Abstract
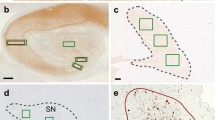
Recent studies have shown the co-existence of α-synuclein and phosphorylated tau (pTau) in several neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we report two autopsy cases of combined multiple system atrophy (MSA) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In both cases, abundant α-synuclein-positive glial and neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions were found in the brainstem, amygdala and hippocampal formation. pTau-positive neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) were widely distributed in case 1 (Braak stage VI) and moderate in case 2 (Braak stage III). Although α-synuclein and pTau pathology co-occurred in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex, only a few neurons showed co-existence of these two proteins. Immunoreactivity for p62, a ubiquitin proteasome system related protein, was found in the majority of NFTs, but in only a small proportion of neuronal α-synuclein inclusions. In addition, UBB+1, a mutant form of ubiquitin and a marker for proteasomal dysfunction, was present in the majority of NFTs, whereas co-existence of α-synuclein and UBB+1 was found in only a few neurons. These findings indicate that α-synuclein and phosphorylated tau co-occur in certain brain regions in cases of combined MSA and AD and that the proteasomal pathways differ between α-synuclein- and pTau-bearing neurons.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arima K, Hirai S, Sunohara N, Aoto K, Izumiyama Y, Ueda K, Ikeda K, Kawai M (1999) Cellular co-localization of phosphorylated tau- and NACP/alpha-synuclein-epitopes in Lewy bodies in sporadic Parkinson’s disease and in dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Res 843:53–61
Arima K, Ueda K, Sunohara N, Arakawa K, Hirai S, Nakamura M, Tonozuka-Uehara H, Kawai M (1998) NACP/alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity in fibrillary components of neuronal and oligodendroglial cytoplasmic inclusions in the pontine nuclei in multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 96:439–444
Braak H, Alafuzoff I, Arzberger T, Kretszchmar H, Del Tredici K (2006) Staging of Alzheimer disease-associated neurofibrillary pathology using paraffin sections and immunocytochemistry. Acta Neuropathol 112:389–404
Braak H, Braak E (1999) Temporal sequence of Alzheimer’s disease related pathology. In:Peter J, Morrison JH (eds). Cerebral cortex, vol 14, Neurodegenerative and age-related changes in structure and function of cerebral cortex. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, Boston, pp 475–512
Buee L, Bussiere T, Buee-Scherrer V, Delacourte A, Hof PR (2000) Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 33:95–130
Campbell BC, McLean CA, Culvenor JG, Gai WP, Blumbergs PC, Jakala P, Beyreuther K, Masters CL, Li QX (2001) The solubility of alpha-synuclein in multiple system atrophy differs from that of dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 76:87–96
de Pril R, Fischer DF, Maat-Schieman ML, Hobo B, De Vos RA, Brunt ER, Hol EM, Roos RA, van Leeuwen FW (2004) Accumulation of aberrant ubiquitin induces aggregate formation and cell death in polyglutamine diseases. Hum Mol Genet 13:1803–1813
de Pril R, Fischer DF, van Leeuwen FW (2006) Conformational diseases: an umbrella for various neurological disorders with an impaired ubiquitin-proteasome system. Neurobiol Aging 27:515–523
Dickson DW, Liu W, Hardy J, Farrer M, Mehta N, Uitti R, Mark M, Zimmerman T, Golbe L, Sage J Sima A, D’Amato C, Albin R, Gilman S, Yen SH (1999) Widespread alterations of alpha-synuclein in multiple system atrophy. Am J Pathol 155:1241–1251
Duda JE, Giasson BI, Mabon ME, Miller DC, Golbe LI, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2002) Concurrence of alpha-synuclein and tau brain pathology in the Contursi kindred. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 104:7–11
Fischer DF, De Vos RA, Van DR, De Vrij FM, Proper EA, Sonnemans MA, Verhage MC, Sluijs JA, Hobo B, Zouambia M, Steur EN, Kamphorst W, Hol EM, van Leeuwen FW (2003) Disease-specific accumulation of mutant ubiquitin as a marker for proteasomal dysfunction in the brain. FASEB J 17:2014–2024
Frasier M, Walzer M, McCarthy L, Magnuson D, Lee JM, Haas C, Kahle P, Wolozin B (2005) Tau phosphorylation increases in symptomatic mice overexpressing A30P alpha-synuclein. Exp Neurol 192:274–287
Frasier M, Wolozin B (2004) Following the leader: fibrillization of alpha-synuclein and tau. Exp Neurol 187:235–239
Gai WP, Pountney DL, Power JH, Li QX, Culvenor JG, McLean CA, Jensen PH, Blumbergs PC (2003) alpha-Synuclein fibrils constitute the central core of oligodendroglial inclusion filaments in multiple system atrophy. Exp Neurol 181:68–78
Gamblin TC, Chen F, Zambrano A, Abraha A, Lagalwar S, Guillozet AL, Lu M, Fu Y, Garcia-Sierra F, LaPointe N, Miller R, Berry RW, Binder LI, Cryns VL (2003) Caspase cleavage of tau: linking amyloid and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:10032–10037
Geddes JW (2005) α-synuclein: a potent inducer of tau pathology. Exp Neurol 192:244–250
Geetha T, Wooten MW (2002) Structure and functional properties of the ubiquitin binding protein p62. FEBS Lett 512:19–24
Giasson BI, Forman MS, Higuchi M, Golbe LI, Graves CL, Kotzbauer PT, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2003) Initiation and synergistic fibrillization of tau and alpha-synuclein. Science 300:636–640
Glaser CB, Yamin G, Uversky VN, Fink AL (2005) Methionine oxidation, alpha-synuclein and Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1703:157–169
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Cairns NJ, Crowther RA (1992) Tau proteins of Alzheimer paired helical filaments: abnormal phosphorylation of all six brain isoforms. Neuron 8:159–168
Hamilton RL (2000) Lewy bodies in Alzheimer’s disease: a neuropathological review of 145 cases using alpha-synuclein immunohistochemistry. Brain Pathol 10:378–384
Hol EM, van Leeuwen FW, Fischer DF (2005) The proteasome in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: lessons from ubiquitin B+1. Trends Mol Med 11:488–495
Horowitz PM, Patterson KR, Guillozet-Bongaarts AL, Reynolds MR, Carroll CA, Weintraub ST, Bennett DA, Cryns VL, Berry RW, Binder LI (2004) Early N-terminal changes and caspase-6 cleavage of tau in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 24:7895–7902
Ince PG, McKeith IG (2003) Dementia with Lewy bodies. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: The molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders, ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 188–199
Ingram EM, Spillantini MG (2002) Tau gene mutations: dissecting the pathogenesis of FTDP-17. Trends Mol Med 8:555–562
Iseki E, Marui W, Kosaka K, Ueda K (1999) Frequent coexistence of Lewy bodies and neurofibrillary tangles in the same neurons of patients with diffuse Lewy body disease. Neurosci Lett 265:9–12
Ishizawa T, Mattila P, Davies P, Wang D, Dickson DW (2003) Colocalization of tau and alpha-synuclein epitopes in Lewy bodies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:389–397
Jellinger KA, Mizzuno Y (2003) Parkinson’s disease. In: Dickson D (eds) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 159–187
Katsuse O, Iseki E, Arai T, Akiyama H, Togo T, Uchikado H, Kato M, Lees A, Kosaka K (2003) 4-repeat tauopathy sharing pathological and biochemical features of corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 106:251–260
Kobayashi K, Fukutani Y, Hayashi M, Miyazu K, Muramori F, Aoki T, Mukai M, Sasaki K, Isaki K, Koshino Y (1998) Non-familial olivopontocerebellar atrophy combined with late onset Alzheimer’s disease: a clinico-pathological case report. J Neurol Sci 21:106–112
Kotzbauer PT, Giasson BI, Kravitz AV, Golbe LI, Mark MH, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2004) Fibrillization of alpha-synuclein and tau in familial Parkinson’s disease caused by the A53T alpha-synuclein mutation. Exp Neurol 187:279–288
Kuusisto E, Parkkinen L, Alafuzoff I (2003) Morphogenesis of Lewy bodies: dissimilar incorporation of alpha-synuclein, ubiquitin, and p62. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:1241–1253
Kuusisto E, Salminen A, Alafuzoff I (2001) Ubiquitin-binding protein p62 is present in neuronal and glial inclusions in human tauopathies and synucleinopathies. Neuroreport 12:2085–2090
Kuusisto E, Salminen A, Alafuzoff I (2002) Early accumulation of p62 in neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease: possible role in tangle formation. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 28:228–237
Lantos PL, Quinn N (2003) Multiple system atrophy. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 203–214
Lee VM, Goedert M, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1121–1159
Lin WL, DeLucia MW, Dickson DW (2004) Alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity in neuronal nuclear inclusions and neurites in multiple system atrophy. Neurosci Lett 354:99–102
Lindsten K, De Vrij FM, Verhoef LG, Fischer DF, van Leeuwen FW, Hol EM, Masucci MG, Dantuma NP (2002) Mutant ubiquitin found in neurodegenerative disorders is a ubiquitin fusion degradation substrate that blocks proteasomal degradation. J Cell Biol 157:417–427
Lippa C (2003) Lewy bodies in conditions other than disorders of α-synuclein. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration. The molecular pathoology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel pp 200–202
Marui W, Iseki E, Ueda K, Kosaka K (2000) Occurrence of human alpha-synuclein immunoreactive neurons with neurofibrillary tangle formation in the limbic areas of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 174:81–84
Nakaso K, Yoshimoto Y, Nakano T, Takeshima T, Fukuhara Y, Yasui K, Araga S, Yanagawa T, Ishii T, Nakashima K (2004) Transcriptional activation of p62/A170/ZIP during the formation of the aggregates: possible mechanisms and the role in Lewy body formation in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1012:42–51
Paxinou E, Chen Q, Weisse M, Giasson BI, Norris EH, Rueter SM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Ischiropoulos H (2001) Induction of alpha-synuclein aggregation by intracellular nitrative insult. J Neurosci 21:8053–8061
Piao YS, Hayashi S, Hasegawa M, Wakabayashi K, Yamada M, Yoshimoto M, Ishikawa A, Iwatsubo T, Takahashi H (2001) Co-localization of alpha-synuclein and phosphorylated tau in neuronal and glial cytoplasmic inclusions in a patient with multiple system atrophy of long duration. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 101:285–293
Reynolds MR, Berry RW, Binder LI (2005) Site-specific nitration and oxidative dityrosine bridging of the tau protein by peroxynitrite: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry 44:1690–1700
Santpere G, Puig B, Ferrer I (2006) Low molecular weight species of tau in Alzheimer’s disease are dependent on tau phosphorylation sites but not on delayed post-mortem delay in tissue processing. Neurosci Lett 399:106–110
Schmidt ML, Martin JA, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (1996) Convergence of Lewy bodies and neurofibrillary tangles in amygdala neurons of Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol 91:475–481
Schweers O, Mandelkow EM, Biernat J, Mandelkow E (1995) Oxidation of cysteine-322 in the repeat domain of microtubule-associated protein tau controls the in vitro assembly of paired helical filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8463–8467
Scott IS, Lowe JS (2006) The ubiquitin-binding protein p62 identifies argyrophilic grain pathology with greater sensitivity than conventional silver stains. Acta Neuropathol 5 December 2006 (on line)
Seibenhener ML, Babu JR, Geetha T, Wong HC, Krishna NR, Wooten MW (2004) Sequestosome 1/p62 is a polyubiquitin chain binding protein involved in ubiquitin proteasome degradation. Mol Cell Biol 24:8055–8068
Sergeant N, Delacourte A, Buee L (2005) Tau protein as a differential biomarker of tauopathies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1739:179–197
Sergeant N, Wattez A, Delacourte A (1999) Neurofibrillary degeneration in progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration: tau pathologies with exclusively “exon 10” isoforms. J Neurochem 72:1243–1249
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Takanashi M, Ohta S, Matsuoka S, Mori H, Mizuno Y (2002) Mixed multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy: a clinical and pathological report of one case. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 103:82–87
Thal DR, Rub U, Orantes M, Braak H (2002) Phases of Abeta-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology 58:1791–1800
Tofaris GK, Layfield R, Spillantini MG (2001) alpha-synuclein metabolism and aggregation is linked to ubiquitin-independent degradation by the proteasome. FEBS Lett 509:22–26
Trembath Y, Rosenberg C, Ervin JF, Schmechel DE, Gaskell P, Pericak-Vance M, Vance J, Hulette CM (2003) Lewy body pathology is a frequent co-pathology in familial Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 105:484–488
Tu PH, Galvin JE, Baba M, Giasson B, Tomita T, Leight S, Nakajo S, Iwatsubo T, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (1998) Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in white matter oligodendrocytes of multiple system atrophy brains contain insoluble alpha-synuclein. Ann Neurol 44:415–422
Uchikado H, DelleDonne A, Uitti R, Dickson DW (2006) Coexistence of PSP and MSA: a case report and review of the literature. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 111:186–192
Uchikado H, Lin WL, DeLucia MW, Dickson DW (2006) Alzheimer disease with amygdala Lewy bodies: a distinct form of alpha-synucleinopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:685–697
Vadlamudi RK, Joung I, Strominger JL, Shin J (1996) p62, a phosphotyrosine-independent ligand of the SH2 domain of p56lck, belongs to a new class of ubiquitin-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 271:20235–20237
van Leeuwen FW, de Kleijn DP, van den Hurk HH, Neubauer A, Sonnemans MA, Sluijs JA, Koycu S, Ramdjielal RD, Salehi A, Martens GJ, Grosveld FG, Peter J, Burbach H, Hol EM (1998) Frameshift mutants of beta amyloid precursor protein and ubiquitin-B in Alzheimer’s and Down patients. Science 279:242–247
Wakabayashi K, Yoshimoto M, Tsuji S, Takahashi H (1998) Alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity in glial cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy. Neurosci Lett 249:180–182
Wilhelmsen KC, Forman MS, Rosen HJ, Alving LI, Goldman J, Feiger J, Lee JV, Segall SK, Kramer JH, Lomen-Hoerth C, Rakin KP, Johnson J, Feiler HS, Weiner MW, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Miller BL (2004) 17q-linked frontotemporal dementia-amyotrophic lateral sclerosis without tau mutations with tau and alpha-synuclein inclusions. Arch Neurol 61:398–406
Yancopoulou D, Xuereb JH, Crowther RA, Hodges JR, Spillantini MG (2005) Tau and alpha-synuclein inclusions in a case of familial frontotemporal dementia and progressive aphasia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:245–253
Zatloukal K, Stumptner C, Fuchsbichler A, Heid H, Schnoelzer M, Kenner L, Kleinert R, Prinz M, Aguzzi A, Denk H (2002) p62 Is a common component of cytoplasmic inclusions in protein aggregation diseases. Am J Pathol 160:255–263
Acknowledgments
BT is the recipient of a Beatriu de Pinós grant from the Generalitat de Catalunya. This work was funded by grants from the Spanish Ministry of Health, Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI05/1570), and supported by the European Commission under the Sixth Framework Programme (BrainNet Europe II, LSHM-CT-2004-503039). FWVL is grateful for the support of the Jan Dekker and Ludgardine Bouwman funds, Matty Brand Stichting and the Society for PSP (grant #440-04). We wish to thank T. Yohannan for the editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terni, B., Rey, M.J., Boluda, S. et al. Mutant ubiquitin and p62 immunoreactivity in cases of combined multiple system atrophy and Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 113, 403–416 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0192-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0192-3