Abstract
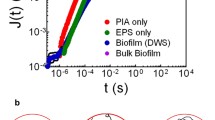
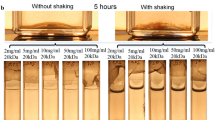
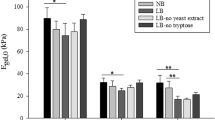
In this publication we present a detailed study of viscoelastic biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sample solutions were extracted from biofilm layers grown on Pseudomonas isolation agar. This aqueous solutions of extracellular polymeric substances exhibit weak elastic effects caused by entanglements and a small number of permanent junction points formed by calcium ions. The cross-linking mechanisms are confirmed by the Cox–Merz rule and dynamic frequency sweep tests, which result in an average lifetime of junction points of the order of 17 ms. The experimental data reveal 3.4×1017 elastically effective chains per liter of solution and no significant temperature effects in the regime between 2 and 24 °C. This result coincides pretty well with the concentration of dissolved polymer chains (2.9×1017 molecules/l). Upon addition of calcium ions, one observes the formation of stable supermolecular networks with permanent junction points. These cross-linking points did not show thermal fluctuations in time zones between 10 ms and several hours. The entanglement density of these gels is of the same order as observed in the non-cross-linked sol state (entrapped entanglements). In spite of the different molecular composition alginate gels show the same type of cross-linking mechanism as gels of extracellular polymeric substances.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Costerton JW, Irvin RT (1981) Annu Rev Microbiol 35:299–324
Sutherland IW (2001) Water Sci Techol 43: 77–86
Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming H-C, (1999) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Mayer C, Moritz R, Kirschner C, Borchard W, Maibaum R, Wingender J, Flemming H-C (1999) Int J Biol Macromol 26:3–16
Costerton JW, Stewart PS (2001) Spektrum Wiss 11:58–65
Körstgens V, Flemming H-C, Wingender J, Borchard W (2001) J Microbiol Methods 46:9–17
Flemming H-C, Wingender J, Mayer C, Körstgens V, Borchard W (2000) Community structure and co-operation in biofilms. SGM symposium 59. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 87–105
Charaklis WG (1979) Biofilm development and destruction. Electric Power Institute, Palo Alto
Stoodley P, Lewandowski Z, Boyle JD, Lappin-Scott HM (1999) Biotechnol Bioeng 65:83–92
Ohashi A, Koyama T, Syutsubo K, Harada H (1999) Water SciTechnol 39:261–268
Nielsen PH, Jahn A (1999) In: Wingender J, Neu T, Flemming H-C(eds) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 49–72
Wingender J et al (2001) Methods Enzymol 336:302–314
Draget KI, Ostgaard K, Smidsrod O (1989) Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31:79–83
Draget KI, Ostgaard K, Smidsrod O (1991) Carbohydr Polym 14:159–178
Thiele H (1967) Histolyse und Histogenese. Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft, Frankfurt am Main
Fischer P, Rehage H (1997) Rheol Acta 36:13–27
Gehm L(1998) Rheologie—praxisorientierte Grundlagen und Glossar, Vincentz, Hanover
Mezger T (2000) Das Rheologie-Handbuch. Vincentz, Hanover
Rehage H, Hoffmann H (1991) Mol Phys 74:933–973
Löbl M, Thurn H, Hoffmann H (1984) Ber Bunsenges Phys Chem 88:1102
Thurn H, Löbl M, Hoffmann H (1985) J Phys Chem 89:517
Tschoegl NW (1989) The phenomenological theory of linear viscoelastic behavior. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Honerkamp J, Weese J (1993) Rheol Acta 32:65–73
Ferry JD (1980) Viscoelastic properties of polymers. Wiley, New York
Kulicke W-M (1986) Fliessverhalten von Stoffen und Stoffgemischen. Hüthig and Wepf, Basel
Rehage H (1982) Rheologische Untersuchungen an viskoelastischen Tensidlösungen. Dissertation. University of Bayreuth, Germany
Filisetti-Cozzi TMCC, Carpita NC (1991) Anal Biochem 197:157–162
Grobe S, Wingender J, Trüper HG (1995) J Appl Bacteriol 79:94–102
Winter HH (1987) Polym Eng Sci 27,22:1698–1702
Dominguez A, Fernandez A, Gonzales N, Iglesias E, Montenegro L (1997) J Chem Educ 74:1227–1231
Geddie JL, Sutherland IW (1994) Biotechnol Appl Biochem 20:117–129
Acknowledgements
Financial support by grants of the “Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft” (DFG Re 681/12-1) and the “Fonds der Chemischen Industrie” are gratefully acknowledged. The authors are particularly grateful to W. Borchard for his valuable suggestions and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wloka, M., Rehage, H., Flemming, HC. et al. Rheological properties of viscoelastic biofilm extracellular polymeric substances and comparison to the behavior of calcium alginate gels. Colloid Polym Sci 282, 1067–1076 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-003-1033-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-003-1033-8