Abstract
Background
Early repolarization pattern (ER) gained attention as a risk factor for ventricular arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death in the general population. While electrocardiographic abnormalities are frequent findings in stroke patients, data on ER pattern in this population are lacking.
Methods
We assessed the prevalence of ER pattern in consecutive acute stroke patients at a tertiary stroke center. Functional outcome after 90 days was analyzed to determine the effect of an ER pattern on mortality. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify factors associated with an ER pattern.
Results
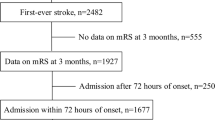
Out of 1141 consecutive stroke patients 771 patients remained for analysis after application of exclusion criteria. ER was observed in 62 (8.04 %) patients. ER was more prevalent among subjects with intracerebral and subarachnoidal hemorrhage (13.0 %) than among patients with ischemic stroke (7.0 %; p = 0.024). Multiple regression analysis revealed QRS-duration (OR 0.972 95 % CI 0.950–0.994, p = 0.012), QT-duration (OR 1.009, 95 % CI 1.004–1.014, p = 0.001) and mechanical ventilation on admission (OR 0.320, 95 % CI 0.136–0.752, p = 0.009) as independent predictors for ER. Overall ER on admission was not associated with increased mortality at 3-month follow-up (ER 11.3 % vs. non-ER 9.2 %; p = 0.582).
Conclusions
ER is frequently found among patients with acute cerebrovascular events and is more prevalent in patients with hemorrhagic compared to ischemic events. Our study yields no evidence that ER is associated with worse outcome or mortality after stroke.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klingelhofer J, Sander D (1997) Cardiovascular consequences of clinical stroke. Baillieres Clin Neurol 6:309–335
Prosser J, MacGregor L, Lees KR, Diener HC, Hacke W, Davis S (2007) Predictors of early cardiac morbidity and mortality after ischemic stroke. Stroke 38:2295–2302
Christensen H, Boysen G, Johannesen HH (2004) Serum-cortisol reflects severity and mortality in acute stroke. J Neurol Sci 217:175–180
Feibel JH, Hardy PM, Campbell RG, Goldstein MN, Joynt RJ (1977) Prognostic value of the stress response following stroke. JAMA J Am Med Assoc 238:1374–1376
Soros P, Hachinski V (2012) Cardiovascular and neurological causes of sudden death after ischaemic stroke. Lancet Neurol 11:179–188
Koppikar S, Baranchuk A, Guzman JC, Morillo CA (2013) Stroke and ventricular arrhythmias. Int J Cardiol 168:653–659
Tobias SL, Bookatz BJ, Diamond TH (1987) Myocardial damage and electrocardiographic changes in acute cerebrovascular hemorrhage: a report of three cases and review. Heart Lung J Crit Care 16:521–526
Micieli G, Cavallini A (2008) The autonomic nervous system and ischemic stroke: a reciprocal interdependence. Clin Auton Res 18:308–317
Samuels MA (2007) The brain-heart connection. Circulation 116:77–84
Oppenheimer S (2006) Cerebrogenic cardiac arrhythmias: cortical lateralization and clinical significance. Clin Auton Res 16:6–11
Katsanos AH, Korantzopoulos P, Tsivgoulis G, Kyritsis AP, Kosmidou M, Giannopoulos S (2013) Electrocardiographic abnormalities and cardiac arrhythmias in structural brain lesions. Int J Cardiol 167:328–334
Cropp GJ, Manning GW (1960) Electrocardiographic changes simulating myocardial ischemia and infarction associated with spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage. Circulation 22:25–38
Byer E, Ashman R, Toth LA (1947) Electrocardiograms with large, upright T waves and long Q-T intervals. Am Heart J 33:796–806
Fentz V, Gormsen J (1962) Electrocardiographic patterns in patients with cerebrovascular accidents. Circulation 25:22–28
Khechinashvili G, Asplund K (2002) Electrocardiographic changes in patients with acute stroke: a systematic review. Cerebrovasc Dis 14:67–76
Goldstein DS (1979) The electrocardiogram in stroke: relationship to pathophysiological type and comparison with prior tracings. Stroke 10:253–259
Kallmunzer B, Breuer L, Kahl N, Bobinger T, Raaz-Schrauder D, Huttner HB et al (2012) Serious cardiac arrhythmias after stroke: incidence, time course, and predictors–a systematic, prospective analysis. Stroke 43:2892–2897
Christensen H, Fogh Christensen A, Boysen G (2005) Abnormalities on ECG and telemetry predict stroke outcome at 3 months. J Neurol Sci 234:99–103
Dogan A, Tunc E, Ozturk M, Kerman M, Akhan G (2004) Electrocardiographic changes in patients with ischaemic stroke and their prognostic importance. Int J Clin Pract 58:436–440
Providencia R, Barra S, Paiva L (2013) Atrial fibrillation, elevated troponin, ischemic stroke and adverse outcomes: understanding the connection. Clin Res Cardiol Off J Ger Card Soc 102:701–711
Haissaguerre M, Derval N, Sacher F, Jesel L, Deisenhofer I, de Roy L et al (2008) Sudden cardiac arrest associated with early repolarization. N Engl J Med 358:2016–2023
Sinner MF, Reinhard W, Muller M, Beckmann BM, Martens E, Perz S, et al. (2010) Association of early repolarization pattern on ECG with risk of cardiac and all-cause mortality: a population-based prospective cohort study (MONICA/KORA). PLoS Med 7: e1000314
Kallmunzer B, Kuramatsu J, Breuer L, Engelhorn T, Kohrmann M (2011) Early repolarisation syndrome and ischemic stroke: is there a link? Cerebrovasc Dis 31:414–415
Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, Bruno A, Connors JJ, Demaerschalk BM et al (2013) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 44:870–947
Kasner SE (2006) Clinical interpretation and use of stroke scales. Lancet Neurol 5:603–612
European Stroke Organisation (ESO) Executive Committee (2008) Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack. Cerebrovasc Dis 25: 457–507
Laufs U, Hoppe UC, Rosenkranz S, Kirchhof P, Bohm M, Diener HC et al (2010) Cardiological evaluation after cerebral ischaemia : consensus statement of the Working Group Heart and Brain of the German Cardiac Society-Cardiovascular Research (DGK) and the German Stroke Society (DSG). Clin Res Cardiol Off J Ger Cardiac Soc 99:609–625
Sulter G, Steen C, De Keyser J (1999) Use of the Barthel index and modified Rankin scale in acute stroke trials. Stroke 30:1538–1541
O’Keefe JH (2002) The complete guide to ECGs. 2nd ed. Royal Physicians Press, Oak
Villa A, Bacchetta A, Milani O, Omboni E (2001) QT interval prolongation as predictor of early mortality in acute ischemic stroke patients. Am J Emerg Med 19:332–333
Tikkanen JT, Junttila MJ, Anttonen O, Aro AL, Luttinen S, Kerola T et al (2011) Early repolarization: electrocardiographic phenotypes associated with favorable long-term outcome. Circulation 123:2666–2673
Tikkanen JT, Anttonen O, Junttila MJ, Aro AL, Kerola T, Rissanen HA et al (2009) Long-term outcome associated with early repolarization on electrocardiography. N Engl J Med 361:2529–2537
Tikkanen JT, Huikuri HV (2013) Early repolarization ECG pattern in the Finnish general population. J Electrocardiol 46:439–441
Walsh JA 3rd, Ilkhanoff L, Soliman EZ, Prineas R, Liu K, Ning H et al (2013) Natural history of the early repolarization pattern in a biracial cohort: CARDIA (Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults) Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 61:863–869
Furukawa Y, Yamada T, Morita T, Iwasaki Y, Kawasaki M, Kikuchi A et al (2013) Early repolarization pattern associated with sudden cardiac death: long-term follow-up in patients with chronic heart failure. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 24:632–639
Hajhosseiny R, Rajani R, Khavandi K, Sebag FA, Mashayekhi S, Wright M et al (2013) The prevalence of electrocardiographic early repolarization in an adult cohort with chronic kidney disease and its impact upon all-cause mortality and progression to dialysis. Front Physiol 4:127
Noseworthy PA, Weiner R, Kim J, Keelara V, Wang F, Berkstresser B, et al. (2011) Early repolarization pattern in competitive athletes: clinical correlates and the effects of exercise training. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 4: 432–440
Rollin A, Maury P, Bongard V, Sacher F, Delay M, Duparc A et al (2012) Prevalence, prognosis, and identification of the malignant form of early repolarization pattern in a population-based study. Am J Cardiol 110:1302–1308
Uberoi A, Jain NA, Perez M, Weinkopff A, Ashley E, Hadley D et al (2011) Early repolarization in an ambulatory clinical population. Circulation 124:2208–2214
Wu SH, Lin XX, Cheng YJ, Qiang CC, Zhang J (2013) Early repolarization pattern and risk for arrhythmia death: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 61:645–650
Greenfield JC Jr, Rembert JC (2013) The prevalence of lateral lead early repolarization in otherwise normal electrocardiograms as a function of age. J Electrocardiol 46:334–335
Antzelevitch C, Yan GX (2010) J wave syndromes. Heart Rhythm 7:549–558
Benito B, Guasch E, Rivard L, Nattel S (2010) Clinical and mechanistic issues in early repolarization of normal variants and lethal arrhythmia syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol 56:1177–1186
Conflict of interest
The authors report no disclosures relevant to the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bobinger, T., Kallmünzer, B., Kopp, M. et al. Prevalence and impact on outcome of electrocardiographic early repolarization patterns among stroke patients: a prospective observational study. Clin Res Cardiol 104, 666–671 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-015-0831-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-015-0831-6