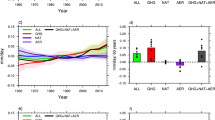
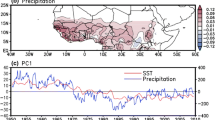
Abstract
Recent studies point to combined effects of changes in regional land-use, anthropogenic aerosol forcing and sea surface temperature (SST) gradient on declining trends in the South Asian monsoon (SAM). This study attempted disentangling the effects produced by changes in SST gradient from those by aerosol levels in an atmospheric general circulation model. Two pairs of transient ensemble simulations were made, for a 40-year period from 1971 to 2010, with evolving versus climatological SSTs and with anthropogenic aerosol emissions fixed at 1971 versus 2010, in each case with evolution of the other forcing element, as well as GHGs. Evolving SST was linked to a widespread feedback on increased surface temperature, reduced land–sea thermal contrast and a weakened Hadley circulation, with weakening of cross-equatorial transport of moisture transport towards South Asia. Increases in anthropogenic aerosol levels (1971 versus 2010), led to an intensification of drying in the peninsular Indian region, through several regional pathways. Aerosol forcing induced north–south asymmetries in temperature and sea-level pressure response, and a cyclonic circulation in the Bay of Bengal, leading to an easterly flow, which opposes the monsoon flow, suppressing moisture transport over peninsular India. Further, aerosol induced decreases in convection, vertically integrated moisture flux convergence, evaporation flux and cloud fraction, in the peninsular region, were spatially congruent with reduced convective and stratiform rainfall. Overall, evolution of SST acted through a weakening of cross-equatorial moisture flow, while increases in aerosol levels acted through suppression of Arabian Sea moisture transport, as well as, of convection and vertical moisture transport, to influence the suppression of SAM rainfall.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman AS, Toon O, Stevens D, Heymsfield A, Ramanathan V, Welton E (2000) Reduction of tropical cloudiness by soot. Science 288(5468):1042–1047
Andres R, Kasgnoc A (1998) A time-averaged inventory of subaerial volcanic sulfur emissions. J Geophys Res Atmos 103(D19):25251–25261
Annamalai H, Hamilton K, Sperber KR (2007) The south Asian summer monsoon and its relationship with ENSO in the IPCC AR4 simulations. J Clim 20(6):1071–1092
Bollasina MA, Ming Y, Ramaswamy V (2011) Anthropogenic aerosols and the weakening of the south Asian summer monsoon. Science 334(6055):502–505
Bollasina MA, Ming Y, Ramaswamy V, Schwarzkopf MD, Naik V (2014) Contribution of local and remote anthropogenic aerosols to the twentieth century weakening of the south Asian monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 41(2):680–687
Bookhagen B, Burbank DW (2010) Toward a complete Himalayan hydrological budget: spatiotemporal distribution of snowmelt and rainfall and their impact on river discharge. J Geophys Res Earth Surf. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JF001426
Brovkin V, Boysen L, Raddatz T, Gayler V, Loew A, Claussen M (2013) Evaluation of vegetation cover and land-surface albedo in MPI-ESM CMIP5 simulations. J Adv Model Earth Syst 5(1):48–57
Cherchi A, Alessandri A, Masina S, Navarra A (2011) Effects of increased CO2 levels on monsoons. Clim Dyn 37(1–2):83–101
Cherian R, Venkataraman C, Quaas J, Ramachandran S (2013) GCM simulations of anthropogenic aerosol-induced changes in aerosol extinction, atmospheric heating and precipitation over India. J Geophys Res Atmos 118(7):2938–2955
Chung CE, Ramanathan V (2006) Weakening of north Indian SST gradients and the monsoon rainfall in India and the Sahel. J Clim 19(10):2036–2045
Cowan T, Cai W (2011) The impact of Asian and non-Asian anthropogenic aerosols on 20th century Asian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL047268
Dash S, Kulkarni MA, Mohanty U, Prasad K (2009) Changes in the characteristics of rain events in India. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD010572
Dash S, Mamgain A, Pattnayak K, Giorgi F (2013) Spatial and temporal variations in Indian summer monsoon rainfall and temperature: an analysis based on REGCM3 simulations. Pure Appl Geophys 170(4):655–674
Déandreis C et al (2012) ‘Radiative forcing estimates of sulfate aerosol in coupled climate-chemistry models with emphasis on the role of the temporal variability’. Atmos Chem Phys Copernicus GmbH 12(12):5583–5602
Dentener F, Kinne S, Bond T, Boucher O, Cofala J, Generoso S, Ginoux P, Gong S, Hoelzemann J, Ito A et al (2006) Emissions of primary aerosol and precursor gases in the years 2000 and 1750 prescribed data-sets for AEROCOM. Atmos Chem Phys 6(12):4321–4344
Dey S, Di Girolamo L (2010) A climatology of aerosol optical and microphysical properties over the Indian subcontinent from 9 years (2000–2008) of multiangle imaging spectroradiometer (MISR) data. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD013395
Dey S, Tripathi SN, Singh RP, Holben B (2004) Influence of dust storms on the aerosol optical properties over the Indo-Gangetic basin. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JD004924
Fan F, Mann ME, Lee S, Evans JL (2010) Observed and modeled changes in the south Asian summer monsoon over the historical period. J Clim 23(19):5193–5205
Ganguly D, Rasch PJ, Wang H, Yoon JH (2012) Climate response of the south Asian monsoon system to anthropogenic aerosols. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JD017508
Ghosh S, Luniya V, Gupta A (2009) Trend analysis of Indian summer monsoon rainfall at diff erent spatial scales. Atmos Sci Lett 10(4):285–290
Giorgetta M, Manzini E, Roeckner E, Esch M, Bengtsson L (2006) Climatology and forcing of the quasi-biennial oscillation in the maecham5 model. J Clim 19(16):3882–3901
Giorgetta M, Roeckner E, Mauritsen T, Stevens B, Bader J, Crueger T, Esch M, Rast S, Kornblueh L, Schmidt H et al (2012) The atmospheric general circulation model echam6. Model description. Max Planck Inst for Meteorol, Hamburg
Guo L, Turner AG, Highwood EJ (2015) Impacts of 20th century aerosol emissions on the south Asian monsoon in the cmip5 models. Atmos Chem Phys 15(11):6367–6378
Guo L, Turner AG, Highwood EJ (2016) Local and remote impacts of aerosol species on Indian summer monsoon rainfall in a gcm. J Clim 29(19):6937–6955
Hansen J, Sato M, Ruedy R, Nazarenko L, Lacis A, Schmidt G, Russell G, Aleinov I, Bauer M, Bauer S et al (2005) Efficacy of climate forcings. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD005776
Harris I, Jones P, Osborn T, Lister D (2014) Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations-the cru ts3. 10 dataset. Int J Climatol 34(3):623–642
Hasson S, Lucarini V, Pascale S (2013) Hydrological cycle over south and southeast asian river basins as simulated by PCMDI/CMIP3 experiments. Earth Syst Dyn 4:199–217
Held IM, Soden BJ (2006) Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming. J Clim 19(21):5686–5699
Hendricks J, Kärcher B, Döpelheuer A, Feichter J, Lohmann U (2004) Potential impact of aviation-induced black carbon on cirrus clouds: global model studies with the ECHAM GCM. Project Report. 83, 249 S
Herman J, Bhartia P, Torres O, Hsu C, Seftor C, Celarier E (1997) Global distribution of uv-absorbing aerosols from nimbus 7/TOMS data. J Geophys Res Atmos 102(D14):16911–16922
Infanti JM, Kirtman BP (2017) CGCM and AGCM seasonal climate predictions—a study in CCSM4. J Geophys Res Atmos 122:7416–7432
Khairoutdinov M, Kogan Y (2000) A new cloud physics parameterization in a large-eddy simulation model of marine stratocumulus. Mon Weather Rev 128(1):229–243
Kitoh A, Endo H, Krishna Kumar K, Cavalcanti IF, Goswami P, Zhou T (2013) Monsoons in a changing world: a regional perspective in a global context. J Geophys Res Atmos 118(8):3053–3065. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50258
Klein SA, Hartmann DL (1993) The seasonal cycle of low stratiform clouds. J Clim 6(8):1587–1606
Koren I, Martins JV, Remer LA, Afargan H (2008) Smoke invigoration versus inhibition of clouds over the Amazon. Science 321(5891):946–949
Kripalani R, Oh J, Kulkarni A, Sabade S, Chaudhari H (2007) South Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability: coupled climate model simulations and projections under IPCC AR4. Theor Appl Climatol 90(3–4):133–159
Krishnan R, Sabin T, Vellore R, Mujumdar M, Sanjay J, Goswami B, Hour-din F, Dufresne JL, Terray P (2015) Deciphering the desiccation trend of the south Asian monsoon hydroclimate in a warming world. Clim Dyn 47(3–4):1007–1027
Lau WKM, Kim KM (2017) Competing influences of greenhouse warming and aerosols on Asian summer monsoon circulation and rainfall. Asia Pacif J Atmos Sci 53(2):181–194
Lau K, Kim M, Kim K (2006) Asian summer monsoon anomalies induced by aerosol direct forcing: the role of the Tibetan plateau. Clim Dyn 26(7–8):855–864
Li G, Xie SP (2014) Tropical biases in CMIP5 multimodel ensemble: the excessive equatorial Pacific cold tongue and double ITCZ problems. J Clim 27(4):1765–1780
Lohmann U, Stier P, Hoose C, Ferrachat S, Kloster S, Roeckner E, Zhang J (2007) Cloud microphysics and aerosol indirect effects in the global climate model ECHAM5-HAM. Atmos Chem Phys 7(13):3425–3446
Manoj M, Devara P, Safai P, Goswami B (2011) Absorbing aerosols facilitate transition of Indian monsoon breaks to active spells. Clim Dyn 37(11–12):2181–2198
Manzini E, Giorgetta M, Esch M, Kornblueh L, Roeckner E (2006) The influence of sea surface temperatures on the northern winter stratosphere: ensemble simulations with the maecham5 model. J Clim 19(16):3863–3881
Meehl GA, Arblaster JM (2002) Indian monsoon GCM sensitivity experiments testing tropospheric biennial oscillation transition conditions. J Clim 15(9):923–944
Meehl GA, Arblaster JM, Collins WD (2008) Effects of black carbon aerosols on the Indian monsoon. J Clim 21(12):2869–2882
Menon S, Hansen J, Nazarenko L, Luo Y (2002) Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in china and India. Science 297(5590):2250–2253
Menon A, Levermann A, Schewe J, Lehmann J, Frieler K (2013) Consistent in-crease in Indian monsoon rainfall and its variability across CMIP-5 models. Earth Syst Dyn 4:287–300
Ming Y, Ramaswamy V (2009) Nonlinear climate and hydrological responses to aerosol effects. J Clim 22(6):1329–1339
Mishra V, Smoliak BV, Lettenmaier DP, Wallace JM (2012) A prominent pattern of year-to-year variability in Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(19):7213–7217
Mu Q, Zhao M, Running SW (2011) Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens Environ 115(8):1781–1800
Neubauer D, Lohmann U, Hoose C, Frontoso M (2014) Impact of the representation of marine stratocumulus clouds on the anthropogenic aerosol effect. Atmos Chem Phys 14(21):11–997
Padma Kumari B, Goswami B (2010) Seminal role of clouds on solar dimming over the Indian monsoon region. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL042133
Pai D, Sridhar L, Badwaik M, Rajeevan M (2014) Analysis of the daily rainfall events over India using a new long period (1901–2010) high resolution (0.25 0.25) gridded rainfall data set. Clim Dyn 45(3–4):755–776
Pandithurai G, Dipu S, Prabha TV, Maheskumar R, Kulkarni J, Goswami B (2012) Aerosol e effect on droplet spectral dispersion in warm continental cumuli. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JD016532
Pathak A, Ghosh S, Kumar P (2014) Precipitation recycling in the Indian subcontinent during summer monsoon. J Hydrometeorol 15(5):2050–2066
Pathak A, Ghosh S, Martinez JA, Dominguez F, Kumar P (2017) Role of oceanic and land moisture sources and transport in the seasonal and interannual variability of summer monsoon in India. J Clim 30(5):1839–1859
Paul S, Ghosh S, Oglesby R, Pathak A, Chandrasekharan A, Ramsankaran R (2016) Weakening of Indian summer monsoon rainfall due to changes in land use land cover. Sci Rep 6:32177
Pokhrel S, Sikka D (2013) Variability of the TRMM-PR total and convective and stratiform rain fractions over the Indian region during the summer monsoon. Clim Dyn 41(1):21–44
Polson D, Bollasina M, Hegerl G, Wilcox L (2014) Decreased monsoon precipitation in the northern hemisphere due to anthropogenic aerosols. Geophys Res Lett 41(16):6023–6029
Raddatz T, Reick C, Knorr W, Kattge J, Roeckner E, Schnur R, Schnitzler KG, Wetzel P, Jungclaus J (2007) Will the tropical land biosphere dominate the climate-carbon cycle feedback during the twenty-first century? Clim Dyn 29(6):565–574
Ramanathan V, Chung C, Kim D, Bettge T, Buja L, Kiehl J, Washington W, Fu Q, Sikka D, Wild M (2005) Atmospheric brown clouds: Impacts on south Asian climate and hydrological cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(15):5326–5333
Reddy MS, Boucher O (2004) A study of the global cycle of carbonaceous aerosols in the LMDZT general circulation model. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JD004048
Roeckner E, Bauml G, Bonaventura L, Brokopf R, Esch M, Giorgetta M, Hagemann S, Kirchner I, Kornblueh L, Manzini E et al (2003) The atmospheric general circulation model echam 5. part I: model description. MPI-Report 349, Hamburg
Roxy MK, Ritika K, Terray P, Murtugudde R, Ashok K, Goswami B (2015) Drying of Indian subcontinent by rapid indian ocean warming and a weakening land–sea thermal gradient. Nat Commun 6:ncomms8423
Sabade S, Kulkarni A, Kripalani R (2011) Projected changes in south Asian summer monsoon by multi-model global warming experiments. Theoret Appl Climatol 103(3–4):543–565
Saha A, Ghosh S, Sahana A, Rao E (2014) Failure of CMIP5 climate models in simulating post-1950 decreasing trend of Indian monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 41(20):7323–7330
Salzmann M, Weser H, Cherian R (2014) Robust response of Asian summer monsoon to anthropogenic aerosols in CMIP5 models. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD021783
Sanap S, Pandithurai G, Manoj M (2015) On the response of Indian summer monsoon to aerosol forcing in cmip5 model simulations. Clim Dyn 45(9–10):2949–2961
Sooraj K, Terray P, Mujumdar M (2015) Global warming and the weakening of the Asian summer monsoon circulation: assessments from the CMIP5 models. Clim Dyn 45(1–2):233–252
Sperber KR, Annamalai H, Kang IS, Kitoh A, Moise A, Turner A, Wang B, Zhou T (2013) The Asian summer monsoon: an intercomparison of CMIP5 vs. CMIP3 simulations of the late 20th century. Clim Dyn 41(9–10):2711–2744
Swapna P, Krishnan R, Wallace J (2014) Indian ocean and monsoon coupled interactions in a warming environment. Clim Dyn 42(9–10):2439–2454
Taylor KE, Stouffer RJ, Meehl GA (2012) An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design. Bull Am Meteor Soc 93(4):485–498
Tegen I, Harrison SP, Kohfeld K, Prentice IC, Coe M, Heimann M (2002) Impact of vegetation and preferential source areas on global dust aerosol: results from a model study. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JD000963
Torres O, Tanskanen A, Veihelmann B, Ahn C, Braak R, Bhartia PK, Veefkind P, Levelt P (2007) Aerosols and surface uv products from ozone monitoring instrument observations: an overview. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD008809
Turner AG, Annamalai H (2012) Climate change and the south Asian summer monsoon. Nat Clim Change 2(8):587–595
Turner AG, Slingo JM (2009) Uncertainties in future projections of extreme precipitation in the Indian monsoon region. Atmos Sci Lett 10(3):152–158
Ueda H, Iwai A, Kuwako K, Hori ME (2006) Impact of anthropogenic forcing on the Asian summer monsoon as simulated by eight GCMs. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL025336
Vignati E, Wilson J, Stier P (2004) M7: a size resolved aerosol mixture module for the use in global aerosol models. J Geophys Res 109(D22):202
Vinoj V, Rasch PJ, Wang H, Yoon JH, Ma PL, Landu K, Singh B (2014) Short-term modulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall by west Asian dust. Nat Geosci 7(4):308–313
Wang C, Kim D, Ekman AM, Barth MC, Rasch PJ (2009) Impact of anthropogenic aerosols on Indian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL040114
Wood R, Hartmann DL (2006) Spatial variability of liquid water path in marine low cloud: The importance of mesoscale cellular convection. J Clim 19(9):1748–1764
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Centre of Excellence in Climate Studies (IITB-CoECS) project of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India. The ECHAM6-HAM simulations were performed on the IITB-CoECS HPC. We acknowledge Dr. S. Sajani and Dr. K. Rajendran from CSIR-4PI, Bangalore, India for their technical assistance in model porting and simulation set-up at IITB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, N., Venkataraman, C., Muduchuru, K. et al. Disentangling sea-surface temperature and anthropogenic aerosol influences on recent trends in South Asian monsoon rainfall. Clim Dyn 52, 2287–2302 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4251-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4251-y