kiffin R, Christian C, Knecht E, Cuervo AM (2004) Activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy during oxidative stress. Mol Biol Cell 15(11):4829–4840. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-06-0477
Kiffin R, Kaushik S, Zeng M, Bandyopadhyay U, Zhang C, Massey AC, Cuervo AM (2007) Altered dynamics of the lysosomal receptor for chaperone-mediated autophagy with age. J Cell Sci 120(Pt 5):782–791. doi:10.1242/jcs.001073
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, Guan KL (2011) AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol 13(2):132–141. doi:10.1038/ncb2152
Knaevelsrud H, Simonsen A (2010) Fighting disease by selective autophagy of aggregate-prone proteins. FEBS Lett 584:2635–2645
Knoferle J, Koch JC, Ostendorf T, Michel U, Planchamp V, Vutova P et al (2010) Mechanisms of acute axonal degeneration in the optic nerve in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(13):6064–6069. doi:10.1073/pnas.0909794107
Koike M, Nakanishi H, Saftig P, Ezaki J, Isahara K, Ohsawa Y et al (2000) Cathepsin D deficiency induces lysosomal storage with ceroid lipofuscin in mouse CNS neurons. J Neurosci 20(18):6898–6906
Kollmann K, Damme M, Markmann S, Morelle W, Schweizer M, Hermans-Borgmeyer I et al (2012) Lysosomal dysfunction causes neurodegeneration in mucolipidosis II ‘knock-in’ mice. Brain 135(Pt 9):2661–2675. doi:10.1093/brain/aws209
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T, Murata S, Iwata J, Tanida I et al (2006) Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature 441(7095):880–884
Komatsu M, Wang QJ, Holstein GR, Friedrich VL Jr, Iwata J, Kominami E et al (2007) Essential role for autophagy protein Atg7 in the maintenance of axonal homeostasis and the prevention of axonal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(36):14489–14494
Koren I, Reem E, Kimchi A (2010) DAP1, a novel substrate of mTOR, negatively regulates autophagy. Curr Biol 20(12):1093–1098. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2010.04.041
Kramer H (2013) Route to destruction: autophagosomes SNARE lysosomes. J Cell Biol 201(4):495–497. doi:10.1083/jcb.201304065
Lamark T, Johansen T (2012) Aggrephagy: selective disposal of protein aggregates by macroautophagy. Inte J Cell Biol 2012:736905. doi:10.1155/2012/736905
Lee HJ, Cho ED, Lee KW, Kim JH, Cho SG, Lee SJ (2013) Autophagic failure promotes the exocytosis and intercellular transfer of alpha-synuclein. Exp Mol Med 45:e22. doi:10.1038/emm.2013.45
Lee JA, Beigneux A, Ahmad ST, Young SG, Gao FB (2007) ESCRT-III dysfunction causes autophagosome accumulation and neurodegeneration. Curr Biol 17(18):1561–1567. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2007.07.029
Lee JY, Koga H, Kawaguchi Y, Tang W, Wong E, Gao YS et al (2010) HDAC6 controls autophagosome maturation essential for ubiquitin-selective quality-control autophagy. EMBO J 29(5):969–980. doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.405
Lee JY, Nagano Y, Taylor JP, Lim KL, Yao TP (2010) Disease-causing mutations in parkin impair mitochondrial ubiquitination, aggregation, and HDAC6-dependent mitophagy. J Cell Biol 189(4):671–679. doi:10.1083/jcb.201001039
Lee KM, Hwang SK, Lee JA (2013) Neuronal autophagy and neurodevelopmental disorders. Exp Neurobiol 22(3):133–142. doi:10.5607/en.2013.22.3.133
Lee S, Sato Y, Nixon RA (2011) Lysosomal proteolysis inhibition selectively disrupts axonal transport of degradative organelles and causes an Alzheimer’s-like axonal dystrophy. J Neurosci 31(21):7817–7830. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6412-10.2011
Liang CC, Wang C, Peng X, Gan B, Guan JL (2010) Neural-specific deletion of FIP200 leads to cerebellar degeneration caused by increased neuronal death and axon degeneration. J Biol Chem 285(5):3499–3509. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.072389
Liao G, Yao Y, Liu J, Yu Z, Cheung S, Xie A et al (2007) Cholesterol accumulation is associated with lysosomal dysfunction and autophagic stress in Npc1−/− mouse brain. Am J Pathol 171(3):962–975. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.070052
Liberski PP, Sikorska B, Bratosiewicz-Wasik J, Gajdusek DC, Brown P (2004) Neuronal cell death in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (prion diseases) revisited: from apoptosis to autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(12):2473–2490. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2004.04.016
Lipinski MM, Zheng B, Lu T, Yan Z, Py BF, Ng A et al (2010) Genome-wide analysis reveals mechanisms modulating autophagy in normal brain aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(32):14164–14169. doi:10.1073/pnas.1009485107
Liu L, Feng D, Chen G, Chen M, Zheng Q, Song P et al (2012) Mitochondrial outer-membrane protein FUNDC1 mediates hypoxia-induced mitophagy in mammalian cells. Nat Cell Biol 14(2):177–185. doi:10.1038/ncb2422
Long X, Ortiz-Vega S, Lin Y, Avruch J (2005) Rheb binding to mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is regulated by amino acid sufficiency. J Biol Chem 280(25):23433–23436. doi:10.1074/jbc.C500169200
Longatti A, Lamb CA, Razi M, Yoshimura S, Barr FA, Tooze SA (2012) TBC1D14 regulates autophagosome formation via Rab11-and ULK1-positive recycling endosomes. J Cell Biol 197(5):659–675. doi:10.1083/jcb.201111079
Lu T, Aron L, Zullo J, Pan Y, Kim H, Chen Y et al (2014) REST and stress resistance in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 507(7493):448–454. doi:10.1038/nature13163
Lv L, Li D, Zhao D, Lin R, Chu Y, Zhang H et al (2011) Acetylation targets the M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase for degradation through chaperone-mediated autophagy and promotes tumor growth. Mol Cell 42(6):719–730. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2011.04.025
Lynch-Day MA, Mao K, Wang K, Zhao M, Klionsky DJ (2012) The role of autophagy in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2(4):a009357. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a009357
Maday S, Wallace KE, Holzbaur EL (2012) Autophagosomes initiate distally and mature during transport toward the cell soma in primary neurons. J Cell Biol 196(4):407–417. doi:10.1083/jcb.201106120
Maejima I, Takahashi A, Omori H, Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Saitoh T et al (2013) Autophagy sequesters damaged lysosomes to control lysosomal biogenesis and kidney injury. EMBO J 32(17):2336–2347. doi:10.1038/emboj.2013.171
Maetzel D, Sarkar S, Wang H, Abi-Mosleh L, Xu P, Cheng AW et al (2014) Genetic and chemical correction of cholesterol accumulation and impaired autophagy in hepatic and neural cells derived from Niemann–Pick type C patient-specific iPS cells. Stem Cell Rep 2(6):866–880. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.03.014
Manzoni C, Lewis PA (2013) Dysfunction of the autophagy/lysosomal degradation pathway is a shared feature of the genetic synucleinopathies. FASEB J 27(9):3424–3429. doi:10.1096/fj.12-223842
Martina JA, Chen Y, Gucek M, Puertollano R (2012) MTORC1 functions as a transcriptional regulator of autophagy by preventing nuclear transport of TFEB. Autophagy 8(6):903–914. doi:10.4161/auto.19653
Martina JA, Diab HI, Lishu L, Jeong AL, Patange S, Raben N, Puertollano R (2014) The nutrient-responsive transcription factor TFE3 promotes autophagy, lysosomal biogenesis, and clearance of cellular debris. Sci Signal 7(309):ra9. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2004754
Martina JA, Puertollano R (2013) Rag GTPases mediate amino acid-dependent recruitment of TFEB and MITF to lysosomes. J Cell Biol 200(4):475–491. doi:10.1083/jcb.201209135
Martina JA, Puertollano R (2013) RRAG GTPases link nutrient availability to gene expression, autophagy and lysosomal biogenesis. Autophagy 9(6):928–930. doi:10.4161/auto.24371
Martinez-Vicente M, Talloczy Z, Kaushik S, Massey AC, Mazzulli J, Mosharov EV et al (2008) Dopamine-modified alpha-synuclein blocks chaperone-mediated autophagy. J Clin Invest 118(2):777–788. doi:10.1172/JCI32806
Massey AC, Kaushik S, Sovak G, Kiffin R, Cuervo AM (2006) Consequences of the selective blockage of chaperone-mediated autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(15):5805–5810. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507436103
Matsunaga K, Morita E, Saitoh T, Akira S, Ktistakis NT, Izumi T et al (2010) Autophagy requires endoplasmic reticulum targeting of the PI3-kinase complex via Atg14L. J Cell Biol 190(4):511–521. doi:10.1083/jcb.200911141
Mazure NM, Pouyssegur J (2010) Hypoxia-induced autophagy: cell death or cell survival? Curr Opin Cell Biol 22(2):177–180. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.11.015
Medina DL, Fraldi A, Bouche V, Annunziata F, Mansueto G, Spampanato C et al (2011) Transcriptional activation of lysosomal exocytosis promotes cellular clearance. Dev Cell 21(3):421–430. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2011.07.016
Melser S, Chatelain EH, Lavie J, Mahfouf W, Jose C, Obre E et al (2013) Rheb regulates mitophagy induced by mitochondrial energetic status. Cell Metab 17(5):719–730. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2013.03.014
Meyer H, Bug M, Bremer S (2012) Emerging functions of the VCP/p97 AAA-ATPase in the ubiquitin system. Nat Cell Biol 14(2):117–123. doi:10.1038/ncb2407
Micsenyi MC, Sikora J, Stephney G, Dobrenis K, Walkley SU (2013) Lysosomal membrane permeability stimulates protein aggregate formation in neurons of a lysosomal disease. J Neurosci 33(26):10815–10827. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0987-13.2013
Mizuno Y, Amari M, Takatama M, Aizawa H, Mihara B, Okamoto K (2006) Immunoreactivities of p62, an ubiqutin-binding protein, in the spinal anterior horn cells of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 249(1):13–18. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2006.05.060
Mizushima N, Klionsky DJ (2007) Protein turnover via autophagy: implications for metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 27:19–40. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.27.061406.093749
Mizushima N, Yamamoto A, Matsui M, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y (2004) In vivo analysis of autophagy in response to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a fluorescent autophagosome marker. Mol Biol Cell 15:1101–1111
Moon JH, Lee JH, Park JY, Kim SW, Lee YJ, Kang SJ et al (2014) Caffeine prevents human prion protein-mediated neurotoxicity through the induction of autophagy. Int J Mol Med 34(2):553–558. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2014.1814
Mortimore GE, Schworer CM (1977) Induction of autophagy by amino-acid deprivation in perfused rat liver. Nature 270(5633):174–176
Moskot M, Montefusco S, Jakobkiewicz-Banecka J, Mozolewski P, Wegrzyn A, Di Bernardo D et al (2014) The phytoestrogen genistein modulates lysosomal metabolism and transcription factor EB (TFEB) activation. J Biol Chem 289(24):17054–17069. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.555300
Musiwaro P, Smith M, Manifava M, Walker SA, Ktistakis NT (2013) Characteristics and requirements of basal autophagy in HEK293 cells. Autophagy 9(9):1407–1417
Nakagaki T, Satoh K, Ishibashi D, Fuse T, Sano K, Kamatari YO et al (2013) FK506 reduces abnormal prion protein through the activation of autolysosomal degradation and prolongs survival in prion-infected mice. Autophagy 9(9):1386–1394
Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen DF, Youle RJ (2008) Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol 183(5):795–803. doi:10.1083/jcb.200809125
Nassif M, Valenzuela V, Rojas-Rivera D, Vidal R, Matus S, Castillo K et al (2014) Pathogenic role of BECN1/beclin 1 in the development of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Autophagy 10(7):1256–1271
Nazio F, Strappazzon F, Antonioli M, Bielli P, Cianfanelli V, Bordi M et al (2013) mTOR inhibits autophagy by controlling ULK1 ubiquitylation, self-association and function through AMBRA1 and TRAF6. Nat Cell Biol 15(4):406. doi:10.1038/Ncb2708
Nijholt DA, de Graaf TR, van Haastert ES, Oliveira AO, Berkers CR, Zwart R et al (2011) Endoplasmic reticulum stress activates autophagy but not the proteasome in neuronal cells: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Differ 18(6):1071–1081. doi:10.1038/cdd.2010.176
Nishino I, Fu J, Tanji K, Yamada T, Shimojo S, Koori T et al (2000) Primary LAMP-2 deficiency causes X-linked vacuolar cardiomyopathy and myopathy (Danon disease). Nature 406(6798):906–910. doi:10.1038/35022604
Nishiyama J, Miura E, Mizushima N, Watanabe M, Yuzaki M (2007) Aberrant membranes and double-membrane structures accumulate in the axons of Atg5-null Purkinje cells before neuronal death. Autophagy 3(6):591–596
Nixon RA, Wegiel J, Kumar A, Yu WH, Peterhoff C, Cataldo A, Cuervo AM (2005) Extensive involvement of autophagy in Alzheimer disease: an immuno-electron microscopy study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:113–122
Novak I, Kirkin V, McEwan DG, Zhang J, Wild P, Rozenknop A et al (2010) Nix is a selective autophagy receptor for mitochondrial clearance. EMBO Rep 11(1):45–51. doi:10.1038/embor.2009.256
Ogata M, Hino S, Saito A, Morikawa K, Kondo S, Kanemoto S et al (2006) Autophagy is activated for cell survival after endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol 26(24):9220–9231. doi:10.1128/MCB.01453-06
Olzmann JA, Chin LS (2008) Parkin-mediated K63-linked polyubiquitination: a signal for targeting misfolded proteins to the aggresome-autophagy pathway. Autophagy 4(1):85–87
Olzmann JA, Li L, Chudaev MV, Chen J, Perez FA, Palmiter RD, Chin LS (2007) Parkin-mediated K63-linked polyubiquitination targets misfolded DJ-1 to aggresomes via binding to HDAC6. J Cell Biol 178(6):1025–1038. doi:10.1083/jcb.200611128
Orenstein SJ, Cuervo AM (2010) Chaperone-mediated autophagy: molecular mechanisms and physiological relevance. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21(7):719–726. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.02.005
Orenstein SJ, Kuo SH, Tasset I, Arias E, Koga H, Fernandez-Carasa I et al (2013) Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat Neurosci 16(4):394–406. doi:10.1038/nn.3350
Orvedahl A, Alexander D, Talloczy Z, Sun Q, Wei Y, Zhang W et al (2007) HSV-1 ICP34.5 confers neurovirulence by targeting the beclin 1 autophagy protein. Cell Host Microbe 1(1):23–35
Orvedahl A, MacPherson S, Sumpter R, Talloczy Z, Zou ZJ, Levine B (2010) Autophagy protects against sindbis virus infection of the central nervous system. Cell Host Microbe 7(2):115–127. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2010.01.007
Papadakis M, Hadley G, Xilouri M, Hoyte LC, Nagel S, McMenamin MM et al (2013) Tsc1 (hamartin) confers neuroprotection against ischemia by inducing autophagy. Nat Med 19(3):351–357. doi:10.1038/nm.3097
Papinski D, Schuschnig M, Reiter W, Wilhelm L, Barnes CA, Maiolica A et al (2014) Early steps in autophagy depend on direct phosphorylation of Atg9 by the Atg1 kinase. Mol Cell 53(3):471–483. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.12.011
Parkinson N, Ince PG, Smith MO, Highley R, Skibinski G, Andersen PM et al (2006) ALS phenotypes with mutations in CHMP2B (charged multivesicular body protein 2B). Neurology 67(6):1074–1077
Parzych KR, Klionsky DJ (2014) An overview of autophagy: morphology, mechanism and regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal 20(3):460–473
Platt FM, Boland B, van der Spoel AC (2012) The cell biology of disease: lysosomal storage disorders: the cellular impact of lysosomal dysfunction. J Cell Biol 199(5):723–734. doi:10.1083/jcb.201208152
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A et al (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276(5321):2045–2047
Prusiner SB, Scott MR, DeArmond SJ, Cohen FE (1998) Prion protein biology. Cell 93(3):337–348. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81163-0
Quan W, Kim HK, Moon EY, Kim SS, Choi CS, Komatsu M et al (2012) Role of hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin neuron autophagy in the control of appetite and leptin response. Endocrinology 153(4):1817–1826. doi:10.1210/en.2011-1882
Quintavalle C, Di Costanzo S, Zanca C, Tasset I, Fraldi A, Incoronato M et al (2014) Phosphorylation-regulated degradation of the tumor-suppressor form of PED by chaperone-mediated autophagy in lung cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 229(10):1359–1368. doi:10.1002/jcp.24569
Ramachandran N, Munteanu I, Wang PX, Ruggieri A, Rilstone JJ, Israelian N et al (2013) VMA21 deficiency prevents vacuolar ATPase assembly and causes autophagic vacuolar myopathy. Acta Neuropathol 125(3):439–457. doi:10.1007/s00401-012-1073-6
Ravikumar B, Moreau K, Jahreiss L, Puri C, Rubinsztein DC (2010) Plasma membrane contributes to the formation of pre-autophagosomal structures. Nat Cell Biol 12(8):747–757. doi:10.1038/ncb2078
Redmann M, Dodson M, Boyer-Guittaut M, Darley-Usmar V, Zhang J (2014) Mitophagy mechanisms and role in human diseases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 53C:127–133. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2014.05.010
Richards AL, Jackson WT (2013) How positive-strand RNA viruses benefit from autophagosome maturation. J Virol 87(18):9966–9972. doi:10.1128/JVI.00460-13
Richter-Landsberg C, Leyk J (2013) Inclusion body formation, macroautophagy, and the role of HDAC6 in neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol 126(6):793–807. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1158-x
Roberts DJ, Tan-Sah VP, Ding EY, Smith JM, Miyamoto S (2014) Hexokinase-II positively regulates glucose starvation-induced autophagy through TORC1 inhibition. Mol Cell 53(4):521–533. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.12.019
Roczniak-Ferguson A, Petit CS, Froehlich F, Qian S, Ky J, Angarola B et al (2012) The transcription factor TFEB links mTORC1 signaling to transcriptional control of lysosome homeostasis. Sci Signal 5(228):ra42. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2002790
Rodriguez-Muela N, Boya P (2012) Axonal damage, autophagy and neuronal survival. Autophagy 8(2):286–288. doi:10.4161/auto.8.2.18982
Rodriguez-Muela N, Germain F, Marino G, Fitze PS, Boya P (2012) Autophagy promotes survival of retinal ganglion cells after optic nerve axotomy in mice. Cell Death Differ 19(1):162–169. doi:10.1038/cdd.2011.88
Rodriguez-Navarro JA, Kaushik S, Koga H, Dall’Armi C, Shui G, Wenk MR et al (2012) Inhibitory effect of dietary lipids on chaperone-mediated autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(12):E705–E714. doi:10.1073/pnas.1113036109
Rogov V, Dotsch V, Johansen T, Kirkin V (2014) Interactions between autophagy receptors and ubiquitin-like proteins form the molecular basis for selective autophagy. Mol Cell 53(2):167–178. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.12.014
Rollinson S, Bennion J, Toulson G, Halliwell N, Usher S, Snowden J et al (2012) Analysis of optineurin in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurobiol Aging 33(2):425 e421–422. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.10.002
Rothenberg C, Srinivasan D, Mah L, Kaushik S, Peterhoff CM, Ugolino J et al (2010) Ubiquilin functions in autophagy and is degraded by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Hum Mol Genet 19(16):3219–3232. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq231
Rubino E, Rainero I, Chio A, Rogaeva E, Galimberti D, Fenoglio P et al (2012) SQSTM1 mutations in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 79(15):1556–1562. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e31826e25df
Sakaki K, Wu J, Kaufman RJ (2008) Protein kinase C theta is required for autophagy in response to stress in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 283(22):15370–15380. doi:10.1074/jbc.M710209200
Sardi SP, Clarke J, Viel C, Chan M, Tamsett TJ, Treleaven CM et al (2013) Augmenting CNS glucocerebrosidase activity as a therapeutic strategy for parkinsonism and other Gaucher-related synucleinopathies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(9):3537–3542. doi:10.1073/pnas.1220464110
Sardiello M, Palmieri M, di Ronza A, Medina DL, Valenza M, Gennarino VA et al (2009) A gene network regulating lysosomal biogenesis and function. Science 325(5939):473–477. doi:10.1126/science.1174447
Schatzl HM, Laszlo L, Holtzman DM, Tatzelt J, DeArmond SJ, Weiner RI et al (1997) A hypothalamic neuronal cell line persistently infected with scrapie prions exhibits apoptosis. J Virol 71(11):8821–8831
Scherz-Shouval R, Shvets E, Fass E, Shorer H, Gil L, Elazar Z (2007) Reactive oxygen species are essential for autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4. EMBO J 26(7):1749–1760. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601623
Schreiber A, Peter M (2013) Substrate recognition in selective autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Biochim Biophys Acta 1843(1):163–181. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.03.019
Scotter EL, Vance C, Nishimura AL, Lee YB, Chen HJ, Urwin H et al (2014) Differential roles of the ubiquitin proteasome system and autophagy in the clearance of soluble and aggregated TDP-43 species. J Cell Sci 127(Pt 6):1263–1278. doi:10.1242/jcs.140087
Seibenhener ML, Babu JR, Geetha T, Wong HC, Krishna NR, Wooten MW (2004) Sequestosome 1/p62 is a polyubiquitin chain binding protein involved in ubiquitin proteasome degradation. Mol Cell Biol 24(18):8055–8068. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.18.8055-8068.2004
Sepe S, Nardacci R, Fanelli F, Rosso P, Bernardi C, Cecconi F et al (2013) Expression of Ambra1 in mouse brain during physiological and Alzheimer type aging. Neurobiol Aging 35(1):96–108. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.07.001
Settembre C, Zoncu R, Medina DL, Vetrini F, Erdin S, Erdin S et al (2012) A lysosome-to-nucleus signalling mechanism senses and regulates the lysosome via mTOR and TFEB. EMBO J 31(5):1095–1108. doi:10.1038/emboj.2012.32
Shi R, Weng J, Zhao L, Li XM, Gao TM, Kong J (2012) Excessive autophagy contributes to neuron death in cerebral ischemia. CNS Neurosci Ther 18(3):250–260. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00295.x
Shibutani ST, Yoshimori T (2014) A current perspective of autophagosome biogenesis. Cell Res 24(1):58–68. doi:10.1038/cr.2013.159
Sikorska B, Liberski PP, Giraud P, Kopp N, Brown P (2004) Autophagy is a part of ultrastructural synaptic pathology in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a brain biopsy study. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(12):2563–2573. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2004.04.014
Simonsen A, Birkeland HC, Gillooly DJ, Mizushima N, Kuma A, Yoshimori T et al (2004) Alfy, a novel FYVE-domain-containing protein associated with protein granules and autophagic membranes. J Cell Sci 117:4239–4251
Skibinski G, Parkinson NJ, Brown JM, Chakrabarti L, Lloyd SL, Hummerich H et al (2005) Mutations in the endosomal ESCRTIII-complex subunit CHMP2B in frontotemporal dementia. Nat Genet 37(8):806–808. doi:10.1038/ng1609
Song W, Wang F, Lotfi P, Sardiello M, Segatori L (2014) 2-Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin promotes transcription factor EB-mediated activation of autophagy: implications for therapy. J Biol Chem 289(14):10211–10222. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.506246
Spampanato C, Feeney E, Li L, Cardone M, Lim JA, Annunziata F et al (2013) Transcription factor EB (TFEB) is a new therapeutic target for Pompe disease. EMBO Mol Med 5(5):691–706. doi:10.1002/emmm.201202176
Spencer B, Potkar R, Trejo M, Rockenstein E, Patrick C, Gindi R et al (2009) Beclin 1 gene transfer activates autophagy and ameliorates the neurodegenerative pathology in alpha-synuclein models of Parkinson’s and Lewy body diseases. J Neurosci 29(43):13578–13588. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4390-09.2009
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388(6645):839–840. doi:10.1038/42166
Stanley RE, Ragusa MJ, Hurley JH (2014) The beginning of the end: how scaffolds nucleate autophagosome biogenesis. Trends Cell Biol 24(1):73–81. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2013.07.008
Stefanis L, Larsen KE, Rideout HJ, Sulzer D, Greene LA (2001) Expression of A53T mutant but not wild-type alpha-synuclein in PC12 cells induces alterations of the ubiquitin-dependent degradation system, loss of dopamine release, and autophagic cell death. J Neurosci 21(24):9549–9560
Sulzer D, Mosharov E, Talloczy Z, Zucca FA, Simon JD, Zecca L (2008) Neuronal pigmented autophagic vacuoles: lipofuscin, neuromelanin, and ceroid as macroautophagic responses during aging and disease. J Neurochem 106(1):24–36. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05385.x
Takahashi Y, Meyerkord CL, Hori T, Runkle K, Fox TE, Kester M et al (2011) Bif-1 regulates Atg9 trafficking by mediating the fission of Golgi membranes during autophagy. Autophagy 7(1):61–73. doi:10.4161/auto.7.1.14015
Tan D, Cai Y, Wang J, Zhang J, Menon S, Chou HT et al (2013) The EM structure of the TRAPPIII complex leads to the identification of a requirement for COPII vesicles on the macroautophagy pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(48):19432–19437. doi:10.1073/pnas.1316356110
Tan JM, Wong ES, Kirkpatrick DS, Pletnikova O, Ko HS, Tay SP et al (2008) Lysine 63-linked ubiquitination promotes the formation and autophagic clearance of protein inclusions associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Hum Mol Genet 17(3):431–439. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm320
Tanaka A (2010) Parkin-mediated selective mitochondrial autophagy, mitophagy: Parkin purges damaged organelles from the vital mitochondrial network. FEBS Lett 584(7):1386–1392. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2010.02.060
Tanaka Y, Guhde G, Suter A, Eskelinen EL, Hartmann D, Lullmann-Rauch R et al (2000) Accumulation of autophagic vacuoles and cardiomyopathy in LAMP-2-deficient mice. Nature 406(6798):902–906. doi:10.1038/35022595
Tanji K, Zhang HX, Mori F, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K (2012) p62/sequestosome 1 binds to TDP-43 in brains with frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 inclusions. J Neurosci Res 90(10):2034–2042. doi:10.1002/Jnr.23081
Tatsuta T, Langer T (2008) Quality control of mitochondria: protection against neurodegeneration and ageing. EMBO J 27(2):306–314. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601972
Thelen M, Damme M, Schweizer M, Hagel C, Wong AM, Cooper JD et al (2012) Disruption of the autophagy-lysosome pathway is involved in neuropathology of the nclf mouse model of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. PLoS One 7(4):e35493. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035493
Thomas M, Alegre-Abarrategui J, Wade-Martins R (2013) RNA dysfunction and aggrephagy at the centre of an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/frontotemporal dementia disease continuum. Brain 136(Pt 5):1345–1360. doi:10.1093/brain/awt030
Torres CA, Sulzer D (2012) Macroautophagy can press a brake on presynaptic neurotransmission. Autophagy 8(10):1540–1541. doi:10.4161/Auto.21330
Treff W (1974) Das involutionsmuster des nucleus dentatus. In: Platt D (ed) Altern. Schattauer, Stuttgart, pp 37–54
Trempe JF, Fon EA (2013) Structure and function of Parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1, the three musketeers of neuroprotection. Front Neurol 4:38. doi:10.3389/fneur.2013.00038
Tresse E, Salomons FA, Vesa J, Bott LC, Kimonis V, Yao TP et al (2010) VCP/p97 is essential for maturation of ubiquitin-containing autophagosomes and this function is impaired by mutations that cause IBMPFD. Autophagy 6(2):217–227
Uemura T, Yamamoto M, Kametaka A, Sou YS, Yabashi A, Yamada A et al (2014) A cluster of thin tubular structures mediates transformation of the endoplasmic reticulum to autophagic isolation membrane. Mol Cell Biol 34(9):1695–1706. doi:10.1128/MCB.01327-13
Wager K, Russell C (2013) Mitophagy and neurodegeneration: the zebrafish model system. Autophagy 9(11):1693–1709. doi:10.4161/auto.25082
Walkley SU, Vanier MT (2009) Secondary lipid accumulation in lysosomal disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793(4):726–736. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.11.014
van der Vaart A, Griffith J, Reggiori F (2010) Exit from the golgi is required for the expansion of the autophagosomal phagophore in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 21(13):2270–2284. doi:10.1091/mbc.E09-04-0345
Van Humbeeck C, Cornelissen T, Hofkens H, Mandemakers W, Gevaert K, De Strooper B, Vandenberghe W (2011) Parkin interacts with Ambra1 to induce mitophagy. J Neurosci 31(28):10249–10261. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1917-11.2011
Wang IF, Guo BS, Liu YC, Wu CC, Yang CH, Tsai KJ, Shen CK (2012) Autophagy activators rescue and alleviate pathogenesis of a mouse model with proteinopathies of the TAR DNA-binding protein 43. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(37):15024–15029. doi:10.1073/pnas.1206362109
Wang QJ, Ding Y, Kohtz DS, Mizushima N, Cristea IM, Rout MP et al (2006) Induction of autophagy in axonal dystrophy and degeneration. J Neurosci 26(31):8057–8068. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2261-06.2006
Wang Y, Martinez-Vicente M, Kruger U, Kaushik S, Wong E, Mandelkow EM et al (2009) Tau fragmentation, aggregation and clearance: the dual role of lysosomal processing. Hum Mol Genet 18(21):4153–4170. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddp367
Vazquez P, Arroba AI, Cecconi F, de la Rosa EJ, Boya P, de Pablo F (2012) Atg5 and Ambra1 differentially modulate neurogenesis in neural stem cells. Autophagy 8(2):187–199. doi:10.4161/auto.8.2.18535
Wei K, Wang P, Miao CY (2012) A double-edged sword with therapeutic potential: an updated role of autophagy in ischemic cerebral injury. CNS Neurosci Ther 18(11):879–886. doi:10.1111/cns.12005
Venugopal B, Mesires NT, Kennedy JC, Curcio-Morelli C, Laplante JM, Dice JF, Slaugenhaupt SA (2009) Chaperone-mediated autophagy is defective in mucolipidosis type IV. J Cell Physiol 219(2):344–353. doi:10.1002/jcp.21676
Vergarajauregui S, Connelly PS, Daniels MP, Puertollano R (2008) Autophagic dysfunction in mucolipidosis type IV patients. Hum Mol Genet 17(17):2723–2737. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddn174
Wild P, Farhan H, McEwan DG, Wagner S, Rogov VV, Brady NR et al (2011) Phosphorylation of the autophagy receptor optineurin restricts Salmonella growth. Science 333(6039):228–233. doi:10.1126/science.1205405
Winslow AR, Chen CW, Corrochano S, Acevedo-Arozena A, Gordon DE, Peden AA et al (2010) Alpha-synuclein impairs macroautophagy: implications for Parkinson’s disease. J Cell Biol 190(6):1023–1037. doi:10.1083/jcb.201003122
Vogiatzi T, Xilouri M, Vekrellis K, Stefanis L (2008) Wild type alpha-synuclein is degraded by chaperone-mediated autophagy and macroautophagy in neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 283(35):23542–23556. doi:10.1074/jbc.M801992200
Wong E, Cuervo AM (2010) Autophagy gone awry in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Neurosci 13(7):805–811. doi:10.1038/nn.2575
Xilouri M, Vogiatzi T, Vekrellis K, Park D, Stefanis L (2009) Abberant alpha-synuclein confers toxicity to neurons in part through inhibition of chaperone-mediated autophagy. PLoS One 4(5):e5515. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005515
Xu F, Gu JH, Qin ZH (2012) Neuronal autophagy in cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Bull 28(5):658–666. doi:10.1007/s12264-012-1268-9
Yang Q, She H, Gearing M, Colla E, Lee M, Shacka JJ, Mao Z (2009) Regulation of neuronal survival factor MEF2D by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Science 323(5910):124–127. doi:10.1126/science.1166088
Yang Y, Coleman M, Zhang L, Zheng X, Yue Z (2013) Autophagy in axonal and dendritic degeneration. Trends Neurosci 36(7):418–428. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2013.04.001
Yang Y, Feng LQ, Zheng XX (2011) Microtubule and kinesin/dynein-dependent, bi-directional transport of autolysosomes in neurites of PC12 cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43(8):1147–1156. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2011.04.007
Yla-Anttila P, Vihinen H, Jokitalo E, Eskelinen EL (2009) 3D tomography reveals connections between the phagophore and endoplasmic reticulum. Autophagy 5(8):1180–1185
Yordy B, Iijima N, Huttner A, Leib D, Iwasaki A (2012) A Neuron-specific role for autophagy in antiviral defense against herpes simplex virus. Cell Host Microbe 12(3):334–345. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2012.07.013
Yordy B, Iwasaki A (2011) Autophagy in the control and pathogenesis of viral infection. Curr Opin Virol 1(3):196–203. doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2011.05.016
Yordy B, Tal MC, Hayashi K, Arojo O, Iwasaki A (2013) Autophagy and selective deployment of Atg proteins in antiviral defense. Int Immunol 25(1):1–10. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxs101
Young AR, Chan EY, Hu XW, Kochl R, Crawshaw SG, High S et al (2006) Starvation and ULK1-dependent cycling of mammalian Atg9 between the TGN and endosomes. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 18):3888–3900
Yu L, McPhee CK, Zheng L, Mardones GA, Rong Y, Peng J et al (2010) Termination of autophagy and reformation of lysosomes regulated by mTOR. Nature 465(7300):942–946. doi:10.1038/nature09076
Yue Z (2007) Regulation of neuronal autophagy in axon: implication of autophagy in axonal function and dysfunction/degeneration. Autophagy 3(2):139–141
Yun SW, Ertmer A, Flechsig E, Gilch S, Riederer P, Gerlach M et al (2007) The tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib mesylate delays prion neuroinvasion by inhibiting prion propagation in the periphery. J Neurovirol 13(4):328–337. doi:10.1080/13550280701361516
Zhang C, Cuervo AM (2008) Restoration of chaperone-mediated autophagy in aging liver improves cellular maintenance and hepatic function. Nat Med 14(9):959–965
Zhang H, Kong X, Kang J, Su J, Li Y, Zhong J, Sun L (2009) Oxidative stress induces parallel autophagy and mitochondria dysfunction in human glioma U251 cells. Toxicol Sci 110(2):376–388. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfp101
Zhang X, Li L, Chen S, Yang D, Wang Y, Wang Z, Le W (2011) Rapamycin treatment augments motor neuron degeneration in SOD1(G93A) mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Autophagy 7(4):412–425
Zhang X, Yan H, Yuan Y, Gao J, Shen Z, Cheng Y et al (2013) Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced autophagy protects against neuronal injury by mitochondrial clearance. Autophagy 9(9):1321–1333
Zhu G, Wu CJ, Zhao Y, Ashwell JD (2007) Optineurin negatively regulates TNFalpha-induced NF-kappaB activation by competing with NEMO for ubiquitinated RIP. Curr Biol 17(16):1438–1443. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2007.07.041
Zhu J, Wang KZ, Chu CT (2013) After the banquet: mitochondrial biogenesis, mitophagy and cell survival. Autophagy 9(11):1663–1676
Zoncu R, Bar-Peled L, Efeyan A, Wang S, Sancak Y, Sabatini DM (2011) mTORC1 senses lysosomal amino acids through an inside-out mechanism that requires the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. Science 334(6056):678–683. doi:10.1126/science.1207056
Acknowledgments
Work in the laboratories P.S. and M.D. is supported through Grants of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG: SFB877, SPP1580, GRK1459, Cluster of Excellence: Inflammation at Interfaces), the VERUM foundation and the Interuniversity Attraction Poles Program IUAP P7/16 of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office. E.L.E. and T.S. are supported by the Academy of Finland, Biocentrum Helsinki, and Sigrid Juselius Foundation. We thank Nicolas Yeung (University of Helsinki) for his contribution to designing Fig. 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
P. Saftig and E.-L. Eskelinen have equal contribution.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damme, M., Suntio, T., Saftig, P. et al. Autophagy in neuronal cells: general principles and physiological and pathological functions. Acta Neuropathol 129, 337–362 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1361-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1361-4