Abstract.
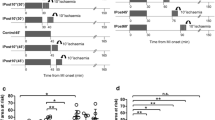
The search for the mechanism of preconditioning-induced cardioprotection has been hampered by controversial results obtained by workers using different animal species, experimental models, protocols and endpoints. The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of the perfusion model (retrograde vs working), the infarct size and severity of ischaemia (regional vs global) as well as the endpoint (functional recovery vs infarct size) in preconditioning. The isolated perfused rat heart was preconditioned by 3 × 5 min global ischaemia, followed by different periods of regional or global ischaemia and reperfusion. Ischaemic preconditioning of working hearts resulted in increased functional recovery after 25–35 min global ischaemia, while retrogradely perfused hearts showed no significant improvement (except after 30 min global ischaemia). In addition, the percentage reduction in functional performance during reperfusion observed in the latter group was significantly less than in working hearts. Hearts were also subjected to regional ischaemia, perfused in either retrograde or working mode and infarct size determined. Regionally ischaemic working as well as retrogradely perfused hearts when preconditioned showed a significant increase in functional recovery after 35 min ischaemia only. In contrast to global ischaemia, the percentage recovery in mechanical performance of regionally ischaemic hearts was not affected by the mode of perfusion. Preconditioning of working hearts caused a significant reduction in infarct size after both 30 and 35 min ischaemia. However, preconditioned retrogradely perfused hearts showed a significant decline in infarct size after 35 min regional ischaemia only. In conclusion, the effect of the perfusion mode on functional recovery is dependent on the size and severity of ischaemia. It also affects the ischaemic time at which infarct size reduction by prior preconditioning occurs in the retrogradely perfused heart.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lochner, A., Genade, S. & Moolman, J.A. Ischemic preconditioning: Infarct size is a more reliable endpoint than functional recovery. Basic Res Cardiol 98, 337–346 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-003-0427-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-003-0427-6