Abstract
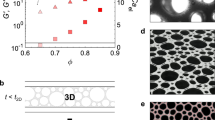
We study the rheological behavior of mixtures of foams and pastes, which can be described as suspensions of bubbles in yield stress fluids. Model systems are designed by mixing monodisperse aqueous foams and concentrated emulsions. The elastic modulus of the bubble suspensions is found to depend on the elastic capillary number \(\textit{Ca}_{_G}\), defined as the ratio of the paste elastic modulus to the bubble capillary pressure. For values of \(\textit{Ca}_{_G}\) larger than \(\simeq 0.5\), the dimensionless elastic modulus of the aerated material decreases as the bubble volume fraction \(\phi \) increases, suggesting that bubbles behave as soft elastic inclusions. Consistently, this decrease is all the sharper as \(\textit{Ca}_{_G}\) is high, which accounts for the softening of the bubbles as compared to the paste. By contrast, we find that the yield stress of most studied materials is not modified by the presence of bubbles. This suggests that their plastic behavior is governed by the plastic capillary number \(\textit{Ca}_{\tau_y}\), defined as the ratio of the paste yield stress to the bubble capillary pressure. At low \(\textit{Ca}_{\tau_y}\) values, bubbles behave as nondeformable inclusions, and we predict that the suspension dimensionless yield stress should remain close to unity, in agreement with our data up to \(\textit{Ca}_{\tau_y}=0.2\). When preparing systems with a larger target value of \(\textit{Ca}_{\tau_y}\), we observe bubble breakup during mixing, which means that they have been deformed by shear. It then seems that a critical value \(\textit{Ca}_{\tau_y}\simeq 0.2\) is never exceeded in the final material. These observations might imply that, in bubble suspensions prepared by mixing a foam and a paste, the suspension yield stress is always close to that of the paste surrounding the bubbles. Finally, at the highest \(\phi \) investigated, the yield stress is shown to increase abruptly with \(\phi \): this is interpreted as a “foamy yield stress fluid” regime, which takes place when the paste mesoscopic constitutive elements (here, the oil droplets) are strongly confined in the films between the bubbles.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Notes
Some aspects of the linear and nonlinear behavior of polydisperse suspensions are discussed in Vu et al. (2010).
Since the elastic moduli of the three systems are measured in the linear regime where their behavior does not depend on the strain amplitude, we also note that different \(g(\phi )\)values can be obtained for a same value of \(\textit{Ca}_\tau \) (see Eq. 13); this shows that \(Ca_{\tau }\) is not a relevant parameter in this regime.
We remind that this should be strictly true in the dilute limit only: we do not yet have a prediction for all values of \(\phi \).
If mixing is rapid and if viscous effects are important, for a constitutive behavior of the form \(\tau =\tau_y+f(\dot \gamma )\), the relevant number might rather be \(\frac {\tau_y+f(\dot \gamma )}{2\sigma _t/d}\).
References
Ancey C, Jorrot H (2001) Yield stress for particle suspensions within a clay dispersion. J Rheol 45:297–319
Baravian C, Lalante A, Parker A (2002) Vane rheometry with a large, finite gap. Appl Rheol 12:81–87
Blanc F, Peters F, Lemaire E (2011) Local transient rheological behavior of concentrated suspensions. J Rheol 55:835–854
Chateau X, Ovarlez G, Luu Trung K (2008) Homogenization approach to the behavior of suspensions of noncolloidal particles in yield stress fluids. J Rheol 52:489–506
Coussot P (2005) Rheometry of pastes, suspensions and granular materials. Wiley, Hoboken
Coussot P, Tabuteau H, Chateau X, Tocquer L, Ovarlez G (2006) Aging and solid or liquid behavior in pastes. J Rheol 50:975–994
Denkov ND, Tcholakova S, Golemanov K, Ananthpadmanabhan KP, Lips A (2009) The role of surfactant type and bubble surface mobility in foam rheology. Soft Matter 5:3389–3408
Dormieux L, Kondo D, Ulm FJ (2006) Microporomechanics. Wiley, Hoboken
Dubash N, Frigaard IA (2004) Conditions for static bubbles in viscoplastic fluids. Phys Fluids 16:4319–4330
Dubash N, Frigaard IA (2007) Propagation and stopping of air bubbles in Carbopol solutions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 142:123–134
Dutta A, Chengara A, Nikolov AD, Wasan DT, Chen K, Campbell B (2004a) Texture and stability of aerated food emulsions–effects of buoyancy and Ostwald ripening. J Food Eng 62:169–175
Dutta A, Chengara A, Nikolov AD, Wasan DT, Chen K, Campbell B (2004b) Destabilization of aerated food products: effects of Ostwald ripening and gas diffusion. J Food Eng 62:177–184
Dzuy NQ, Boger DV (1983) Yield stress measurement for concentrated suspensions. J Rheol 27:321
Frankel NA, Acrivos A (1970) The constitutive equation for a dilute emulsion. J Fluid Mech 44:65–78
Gadala-Maria F, Acrivos A (1980) Shear-induced structure in a concentrated suspension of solid spheres. J Rheol 24:799–814
Gandolfo FG, Rosano HL (1997) Interbubble gas diffusion and the stability of foams. J Colloid Interface Sci 194:31–36
Geiker MA, Brandl M, Thrane L, Nielsen NF (2002a) On the effect of coarse aggregate fraction and shape on the rheological properties of self-compacting concrete. Cem Concr Aggr 24:3–6
Geiker MR, Brandl M, Thrane LN, Bager DH, Wallevik O (2002b) The effect of measuring procedure on the apparent rheological properties of self compacting concrete. Cem Concr Res 32:1791–1795
Gonnermann HM, Manga M (2007) The fluid mechanics inside a volcano. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 39:321–356
Goyon J, Bertrand F, Pitois O, Ovarlez G (2010) Shear induced drainage in foamy yield-stress fluids. Phys Rev Lett 128301:104
Griffiths RW (2000) The dynamics of lava flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 32:477–518
Hashin Z, Shtrikman S (1963) A variational approach to the theory of the elastic behaviour of multiphase materials. J Mech Phys Solids 11:127–140
Keentok M, Milthorpe JF, O’Donovan E (1985) On the shearing zone around rotating vanes in plastic liquids: theory and experiment. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 17:23–35
Koczo K, Lobo LA, Wasan DT (1992) Effect of oil on foam stability: aqueous foams stabilized by emulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 150:492–506
Larson RG (1999) The structure and rheology of complex fluids. Oxford University Press, New York
Leighton D, Acrivos A (1987) The shear-induced migration of particles in concentrated suspensions. J Fluid Mech 181:415–439
Ley MT, Folliard KJ, Hover KC (2009) Observations of air-bubbles escaped from fresh cement paste. Cem Concr Res 39:409–416
Liddell PV, Boger DV (1996) Yield stress measurements with the vane. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 63:235–261
Llewellin EW, Mader HM, Wilson SDR (2002) The rheology of a bubbly liquid. P R Soc A 458:987–1016
Mabille C, Schmitt V, Gorria P, Leal Calderon F, Faye V, Deminière B, Bibette J (2000) Rheological and shearing conditions for the preparation of monodisperse emulsions. Langmuir 16:422–429
Mahaut F, Chateau X, Coussot P, Ovarlez G (2008a) Yield stress and elastic modulus of suspensions of noncolloidal particles in yield stress fluids. J Rheol 52:287–313
Mahaut F, Mokéddem S, Chateau X, Roussel N, Ovarlez G (2008b) Effect of coarse particle volume fraction on the yield stress and thixotropy of cementitious materials. Cem Concr Res 38:1276–1285
Mason TG, Bibette J, Weitz DA (1995) Elasticity of compressed emulsions. Phys Rev Lett 75:2051–2054
Mewis J, Wagner NJ (2012) Colloidal suspension rheology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Mason TG, Bibette J, Weitz DA (1996) Yielding and flow of monodisperse emulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 179:439–448
Nguyen QD, Boger DV (1985) Direct yield stress measurement with the vane method. J Rheol 29:335–347
Ovarlez G, Bertrand F, Rodts S (2006) Local determination of the constitutive law of a dense suspension of noncolloidal particles through magnetic resonance imaging. J Rheol 50:259–292
Ovarlez G, Rodts S, Ragouilliaux A, Coussot P, Goyon J, Colin A (2008) Wide-gap Couette flows of dense emulsions: local concentration measurements, and comparison between macroscopic and local constitutive law measurements through magnetic resonance imaging. Phys Rev E 036307:78
Ovarlez G, Barral Q, Coussot P (2010) Three-dimensional jamming and flows of soft glassy materials. Nat Mater 9:115–119
Ovarlez G, Mahaut F, Bertrand F, Chateau X (2011) Flows and heterogeneities with a vane tool: magnetic resonance imaging measurements. J Rheol 5:197–223
Ovarlez G, Bertrand F, Coussot P, Chateau X (2012) Shear-induced sedimentation in yield stress fluids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 42:148–157
Pal R (2004) Rheological constitutive equation for bubbly suspensions. Ind Eng Chem Res 43:5372–5379
Parsi F, Gadala-Maria F (1987) Fore-and-aft asymmetry in a concentrated suspension of solid spheres. J Rheol 31:725–732
Phillips RJ, Armstrong RC, Brown RA, Graham AL, Abbott JR (1992) A constitutive equation for concentrated suspensions that accounts for shear-induced particle migration. Phys Fluids 4:30–40
Ramamurthy K, Kunhanandan Nambiar EK, Indu Siva Ranjani G (2009) A classification of studies on properties of foam concrete. Cem Concr Compos 31:388–396
Rust AC, Manga M (2002a) Effects of bubble deformation on the viscosity of dilute suspensions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 104:53–63
Rust AC, Manga M (2002b) Bubble shapes and orientations in low Re simple shear flow. J Colloid Interface Sci 249:476–480
Salonen A, Lhermerout R, Rio E, Langevin D, Saint-Jalmes A (2012) Dual gas and oil dispersions in water: production and stability of foamulsion. Soft Matter 8:699–706
Sikorski D, Tabuteau H, de Bruyn J (2009) Motion and shape of bubbles rising through a yield-stress fluid. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 159:10–16
Stickel JJ, Powell RL (2005) Fluid mechanics and rheology of dense suspensions. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 37:129–149
Struble LJ, Jiang Q (2004) Effects of air entrainment on rheology. Materials Journal 101:448–456
Turner D, Dlugogorski B, Palmer T (1999) Factors affecting the stability of foamed concentrated emulsions. Colloids Surf A 150:171–184
Uhlerr PHT, Guo J, Tiu C, Zhang XM, Zhou JZQ, Fang TN (2005) The shear-induced solid-liquid transition in yield stress materials with chemically different structures. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 125:101–119
van Aken GA (2001) Aeration of emulsions by whipping. Colloids Surf A 190:333–354
Vu TS, Ovarlez G, Chateau X (2010) Macroscopic behavior of bidisperse suspensions of noncolloidal particles in yield stress fluids. J Rheol 54:815–833
Acknowledgements
We thank Mohammed Bouricha for help on some of the experiments. We acknowledge funding from Saint-Gobain Recherche.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special issue devoted to novel trends in rheology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kogan, M., Ducloué, L., Goyon, J. et al. Mixtures of foam and paste: suspensions of bubbles in yield stress fluids. Rheol Acta 52, 237–253 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-013-0677-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-013-0677-7