Abstract
Purpose
Obesity predisposes to cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. The amino acid, L-taurine (Tau), regulates glucose and lipid homeostasis and vascular function. Here we investigated whether Tau supplementation prevents endothelial dysfunction in the thoracic aortas of monosodium glutamate-induced obese (MSG) rats.
Methods
Male rats received subcutaneous injections of MSG (4 mg/kg body weight/day) or saline (control group, CTL) during the first five days of life. From 21 to 150 days of age, the rats were distributed into the groups: CTL, MSG, and CTL and MSG supplemented with 2.5% Tau in their drinking water (CTAU and MTAU).
Results
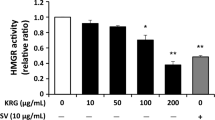
At 150-days old, MSG rats presented massive abdominal fat deposition, hypertriglyceridemia, hyperinsulinemia, glucose intolerance and high plasma levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a lipid peroxidation marker. Tau supplementation attenuated fat accumulation in perigonadal adipose tissue and prevented the increase in triglycerides and MDA plasma levels. Aortic rings of MSG rats presented reduced vasodilation in response to acetylcholine (ACh). No modifications in insulin-induced vasodilatation, or Akt and eNOS phosphorylation, were observed in MSG aortas; thoracic aortas from MSG rats presented reduced tunica media thickness, with a lower aortic wall thickness/lumen diameter ratio and decreased total collagen content. Tau supplementation restored ACh-induced vasodilation and collagen content.
Conclusions
Our study presents the first evidence that Tau prevents disruptions in vascular reactivity and in extracellular matrix composition in thoracic aortas of MSG-obese rats. The vascular protective actions of Tau may be linked to reduced lipid peroxidation and a reduction in cardiovascular risk factors, such as abdominal fat and hypertriglyceridemia.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
King RJ, Ajjan RA (2017) Vascular risk in obesity: facts, misconceptions and the unknown. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res 14(1):2–13. https://doi.org/10.1177/1479164116675488
Sena CM, Pereira AM, Seica R (2013) Endothelial dysfunction—a major mediator of diabetic vascular disease. Biochimi Biophys Acta 1832(12):2216–2231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.08.006
Nemes A, Gavaller H, Csajbok E, Forster T, Csanady M (2008) Obesity is associated with aortic enlargement and increased stiffness: an echocardiographic study. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 24(2):165–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-007-9248-2
Robinson MR, Scheuermann-Freestone M, Leeson P, Channon KM, Clarke K, Neubauer S, Wiesmann F (2008) Uncomplicated obesity is associated with abnormal aortic function assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 10:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1532-429X-10-10
Michel T, Vanhoutte PM (2010) Cellular signaling and NO production. Pflugers Archiv Eur J Physiol 459(6):807–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-009-0765-9
Shimokawa H, Godo S (2016) Diverse functions of endothelial NO synthases system: NO and EDH. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 67(5):361–366. https://doi.org/10.1097/FJC.0000000000000348
Huxtable RJ (1992) Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev 72(1):101–163
Ribeiro RA, Bonfleur ML, Amaral AG, Vanzela EC, Rocco SA, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2009) Taurine supplementation enhances nutrient-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic mice islets. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 25(4):370–379. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.959
Carneiro EM, Latorraca MQ, Araujo E, Beltra M, Oliveras MJ, Navarro M, Berna G, Bedoya FJ, Velloso LA, Soria B, Martin F (2009) Taurine supplementation modulates glucose homeostasis and islet function. J Nutr Biochem 20(7):503–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2008.05.008
Nardelli TR, Ribeiro RA, Balbo SL, Vanzela EC, Carneiro EM, Boschero AC, Bonfleur ML (2011) Taurine prevents fat deposition and ameliorates plasma lipid profile in monosodium glutamate-obese rats. Amino Acids 41(4):901–908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0789-7
Pina-Zentella G, de la Rosa-Cuevas G, Vazquez-Meza H, Pina E, de Pina MZ (2012) Taurine in adipocytes prevents insulin-mediated H2O2 generation and activates Pka and lipolysis. Amino Acids 42(5):1927–1935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0919-x
Bonfleur ML, Borck PC, Ribeiro RA, Caetano LC, Soares GM, Carneiro EM, Balbo SL (2015) Improvement in the expression of hepatic genes involved in fatty acid metabolism in obese rats supplemented with taurine. Life Sci 135:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2015.05.019
Caetano LC, Bonfleur ML, Ribeiro RA, Nardelli TR, Lubaczeuski C, do Nascimento da Silva J, Carneiro EM, Balbo SL (2015) Taurine supplementation regulates Ikappa-Balpha protein expression in adipose tissue and serum IL-4 and TNF-alpha concentrations in MSG obesity. Eur J Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-1114-8
Ogasawara M, Nakamura T, Koyama I, Nemoto M, Yoshida T (1993) Reactivity of taurine with aldehydes and its physiological role. Chem Pharm Bull 41(12):2172–2175
Schaffer SW, Azuma J, Mozaffari M (2009) Role of antioxidant activity of taurine in diabetes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 87(2):91–99. https://doi.org/10.1139/Y08-110
Abebe W, Mozaffari MS (2011) Role of taurine in the vasculature: an overview of experimental and human studies. Am J Cardiovasc Dis 1(3):293–311
Maia AR, Batista TM, Victorio JA, Clerici SP, Delbin MA, Carneiro EM, Davel AP (2014) Taurine supplementation reduces blood pressure and prevents endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in post-weaning protein-restricted rats. PLoS One 9(8):e105851. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105851
Sun Q, Wang B, Li Y, Sun F, Li P, Xia W, Zhou X, Li Q, Wang X, Chen J, Zeng X, Zhao Z, He H, Liu D, Zhu Z (2016) Taurine supplementation lowers blood pressure and improves vascular function in prehypertension: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Hypertension 67(3):541–549. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06624
Ozsarlak-Sozer G, Kerry Z, Gokce G, Oran I, Topcu Z (2011) Oxidative stress in relation to telomere length maintenance in vascular smooth muscle cells following balloon angioplasty. J Physiol Biochem 67(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-010-0046-2
Baek YY, Cho DH, Choe J, Lee H, Jeoung D, Ha KS, Won MH, Kwon YG, Kim YM (2012) Extracellular taurine induces angiogenesis by activating ERK-, Akt-, and FAK-dependent signal pathways. Eur J Pharmacol 674(2–3):188–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.11.022
Olney JW, Adamo NJ, Ratner A (1971) Monosodium glutamate effects. Science 172(3980):294
Balbo SL, Grassiolli S, Ribeiro RA, Bonfleur ML, Gravena C, Brito Mdo N, Andreazzi AE, Mathias PC, Torrezan R (2007) Fat storage is partially dependent on vagal activity and insulin secretion of hypothalamic obese rat. Endocrine 31(2):142–148
Ribeiro RA, Balbo SL, Roma LP, Camargo RL, Barella LF, Vanzela EC, de Freitas Mathias PC, Carneiro EM, Boschero AC, Bonfleur ML (2013) Impaired muscarinic type 3 (M3) receptor/PKC and PKA pathways in islets from MSG-obese rats. Mol Biol Rep 40(7):4521–4528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2546-y
Lobato NS, Filgueira FP, Akamine EH, Davel AP, Rossoni LV, Tostes RC, Carvalho MH, Fortes ZB (2011) Obesity induced by neonatal treatment with monosodium glutamate impairs microvascular reactivity in adult rats: role of NO and prostanoids. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 21 (10):808–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2010.02.006
da Cunha NV, Pinge-Filho P, Panis C, Silva BR, Pernomian L, Grando MD, Cecchini R, Bendhack LM, Martins-Pinge MC (2014) Decreased endothelial nitric oxide, systemic oxidative stress, and increased sympathetic modulation contribute to hypertension in obese rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 306(10):H1472–1480. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00520.2013
Duivenvoorden I, Teusink B, Rensen PC, Romijn JA, Havekes LM, Voshol PJ (2005) Apolipoprotein C3 deficiency results in diet-induced obesity and aggravated insulin resistance in mice. Diabetes 54(3):664–671
Ribeiro RA, Vanzela EC, Oliveira CA, Bonfleur ML, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2010) Taurine supplementation: involvement of cholinergic/phospholipase C and protein kinase A pathways in potentiation of insulin secretion and Ca2+ handling in mouse pancreatic islets. Br J Nutr 104(8):1148–1155. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114510001820
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358
Bernardis LL, Patterson BD (1968) Correlation between ‘Lee index’ and carcass fat content in weanling and adult female rats with hypothalamic lesions. J Endocrinol 40(4):527–528
Medei E, Lima-Leopoldo AP, Pereira-Junior PP, Leopoldo AS, Campos DH, Raimundo JM, Sudo RT, Zapata-Sudo G, Bruder-Nascimento T, Cordellini S, Nascimento JH, Cicogna AC (2010) Could a high-fat diet rich in unsaturated fatty acids impair the cardiovascular system? Can J Cardiol 26(10):542–548
Ribeiro RA, Santos-Silva JC, Vettorazzi JF, Cotrim BB, Mobiolli DD, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2012) Taurine supplementation prevents morpho-physiological alterations in high-fat diet mice pancreatic beta-cells. Amino Acids 43(4):1791–1801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1263-5
Gomez-Roso M, Montero MJ, Carron R, Sevilla MA (2009) Cardiovascular changes in spontaneously hypertensive rats are improved by chronic treatment with zofenopril. Br J Pharmacol 158(8):1911–1921. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00491.x
Solon CS, Franci D, Ignacio-Souza LM, Romanatto T, Roman EA, Arruda AP, Morari J, Torsoni AS, Carneiro EM, Velloso LA (2012) Taurine enhances the anorexigenic effects of insulin in the hypothalamus of rats. Amino Acids 42(6):2403–2410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1045-5
Tangvarasittichai S (2015) Oxidative stress, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 6(3):456–480. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i3.456
Yin H, Xu L, Porter NA (2011) Free radical lipid peroxidation: mechanisms and analysis. Chem Rev 111(10):5944–5972. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200084z
Ayala A, Munoz MF, Arguelles S (2014) Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014:360438. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/360438
da Cunha NV, Lopes FN, Panis C, Cecchini R, Pinge-Filho P, Martins-Pinge MC (2017) iNOS inhibition improves autonomic dysfunction and oxidative status in hypertensive obese rats. Clin Exp Hypertens 39(1):50–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641963.2016.1210628
Lazarin Mde O, Ishii-Iwamoto EL, Yamamoto NS, Constantin RP, Garcia RF, da Costa CE, Vitoriano Ade S, de Oliveira MC, Salgueiro-Pagadigorria CL (2011) Liver mitochondrial function and redox status in an experimental model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by monosodium l-glutamate in rats. Exp Mol Pathol 91(3):687–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2011.07.003
Contini MC, Millen N, Riera L, Mahieu S (2012) Kidney and liver functions and stress oxidative markers of monosodium glutamate-induced obese rats. Food Public Health 2(5):168–177
Aruoma OI, Halliwell B, Hoey BM, Butler J (1988) The antioxidant action of taurine, hypotaurine and their metabolic precursors. Biochem J 256(1):251–255
Ahmad MK, Khan AA, Ali SN, Mahmood R (2015) Chemoprotective effect of taurine on potassium bromate-induced DNA damage, DNA-protein cross-linking and oxidative stress in rat intestine. PLoS One 10(3):e0119137. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119137
Cho YE, Basu A, Dai A, Heldak M, Makino A (2013) Coronary endothelial dysfunction and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in type 2 diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 305(10):C1033-1040. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00234.2013
Duncan ER, Walker SJ, Ezzat VA, Wheatcroft SB, Li JM, Shah AM, Kearney MT (2007) Accelerated endothelial dysfunction in mild prediabetic insulin resistance: the early role of reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293(5):E1311-1319. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00299.2007
Taguchi K, Matsumoto T, Kamata K, Kobayashi T (2012) G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2, with beta-arrestin 2, impairs insulin-induced Akt/endothelial nitric oxide synthase signaling in ob/ob mouse aorta. Diabetes 61(8):1978–1985. https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-1729
Chen H, Kold-Petersen H, Laher I, Simonsen U, Aalkjaer C (2015) Impaired endothelial calcium signaling is responsible for the defective dilation of mesenteric resistance arteries from db/db mice to acetylcholine. Eur J Pharmacol 767:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.09.043
Choi SK, Lim M, Yeon SI, Lee YH (2016) Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress improves coronary artery function in type 2 diabetic mice. Exp Physiol 101(6):768–777. https://doi.org/10.1113/EP085508
King GL, Park K, Li Q (2016) Selective insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular diseases in diabetes: the 2015 Edwin Bierman Award lecture. Diabetes 65(6):1462–1471. https://doi.org/10.2337/db16-0152
Bitar MS, Wahid S, Mustafa S, Al-Saleh E, Dhaunsi GS, Al-Mulla F (2005) Nitric oxide dynamics and endothelial dysfunction in type II model of genetic diabetes. Eur J Pharmacol 511(1):53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.01.014
El Idrissi A, Okeke E, Yan X, Sidime F, Neuwirth LS (2013) Taurine regulation of blood pressure and vasoactivity. Adv Exp Med Biol 775:407–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6130-2_31
Komolafe OA, Adeyemi DO, Adewole OS, Obuotor EM, Abiodun AA (2009) Morphological and morphometric studies of the aorta, pulmonary trunk, and heart of streptozotocin-induced diabetic Wistar rats. Folia Morphol 68(4):207–214
Danias PG, Tritos NA, Stuber M, Botnar RM, Kissinger KV, Manning WJ (2003) Comparison of aortic elasticity determined by cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in obese versus lean adults. Am J Cardiol 91(2):195–199
Burla AK, Lobato NS, Fortes ZB, Oigman W, Neves MF (2013) Cardiac fibrosis and vascular remodeling are attenuated by metformin in obese rats. Int J Cardiol 165(3):483–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.09.012
de Franciscis S, Serra R (2015) Matrix metalloproteinases and endothelial dysfunction: the search for new prognostic markers and for new therapeutic targets for vascular wall imbalance. Thromb Res 136(1):5–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2015.04.022
Myers PR, Tanner MA (1998) Vascular endothelial cell regulation of extracellular matrix collagen: role of nitric oxide. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18 (5):717–722
Xu ZR, Du HK, Wang SX, Liu DW, Chang AH (2006) Effects of taurine on type I and III collagen expression in rats lung exposed to silica. Zhonghua lao dong wei sheng zhi ye bing za zhi = Zhonghua laodong weisheng zhiyebing zazhi = Chin J Ind Hyg Occup Dis 24(9):544–546
Abdel-Moneim AM, Al-Kahtani MA, El-Kersh MA, Al-Omair MA (2015) Free radical-scavenging, anti-inflammatory/anti-fibrotic and hepatoprotective actions of taurine and silymarin against CCl4 induced rat liver damage. PLoS One 10(12):e0144509. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144509
Lee E, Ryu GR, Ko SH, Ahn YB, Yoon KH, Ha H, Song KH (2011) Antioxidant treatment may protect pancreatic beta cells through the attenuation of islet fibrosis in an animal model of type 2 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 414(2):397–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.09.087
Liu Q, Lu Z, Wu H, Zheng L (2015) Chondroprotective effects of taurine in primary cultures of human articular chondrocytes. Tohoku J Exp Med 235(3):201–213. https://doi.org/10.1620/tjem.235.201
Park S, Kim H, Kim SJ (2001) Stimulation of ERK2 by taurine with enhanced alkaline phosphatase activity and collagen synthesis in osteoblast-like UMR-106 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 62(8):1107–1111
McCarty MF (2004) Supplementary taurine may stabilize atheromatous plaque by antagonizing the activation of metalloproteinases by hypochlorous acid. Med Hypotheses 63(3):414–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2003.10.035
Barreto SC, Hopkins CA, Bhowmick M, Ray A (2015) Extracellular matrix in obesity—cancer interactions. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig 22(2):63–77. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2015-0001
Acknowledgements
This study forms part of the M.Sc Thesis of Valéria de Fátima Leão and was supported by grants from Conselho Nacional para o Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Rio de Janeiro (E-26/110.806/2013). We are grateful to Nicola Conran for editing the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All contributing authors report no conflicts of interest.
Research involving animals
All experimental procedures were authorized by the license nº.: MACAE03 from the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Campus UFRJ-Macaé.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leão, V.F., Ferreira, L.L.D.M., Melo, C.M. et al. Taurine supplementation prevents endothelial dysfunction and attenuates structural changes in aortas from hypothalamic obese rats. Eur J Nutr 58, 551–563 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1616-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1616-2