Abstract
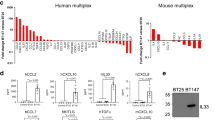
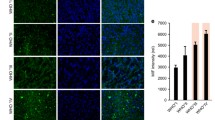
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), which inhibits apoptosis and promotes angiogenesis, is expressed in cancers suppressing immune surveillance. Its biological role in human glioblastoma is, however, only poorly understood. We examined in-vivo expression of MIF in 166 gliomas and 23 normal control brains by immunohistochemistry. MIF immunoreactivity was enhanced in neoplastic astrocytes in WHO grade II glioma and increased significantly in higher tumour grades (III–IV). MIF expression was further assessed in 12 glioma cell lines in vitro. Quantitative RT-PCR showed that MIF mRNA expression was elevated up to 800-fold in malignant glioma cells compared with normal brain. This translated into high protein levels as assessed by immunoblotting of total cell lysates and by ELISA-based measurement of secreted MIF. Wild-type p53-retaining glioma cell lines expressed higher levels of MIF, which may be connected with the previously described role of MIF as a negative regulator of wild-type p53 signalling in tumour cells. Stable knockdown of MIF by shRNA in glioma cells significantly increased tumour cell susceptibility towards NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Furthermore, supernatant from mock-transfected cells, but not from MIF knockdown cells, induced downregulation of the activating immune receptor NKG2D on NK and CD8+ T cells. We thus propose that human glioma cell-derived MIF contributes to the immune escape of malignant gliomas by counteracting NK and cytotoxic T-cell-mediated tumour immune surveillance. Considering its further cell-intrinsic and extrinsic tumour-promoting effects and the availability of small molecule inhibitors, MIF seems to be a promising candidate for future glioma therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Abed Y, Dabideen D, Aljabari B et al (2005) ISO-1 binding to the tautomerase active site of MIF inhibits its pro-inflammatory activity and increases survival in severe sepsis. J Biol Chem 280:36541–36544
Al-Abed Y, Metz CN, Cheng KF et al (2011) Thyroxine is a potential endogenous antagonist of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(20):8224–8227
Amin MA, Volpert OV, Woods JM, Kumar P, Harlow LA, Koch AE (2003) Migration inhibitory factor mediates angiogenesis via mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol kinase. Circ Res 93(4):321–329
Apte RS, Sinha D, Mayhew E, Wistow GJ, Niederkorn JY (1998) Cutting edge: role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in inhibiting NK cell activity and preserving immune privilege. J Immunol 160(12):5693–5696
Bach JP, Deuster O, Balzer-Geldsetzer M, Meyer B, Dodel R, Bacher M (2009) The role of macrophage inhibitory factor in tumourigenesis and central nervous system tumours. Cancer 115:2031–2040
Bacher M, Deuster O, Aljabari B et al (2010) The role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Med 16(3–4):116–121
Bacher M, Meinhardt A, Lan HY et al (1998) MIF expression in the rat brain: implications for neuronal function. Mol Med 4(4):217–230
Bacher M, Schrader J, Thompson N et al (2003) Up-regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene and protein expression in glial tumour cells during hypoxic and hypoglycemic stress indicates a critical role for angiogenesis in glioblastoma multiforme. Am J Pathol 162(1):11–17
Baron N, Deuster O, Noelker C et al (2011) Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in primary glioblastoma multiforme cells. J Neurosci Res 89:711–717
Bauer S, Groh V, Wu J et al (1999) Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science 285:727–729
Baumann R, Casaulta C, Simon D, Conus S, Yousefi S, Simon HU (2003) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor delays apoptosis in neutrophils by inhibiting the mitochondria-dependent death pathway. FASEB J 17(15):2221–2230
Bernhagen J, Krohn R, Lue H et al (2007) MIF is a noncognate ligand of CXC chemokine receptors in inflammatory and atherogenic cell recruitment. Nat Med 13:587–596
Bloom BR, Bennett B (1966) Mechanism of a reaction in vitro associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Science 153:80–82
Bucala R, Donnelly SC (2007) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: a probable link between inflammation and cancer. Immunity 26:281–285
Calandra T, Roger T (2003) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: a regulator of innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 3:791–800
Cludts S, Decaestecker C, Johnson B et al (2010) Increased expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor during progression to hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 30(9):3313–3319
Conroy H, Mawhinney L, Donnelly SC (2010) Inflammation and cancer: macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)—the potential missing link. QJM 103:831–836
Craig-Schapiro R, Kuhn M, Xiong C et al (2011) Multiplexed immunoassay panel identifies novel CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis and prognosis. PLoS One 6(4):e18850
Daun JM, Cannon JG (2000) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor antagonizes hydrocortisone-induced increases in cytosolic IκBα. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279:R1043–R1049
Dumitru CA, Gholaman H, Trellakis S et al (2011) Tumour-derived macrophage migration inhibitory factor modulates the biology of head and neck cancer cells via neutrophil activation. Int J Cancer. doi:10.1002/ijc.25991
Eisele G, Wischhusen J, Mittelbronn M et al (2006) TGF-β and metalloproteinases differentially suppress NKG2D ligand surface expression on malignant glioma cells. Brain 129:2416–2425
Engelhorn T, Savaskan NE, Schwarz MA et al (2009) Cellular characterization of the peritumoural edema zone in malignant brain tumours. Cancer Sci 100(10):1856–1862
Fingerle-Rowson G, Petrenko O, Metz CN et al (2003) The p53-dependent effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor revealed by gene targeting. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(16):9354–9359
Friese MA, Wischhusen J, Wick W et al (2004) RNA interference targeting transforming growth factor-beta enhances NKG2D-mediated antiglioma immune response, inhibits glioma cell migration and invasiveness, and abrogates tumourigenicity in vivo. Cancer Res 64:7596–7603
Groh V, Rhinehart R, Secrist H, Bauer S, Grabstein KH, Spies T (1999) Broad tumour-associated expression and recognition by tumour-derived γδT cells of MICA and MICB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6879–6884
Hudson JD, Shoaibi MA, Maestro R, Carnero A, Hannon GJ, Beach DH (1999) A proinflammatory cytokine inhibits p53 tumour suppressor activity. J Exp Med 190(10):1375–1382
Jung H, Seong HA, Ha H (2008) Direct interaction between NM23–H1 and macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is critical for alleviation of MIF-mediated suppression of p53 activity. J Biol Chem 283(47):32669–32679
Koda M, Nishio Y, Hashimoto M et al (2004) Up-regulation of macrophage migration-inhibitory factor expression after compression-induced spinal cord injury in rats. Acta Neuropathol 108:31–36
Krockenberger M, Dombrowski Y, Weidler C et al (2008) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor contributes to the immune escape of ovarian cancer by down-regulating NKG2D. J Immunol 180(11):7338–7348
Legendre H, Decaestecker C, Nagy N et al (2003) Prognostic values of galectin-3 and the macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in human colorectal cancers. Mod Pathol 16(5):491–504
Leng L, Metz CN, Fang Y et al (2003) MIF signal transduction initiated by binding to CD74. J Exp Med 197:1467–1476
Liao H, Bucala R, Mitchell RA (2003) Adhesion-dependent signaling by macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). J Biol Chem 278:76–81
Matsunaga J, Sinha D, Pannell L et al (1999) Enzyme activity of macrophage migration inhibitory factor toward oxidized catecholamines. J Biol Chem 274(6):3268–3271
Matsunaga J, Sinha D, Solano F, Santis C, Wistow G, Hearing V (1999) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)—its role in catecholamine metabolism. Cell Mol Biol 45(7):1035–1040
Mitchell RA (2004) Mechanisms and effectors of MIF-dependent promotion of tumourigenesis. Cell Signal 16:13–19
Mitchell RA, Bucala R (2000) Tumour growth-promoting properties of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Semin Cancer Biol 10:359–366
Morand EF, Leech M, Bernhagen J (2006) MIF: a new cytokine link between rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:399–410
Munaut C, Boniver J, Foidart JM, Deprez M (2002) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) expression in human glioblastomas correlates with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 28(6):452–460
Nishibori M, Nakaya N, Mori S, Saeki K (1997) Immunohistochemical localization of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in tanycytes, subcommissural organ and choroid plexus in the rat brain. Brain Res 758:259–262
Oda S, Oda T, Nishi K et al (2008) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor activates hypoxia-inducible factor in a p53-dependent manner. PLoS One 3(5):e2215
Ogawa H, Nishihira J, Sato Y et al (2000) An antibody for macrophage migration inhibitory factor suppresses tumour growth and inhibits tumour-associated angiogenesis. Cytokine 12(4):309–314
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2005) Population-based studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64(6):479–489
Ohkawara T, Nishihira J, Takeda H, Asaka M, Sugiyama T (2005) Pathophysiological roles of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in gastrointestinal, hepatic, and pancreatic disorders. J Gastroenterol 40(2):117–122
Østergaard C, Benfield T (2009) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with central nervous system infection. Crit Care 13(3):R101
Petrenko O, Fingerle-Rowson G, Peng T, Mitchell RA, Metz CN (2003) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor deficiency is associated with altered cell growth and reduced susceptibility to Ras-mediated transformation. J Biol Chem 278:11078–11085
Piette C, Deprez M, Roger T, Noël A, Foidart JM, Munaut C (2009) The dexamethasone-induced inhibition of proliferation, migration, and invasion in glioma cell lines is antagonized by macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and can be enhanced by specific MIF inhibitors. J Biol Chem 284(47):32483–32492
Popp J, Bacher M, Kölsch H et al (2009) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. J Psychiatr Res 43(8):749–753
Rendon BE, Roger T, Teneng I et al (2007) Regulation of human lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and invasion by macrophage migration inhibitory factor. J Biol Chem 282(41):29910–29918
Repp AC, Mayhew ES, Apte S, Niederkorn JY (2000) Human uveal melanoma cells produce macrophage migration-inhibitory factor to prevent lysis by NK cells. J Immunol 165:710–715
Sasaki Y, Kasuya K, Nishihira J et al (2002) Suppression of tumour growth through introduction of an antisense plasmid of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Int J Mol Med 10(5):579–583
Schrader J, Deuster O, Rinn B et al (2009) Restoration of contact inhibition in human glioblastoma cell lines after MIF knockdown. BMC Cancer 9:464
Seike T, Fujita K, Yamakawa Y et al (2011) Interaction between lung cancer cells and astrocytes via specific inflammatory cytokines in the microenvironment of brain metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 28:13–25
Shi X, Leng L, Wang T et al (2006) CD44 is the signaling component of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor-CD74 receptor complex. Immunity 25:595–606
Tarnowski M, Grymula K, Liu R et al (2010) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is secreted by rhabdomyosarcoma cells, modulates tumour metastasis by binding to CXCR4 and CXCR7 receptors and inhibits recruitment of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Mol Cancer Res 8(10):1328–1343
Vedder H, Krieg JC, Gerlach B, Gemsa D, Bacher M (2000) Expression and glucocorticoid regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in hippocampal and neocortical rat brain cells in culture. Brain Res 869(1–2):25–30
White ES, Flaherty KR, Carskadon S et al (2003) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor and CXC chemokine expression in non-small cell lung cancer: role in angiogenesis and prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 9(2):853–860
Wischhusen J, Naumann U, Ohgaki H, Rastinejad F, Weller M (2003) CP-31398, a novel p53-stabilizing agent, induces p53-dependent and p53-independent glioma cell death. Oncogene 22:8233–8245
Xia HH, Yang Y, Chu KM et al (2009) Serum macrophage migration-inhibitory factor as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer. Cancer 115(23):5441–5449
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Birgitt Fischer and Evi Horn for their excellent technical assistance and PD Dr Ulrike Naumann for providing tissue specimens.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mittelbronn, M., Platten, M., Zeiner, P. et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) expression in human malignant gliomas contributes to immune escape and tumour progression. Acta Neuropathol 122, 353–365 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0858-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0858-3