Abstract
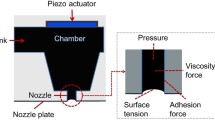
We investigate the effects of viscoelasticity on drop generation in inkjet printing. In drop-on-demand printing, individual ink ‘drops’ are ejected from a nozzle by imposed pressure pulses. Upon exiting the nozzle, the shape of each ‘drop’ is that of a nearly spherical bead with a long thin trailing ligament. This ligament subsequently breaks up under the Rayleigh instability, typically into several small droplets (known as satellite drops). These satellite drops can create unwanted splash on the target substrate and a reduction in printing quality. Satellite drops can potentially be eliminated by adding polymer to the ink; elastic stresses can act to contract the trailing ligament into the main drop before capillary breakup occurs. However, elasticity can also reduce the drop velocity and can delay or even prevent the break-off of the drop from the ink reservoir within the nozzle. To achieve optimal drop shape and speed, non-Newtonian parameters such as the polymer concentration and molecular weight must be chosen correctly. We explore this parameter space via numerical simulations, using the Lagrangian–Eulerian finite-element method of Harlen et al. (J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 60:81–104, 1995). Results are compared with experimental observations taken from real printheads.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The convention used here is that a radius of curvature is positive if the corresponding centre of curvature lies on the jet side of the interface.
In a bubblejet printhead, ink is ejected from the nozzle by the sudden expansion of a vapour bubble formed by a local thermal pulse.
References
Anna SL, McKinley GH (2001) Elasto-capillary thinning and breakup of model elastic liquids. J Rheol 45:115–138
Bazilevskiy AV, Meyer JD, Rozhkov AN (2005) Dynamics and breakup of pulse microjets of polymeric liquids. Fluid Dyn 40:376–392
Bousfield DW, Keunings R, Marrucci G, Denn MM (1986) Nonlinear analysis of the surface tension driven breakup of viscoelastic filaments. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 21:79–97
Castrejón-Pita JR, Martin GD, Hoath SD, Hutchings IM (2008) A simple large-scale droplet generator for studies of inkjet printing. Rev Sci Instrum 79:075108
Chilcott MD, Rallison JM (1988) Creeping flow of dilute polymer solutions past cylinders and spheres. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 29:381–432
Christanti Y, Walker LM (2001) Surface tension driven jet break up of strain-hardening polymer solutions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 100:9–26
Clasen C, Eggers J, Fontelos MA, Li J, McKinley GH (2006a) The beads-on-string structure of viscoelastic threads. J Fluid Mech 556:283–308
Clasen C, Plog JP, Kulicke W-M, Owens M, Macosko C, Scriven LE, Verani M, McKinley GH (2006b) How dilute are dilute solutions in extensional flows? J Rheol 50:849–881
Cooper-White JJ, Fagan JE, Tirtaatmadja V, Lester DR, Boger DV (2002) Drop formation dynamics of constant low-viscosity elastic fluids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 106:29–59
de Gans B-J, Duineveld PC, Schubert US (2004) Inkjet printing of polymers: state of the art and future developments. Adv Mater 16:203–213
de Gans B-J, Xue L, Agarwal US, Schubert US (2005) Ink-Jet printing of linear and star polymers. Macromol Rapid Commun 26:310–314
Dong H, Carr WW, Morris JF (2006) An experimental study of drop-on-demand drop formation. Phys Fluids 18:072102
Edelsbrunner H (2000) Triangulations and meshes in computational geometry. Acta Numer 9:133–213
Entov VM, Hinch EJ (1997) Effect of a spectrum of relaxation times on the capillary thinning of a filament of elastic liquid. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 72:31–53
Étienne J, Hinch EJ, Li J (2006) A Lagrangian-Eulerian approach for the numerical simulation of free-surface flow of a viscoelastic material. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 136:157–166
Goldin M, Yerushalmi J, Pfeffer R, Shinnar R (1969) Breakup of a laminar capillary jet of a viscoelastic fluid. J Fluid Mech 38:689–711
Harlen OG, Rallison JM, Szabó P (1995) A split Lagrangian-Eulerian method for simulating transient viscoelastic flows. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 60:81–104
Hoath SD, Martin GD, Castrejón-Pita JR, Hutchings IM (2007) Satellite formation in drop-on-demand printing of polymer solutions. In: Proc 23rd int conf on non-impact printing (NIP23). Society for Imaging Science and Technology, Anchorage, pp 331–335
Hoath SD, Hutchings IM, Martin GD, Tuladhar TR, Mackley MR, Vadillo D (2009) Links between ink rheology, drop-on-demand jet formation, and printability. J Imaging Sci Technol 53:041208
Hutchings IM, Martin GD, Hoath SD (2007) High speed imaging and analysis of jet and drop formation. J Imaging Sci Technol 51:438–444
Hutchings IM, Martin GD, Hoath SD, Morgan RH (2006) High speed imaging and analysis of jet and drop formation. In: Proc 22nd int conf on non-impact printing (NIP22). Society for Imaging Science and Technology, Denver, pp 91–94
Keunings R (1986) An algorithm for the simulation of transient viscoelastic flows with free surfaces. J Comput Phys 62:199–220
Li J, Fontelos MA (2003) Drop dynamics on the beads-on-string structure for viscoelastic jets: a numerical study. Phys Fluids 15:922–937
Li R, Ashgriz N, Chandra S, Andrews JR (2008) Contraction of free liquid ligaments. AIChE J 54:3084–3091
Liang RF, Mackley MR (1994) Rheological characterization of the time and strain dependence for polyisobutylene solutions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 52:387–405
Martin GD, Hutchings IM, Hoath SD (2006) Jet formation and late-stage ligament instability in drop-on-demand printing. In: Proc 22nd int conf on non-impact printing (NIP22). Society for Imaging Science and Technology, Denver, pp 95–98
Oliveira MSN, Yeh R, McKinley GH (2006) Iterated stretching, extensional rheology and formation of beads-on-a-string structures in polymer solutions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 137:137–148
Paige CC, Saunders MA (1975) Solution of sparse indefinite systems of linear equations. SIAM J Numer Anal 12:617–629
Renardy M (1995) A numerical study of the asymptotic evolution and breakup of Newtonian and viscoelastic jets. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 59:267–282
Sattler R, Wagner C, Eggers J (2008) Blistering pattern and formation of nanofibers in capillary thinning of polymer solutions. Phys Rev Lett 100:164502
Shore HJ, Harrison GM (2005) The effect of added polymers on the formation of drops ejected from a nozzle. Phys Fluids 17:033104
Tuladhar TR, Mackley MR (2008) Filament stretching rheometry and break-up behaviour of low viscosity polymer solutions and inkjet fluids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 148:97–108
Wathen AJ, Silvester DJ (1993) Fast iterative solution of stabilized Stokes systems part I: using simple diagonal preconditioners. SIAM J Numer Anal 30:630–649
Westborg H, Hassager O (1989) Creeping motion of long bubbles and drops in capillary tubes. J Colloid Interface Sci 133:135–147
Xu D, Sánchez Romaguera V, Barbosa S, Travis W, de Wit J, Swan P, Yeates SG (2007) Inkjet printing of polymer solutions and the role of chain entanglement. J Mater Chem 17:4902–4907
Xu Q, Basaran OA (2007) Computational analysis of drop-on-demand drop formation. Phys Fluids 19:102111
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out within the ‘Next-Generation Inkjet Technology’ consortium, which is supported by the UK Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) and by industrial funding. The authors are grateful for the cooperation of the other members of the consortium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morrison, N.F., Harlen, O.G. Viscoelasticity in inkjet printing. Rheol Acta 49, 619–632 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-009-0419-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-009-0419-z