Abstract
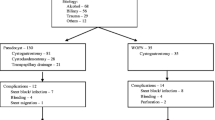
Twelve children with pancreatic pseudocysts were managed for over 10 years at our institute that is a tertiary referral center of our country. A majority of them had posttraumatic pancreatic pseudocysts. Six of them were early referrals and presented within 1–2 weeks of pancreatic injury while the remaining six were referred later than 6 weeks with thick cyst walls. An initial conservative management and observation (with serial ultrasounds) led to a resolution of the pseudocysts in three patients (25% resolution rate). All the remaining subjects were treated using surgical modality (cystogastrostomy). In all the subjects where cystogastrostomy was done, the pseudocysts resolved completely, except in one child, who required the procedure to be repeated. The authors encountered no complications of the pancreatic pseudocyst disease in children i.e. infection, rupture, etc, that have been frequently described for adults. The authors conclude that pancreatic pseudocyst is a comparatively benign entity in children with a better outcome than in adults. Though various sophisticated treatment modalities are in vogue in the developed countries for managing pancreatic pseudocysts in children, cystogastrostomy is still a valid option for this purpose in the developing countries with suboptimal infrastructure and gives good results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawyer SN, Davidson PM, Mc Mullin N, Stokes KB (1989) Pediatric pseudocysts in children. 4:300–302
Warner RL, Othersen HB, Smith CD (1989) Traumatic pancreatitis and pseudocyst in children: current management. J Trauma 29:597–600
Miyano T (1998) The Pancreas. In: O’Neill JA,Rowe MI, Grosfeld JL, Fonkalsrud EW, Coran AG (eds) Pediatric Surgery 5th edn, Mosby, London, pp 1527–1544
Kimble RM, Cohen R, Williams S (1999) Successful endoscopic drainage of a posttraumatic pancreatic pseudocyst in a child. J Pediatr Surg 34:1518–1520
Haluszka O, Campbell A, Horvath K (2002) Endoscopic management of pancreatic pseudocyst in children. Gastroenterol Endosc 55(1):128–131
Holeczy P, Danis J (1998) Laparoscopic transgastric pancreatic pseudocystogastrostomy—first experience with extraluminal approach. Hepatogastroenterology 45:2215–2218
Das KM, Kochhar R, Mehta SK, Suri S, Kaushik SP, Gupta NM, et al (1990) Modified ultrasound guided percutaneous transgastric drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. Surg Endosc 4:209–211
Vane DW (1993) Lesions of the pancreas. In: Ashcraft KW,Holder TM (eds) Pediatric Surgery. 2nd edn, WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 525–534
Warshaw AL, Castillo CF, Rattner DW (2001) Pancreatic cysts, pseudocysts and fistulas. In: Zinner MJ, Schwartz SI,Ellis H, Ashley SW, Mc Fadder DW (eds) Maingot’s Abdominal Surgery. Mc-Graw Hill, London, pp 1917–1940
Bradley ELIII,Clements LJ (1975) Spontaneous resolution of pancreatic pseudocysts: implications for timing of operative intervention. Am J Surg 129:23–28
Mulligan C et al (1995) Conservative management of pediatric pseudocysts using octreotide acetate. Am Surg 61:206
Karaguzel G, Senocak ME, Buyukpamukcu N, Hicsonmez A (1995) Surgical management of the pancreatic pseudocyst in children: long term evaluation. J Pediatr 30(6):777–780
Barsness KA, Bensard DD, Patrick DA, Calkins CM, Hendrickson RJ, Banerjee A, Mc Intyre Jr RC (2004) IL-1 beta induces an exaggerated pro and anti inflammatory response in the peritoneal macrophages of children as compared with adults. Pediat Surg Int 20:238–242
Cooney DR, Grosfeld JL (1975) Operative management of pancreatic pseudocysts in infants and children: a review of 75 cases. Ann Surg 182:590–596
Van Sonnenberg E, Wittich GR, Casola G, Brannigan TC, Karnel F, Stabile BE, Varney RR, Christensen (1989) Percutaneous drainage of infected and noninfected pancreatic pseudocysts: experience in 101 cases. Radiology 170:757–761
Elechi EN, Callender CO, Lefall LD, Kurtz LH (1979) The treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts by external drainage. Surg Gynec Obst 148:707–710
Bridoux-Henno L, Dabadie A, Rambeau M, Le Gall E, Bretagne JF (2004) Successful endoscopic drainage of a pancreatic pseudocyst in a 17-month-old boy. Eur J Pediatr 163(8):482–484
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ratan, S.K., Rattan, K.N., Rohilla, S. et al. Cystogastrostomy: a valid option for treating pancreatic pseudocysts of children in developing countries. Ped Surgery Int 22, 532–535 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-006-1674-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-006-1674-z