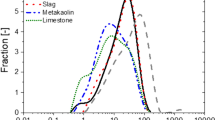
Abstract
Rheological measurements were made on concrete and mortars to characterize the shear thickening behavior of certain concrete mix designs. Shear thickening reduction levers were found by selecting and designing admixtures. Since the shear-thickening phenomena occur at the scale of the finest particles, industrial limestone fillers were studied that behave like cementitious materials. Theories based on previous academic works were relevant. The shear stress-dependent effects of shear thickening and size scaling were very helpful to distinguish between surface interactions, such as lubrication and volumetric contributions and also including the packing effects. The suspension viscosity curves vary accordingly to the Newtonian viscosity of the solvent medium. In both the shear thinning and shear thickening regimes, viscosity is controlled by adjusting the amount of two specific admixtures. The reduction of friction between polymer-coated materials appears to be a key phenomenon to delay onset shear thickening in industrial processes.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aït-Kadi A, Marchal P, Choplin L, Chrissemant AS, Bousmina M (2002) Quantitative analysis of mixer-type rheometers using Couette analogy. Can J Chem Eng 80:1166–1174
Amziane S, Ferraris CF, Koehler EP (2005) Measurement of workability of fresh concrete using a mixing truck. J Res Natl Inst Stand Technol 110:55–66
Artelt C, Garcia E (2008) Impact of superplasticizer concentration and of ultra-fine particles on the rheological behaviour of dense mortar suspensions. Cem Concr Res 38:633–642
Bender J, Wagner NJ (1996) Reversible shear thickening in monodisperse and bidisperse colloidal dispersions. J Rheol 40(5):899–916
Brady JF (1993) The rheological behavior of concentrated colloidal dispersions. J Chem Phys 99:567–581
Choplin L, Marchal P (2007) La rhéologie systémique ou une rhéologie au service d’un génie des procédés et des produits (in French). Rhéologie 12:9–18
Coussot P (2005) Rheometry of pastes, suspensions and granular materials. Wiley, New York, p 350
De Larrard F, Sedran T (2002) Mixture-proportioning of high-performance concrete. Cem Concr Res 11:1699–1704
Egres RG, Wagner NJ (2005) The rheology and microstructure of acicular precipitated calcium carbonate colloidal suspensions through the shear thickening transition. J Rheol 49:719–746
Egres RE, Nettesheim F, Wagner NJ (2006) Rheo-SANS investigation of acicular precipitated calcium carbonate colloidal suspensions through the shear thickening transition. J Rheol h50(5):685–709
Ferraris CF, Brower LE (eds) (2004) Comparison of concrete rheometers: international tests at MB (Cleveland OH, USA) in May, 2003. National Institute of Standards and Technology NISTIR 7154
Feys D, Verhoeven R, De Shutter G (2008) Fresh Self Compacting Concrete, a shear thickening material. Cem Concr Res 38:920–929
Flatt RJ (2004) Towards a prediction of superplasticized concrete rheology. Mat Struct 37:289–300
German RM (1989) Particle Packing Characteristics. Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, 458 pp., ISBN:0-918404-83-5
Gopalakrishnan V, Zukoski CF (2004) Effects of attractions on shear thickening in dense suspensions. J Rheol 48(6):1321–1344
Huang N, Bonn D (2007) Viscosity of a dense suspension in Couette flow. J Fluid Mech 590:497–507
Koehler EP, Fowler DW (2003) Measuring the workability of high fines concrete. ICAR, Texas, International Center for Aggregate Research, report 105.1
Krishnamurthy LN, Wagner N, Mewis J (2005) Shear thickening in polymer stabilized colloidal dispersions. J Rheol 49(6):1347–1360
Leighton D, Acrivos A (1987) The shear-induced migration of particles in concentrated suspensions. J Fluid Mech 181:415
Lewis JA (2000) Collodial processing of ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 83(10):2341–2359
Lombois H, Lootens D, Halary JL, Hebraud P, Colombet P, Lécolier E, Van Damme H (2005) “Sur le rôle ambigu de la lubrification dans la rhéologie des matériaux cimentaires” (in French). Rhéologie 7:11–21
Lootens D, Van Damme H, Hebraud P (2003) Giant stress fluctuations at the jamming transition. Phys Rev Lett 90(17):178301
Maranzano BJ, Wagner NJ (2001a) The effect of particle size on reversible shear thickening of concentrated colloidal dispersions. J Chem Phys 114(23):10514–10527
Maranzano BJ, Wagner NJ (2001b) The effect of interparticle interactions and particle size on reversible shear thickening: Hard-sphere colloidal dispersions. J Rheol 45(5):1205–1222
Maranzano BJ, Wagner NJ (2002) Flow-small angle neutron scattering measurements of colloidal dispersion microstructure evolution through the shear thickening transition. J Chem Phys 117(22):10291–10302
Melrose JR, Ball RC (2004a) Continuous shear thickening transitions in model concentrated colloids—the role of interparticle forces. J Rheol 48(5):937–960
Melrose JR, Ball RC (2004b) Contact networks in continuously shear thickening colloids. J Rheol 48(5):961–978
Raviv U, Glasson S, Kampf N, Gohy J-F, Jérôme R, Klein J (2003) Lubrication by charged polymers. Nature 425:163–165
Raynaud JS, Moucheront P, Baudez JC, Bertrand F, Guilbaud JP, Coussot P (2002) Direct determination by NMR of the thixotropic and yielding behavior of suspensions. J Rheol 46:709–732
Rhodes SK, Lewis JA (2006) Phase behavior, 3-D structure, and rheology of colloidal microsphere–nanoparticle suspensions. J Am Ceram Soc 89(6):1840–1846
Roussel N (2006a) A thixotropy model for fresh fluid concretes: Theory, validation and applications. Cem Concr Res 36:1797–1806
Roussel N (2006b) Correlation between yield stress and slump: Comparison between numerical simulations and concrete rheometers results. Mat Struct 39(4):501–509
Shenoy SS, Wagner NJ (2005) Influence of medium viscosity and adsorbed polymer on the reversible shear thickening transition in concentrated colloidal dispersions. Rheol Acta 44:360–371
Tattersall GH, Banfill PFG (1983) The rheology of fresh concrete. Pitman, London, pp 82–88
Tohver V, Smay JE, Braem A, Braun PV, Lewis JA (2001) Nanoparticle halos: A new colloid stabilization mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98(16):8950–8954
Toussaint F, Juge C, Laye J-M, Pellerin B (2001) Assessment of thixotropic behaviour of self compacting microconcrete. The Second International Symposium of Self-Compacting Concrete, Tokyo
Williams DA, Saak AW, Jennings HM (1999) The influence of mixing on the rheology of fresh cement paste. Cem Concr Res 29:1491–1496
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank Hélène Lombois-Burger for her stimulating discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toussaint, F., Roy, C. & Jézéquel, PH. Reducing shear thickening of cement-based suspensions. Rheol Acta 48, 883–895 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-009-0362-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-009-0362-z