Abstract
Background
Rho-kinase (ROCK) is the primary effector protein in the RhoA pathway, which regulates Ca2+-independent smooth muscle contraction in the human bowel. This pathway has been reported to be hyper-activated in the aganglionic bowel of EDNRB-null (−/−) rats compared to the ganglionic bowel from EDNRB (+/+) rats. We hypothesised that ROCK expression is up-regulated in human aganglionic bowel and designed this study to investigate ROCK 1 and ROCK 2 expression in Hirschsprung’s disease (HSCR) and controls.
Materials and methods
Full-length specimens were collected following pull-through surgery for HSCR (n = 9). Colonic controls (n = 6) were obtained during colostomy closure from patients with anorectal malformations. Distribution of ROCK 1/2 expression was evaluated using double-labelled immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy. ROCK1/2 protein expression was assessed in mucosa and tunica muscularis using western blot analysis.
Results
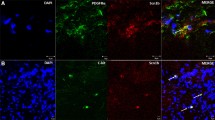
There was strong expression of both ROCK 1 and ROCK 2 in interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) and ganglia. ROCK 1 expression was reduced in aganglionic bowel compared to HSCR ganglionic bowel and controls in both mucosa and tunica muscularis. ROCK 2 expression was similar in the colon of children with HSCR and controls.
Conclusions
This is the first report of strong ROCK expression in colonic ICCs. Although the rat model of aganglionic bowel suggests that Ca2+-independent smooth muscle contraction involving ROCK is hyper-activated, our data indicate ROCK 1 expression is decreased in aganglionic bowel and ROCK 2 expression is unaltered in children with HSCR.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Menezes M, Corbally M, Puri P (2006) Long-term results of bowel function after treatment for Hirschsprung’s disease: a 29-year review. Pediatr Surg Int 22(12):987–990. doi:10.1007/s00383-006-1783-8
Frei E, Huster M, Smital P, Schlossmann J, Hofmann F, Wegener JW (2009) Calcium-dependent and calcium-independent inhibition of contraction by cGMP/cGKI in intestinal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 297(4):G834–G839. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00095.2009
Large RJ, Bradley E, Webb T, O’Donnell AM, Puri P, Hollywood MA, Thornbury KD, McHale NG, Sergeant GP (2012) Investigation of L-type Ca(2 +) current in the aganglionic bowel segment in Hirschsprung’s disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil 24(12):e1126–e1571. doi:10.1111/nmo.12006
Puetz S, Lubomirov LT, Pfitzer G (2009) Regulation of smooth muscle contraction by small GTPases. Physiology (Bethesda) 24:342–356. doi:10.1152/physiol.00023.2009
Schofield AV, Bernard O (2013) Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase (ROCK) signaling and disease. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 48(4):301–316. doi:10.3109/10409238.2013.786671
Patil SB, Bitar KN (2006) RhoA- and PKC-alpha-mediated phosphorylation of MYPT and its association with HSP27 in colonic smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290(1):G83–G95. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00178.2005
Akiyoshi J, Ieiri S, Nakatsuji T, Taguchi T (2009) Mechanism of Rho-kinase-mediated Ca2 + -independent contraction in aganglionic smooth muscle in a rat model of Hirschsprung’s disease. Pediatr Surg Int 25(11):955–960. doi:10.1007/s00383-009-2461-4
Urena J, Lopez-Barneo J (2012) Metabotropic regulation of RhoA/Rho-associated kinase by L-type Ca2 + channels. Trends Cardiovasc Med 22(6):155–160. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2012.07.013
Fernandez-Tenorio M, Porras-Gonzalez C, Castellano A, Del Valle-Rodriguez A, Lopez-Barneo J, Urena J (2011) Metabotropic regulation of RhoA/Rho-associated kinase by L-type Ca2 + channels: new mechanism for depolarization-evoked mammalian arterial contraction. Circ Res 108(11):1348–1357. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.240127
Bayguinov O, Dwyer L, Kim H, Marklew A, Sanders KM, Koh SD (2011) Contribution of Rho-kinase to membrane excitability of murine colonic smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 163(3):638–648. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01241.x
Ayman S, Wallace P, Wayman CP, Gibson A, McFadzean I (2003) Receptor-independent activation of Rho-kinase-mediated calcium sensitisation in smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 139(8):1532–1538. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705394
Menezes M, Pini Prato A, Jasonni V, Puri P (2008) Long-term clinical outcome in patients with total colonic aganglionosis: a 31-year review. J Pediatr Surg 43(9):1696–1699. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2008.01.072
Kaul A, Garza JM, Connor FL, Cocjin JT, Flores AF, Hyman PE, Di Lorenzo C (2011) Colonic hyperactivity results in frequent fecal soiling in a subset of children after surgery for Hirschsprung disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 52(4):433–436. doi:10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181efe551
Moore SW, Albertyn R, Cywes S (1996) Clinical outcome and long-term quality of life after surgical correction of Hirschsprung’s disease. J Pediatr Surg 31(11):1496–1502
Iizuka M, Kimura K, Wang S, Kato K, Amano M, Kaibuchi K, Mizoguchi A (2012) Distinct distribution and localization of Rho-kinase in mouse epithelial, muscle and neural tissues. Cell Struct Funct 37(2):155–175
Peri LE, Sanders KM, Mutafova-Yambolieva VN (2013) Differential expression of genes related to purinergic signaling in smooth muscle cells, PDGFRalpha-positive cells, and interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine colon. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25(9):e609–e620. doi:10.1111/nmo.12174
Koh SD, Rhee PL (2013) Ionic Conductance(s) in Response to Post-junctional Potentials. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 19(4):426–432. doi:10.5056/jnm.2013.19.4.426
Harrington AM, Peck CJ, Liu L, Burcher E, Hutson JM, Southwell BR (2010) Localization of muscarinic receptors M1R, M2R and M3R in the human colon. Neurogastroenterol Motil 22(9):999–1008. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2982.2009.01456.x (e1262-1003)
Kudo M, Khalifeh Soltani SM, Sakuma SA, McKleroy W, Lee TH, Woodruff PG, Lee JW, Huang K, Chen C, Arjomandi M, Huang X, Atabai K (2013) Mfge8 suppresses airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma by regulating smooth muscle contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(2):660–665. doi:10.1073/pnas.1216673110
Brennan PA, Umar T, Zaki GA, Langdon JD, Spedding A, Buckley J, Downie IP (2000) Are myoepithelial cells responsible for the widespread expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in pleomorphic adenoma? An immunohistochemical study. J Oral Pathol Med 29(6):279–283
Yoo J, Rodriguez Perez CE, Nie W, Sinnett-Smith J, Rozengurt E (2013) TNF-α and LPA promote synergistic expression of COX-2 in human colonic myofibroblasts: role of LPA-mediated transactivation of upregulated EGFR. BMC Gastroenterol 13:90. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-13-90
Yang J, Ikezoe T, Nishioka C, Takezaki Y, Hanazaki K, Taguchi T, Yokoyama A (2012) Long-term exposure of gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells to sunitinib induces epigenetic silencing of the PTEN gene. Int J Cancer 130(4):959–966 doi:10.1002/ijc.26095
Rode J, Dhillon AP, Doran JF, Jackson P, Thompson RJ (1985) PGP 9.5, a new marker for human neuroendocrine tumours. Histopathology 9(2):147–158
Acknowledgments
We wish to acknowledge the assistance and guidance of Dr. Luiz Alvarez and the Departments of Histopathology in Our Lady’s Children’s Hospital, Crumlin and Children’s University Hospital, Temple St, Dublin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coyle, D., O’Donnell, A.M., Corcionivoschi, N. et al. Rho-kinase expression in Hirschsprung’s disease. Pediatr Surg Int 31, 1077–1085 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3762-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3762-4